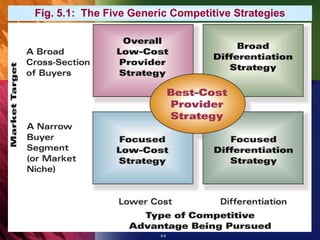
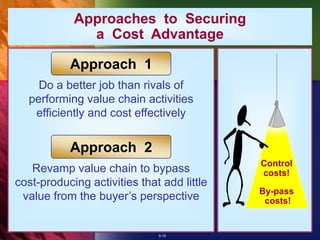
The document summarizes chapter 5 of an organizational strategy textbook. It discusses the five generic competitive strategies businesses can pursue: low-cost provider, differentiation, focused low-cost, focused differentiation, and best-cost provider. It provides examples of companies like Walmart and Nucor that have successfully implemented a low-cost strategy. It also discusses how businesses can achieve differentiation through unique product features, services, or capabilities. The chapter examines the benefits, keys to success, and potential pitfalls of pursuing these competitive strategies.