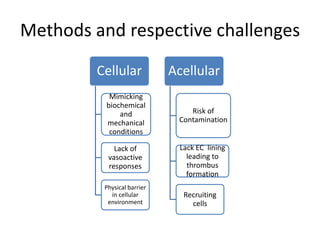
The document discusses the challenges in vascular tissue engineering, including the complexities of growing blood vessels and integrating them into living systems. Key approaches include the use of endothelial cell-seeded synthetic grafts and various biomaterials, each with distinct advantages and limitations. Major challenges involve ensuring non-thrombogenic surfaces, managing immunogenicity, and achieving reproducibility, with suggested remedies like adhesive coatings and the selection of appropriate cell types.