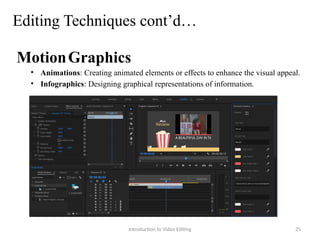
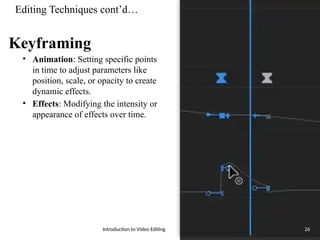
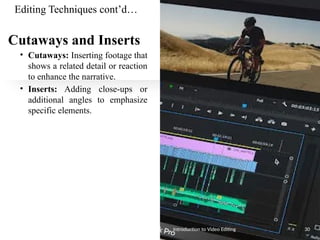
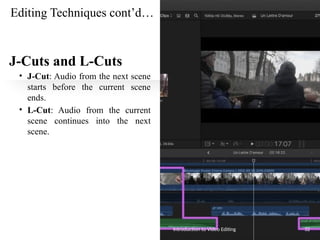
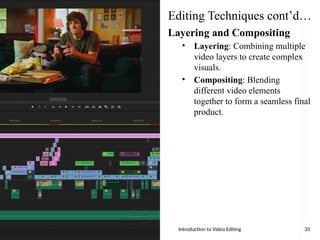
The document serves as an introduction to video editing, covering key topics such as video production phases (pre-production, production, post-production, and distribution), roles in production, and various types and techniques of video editing. It discusses the importance of video editing in storytelling, the workflows involved, and the software options available for editing. Additionally, it outlines editing techniques like transitions, color correction, audio editing, and effects to enhance video quality.