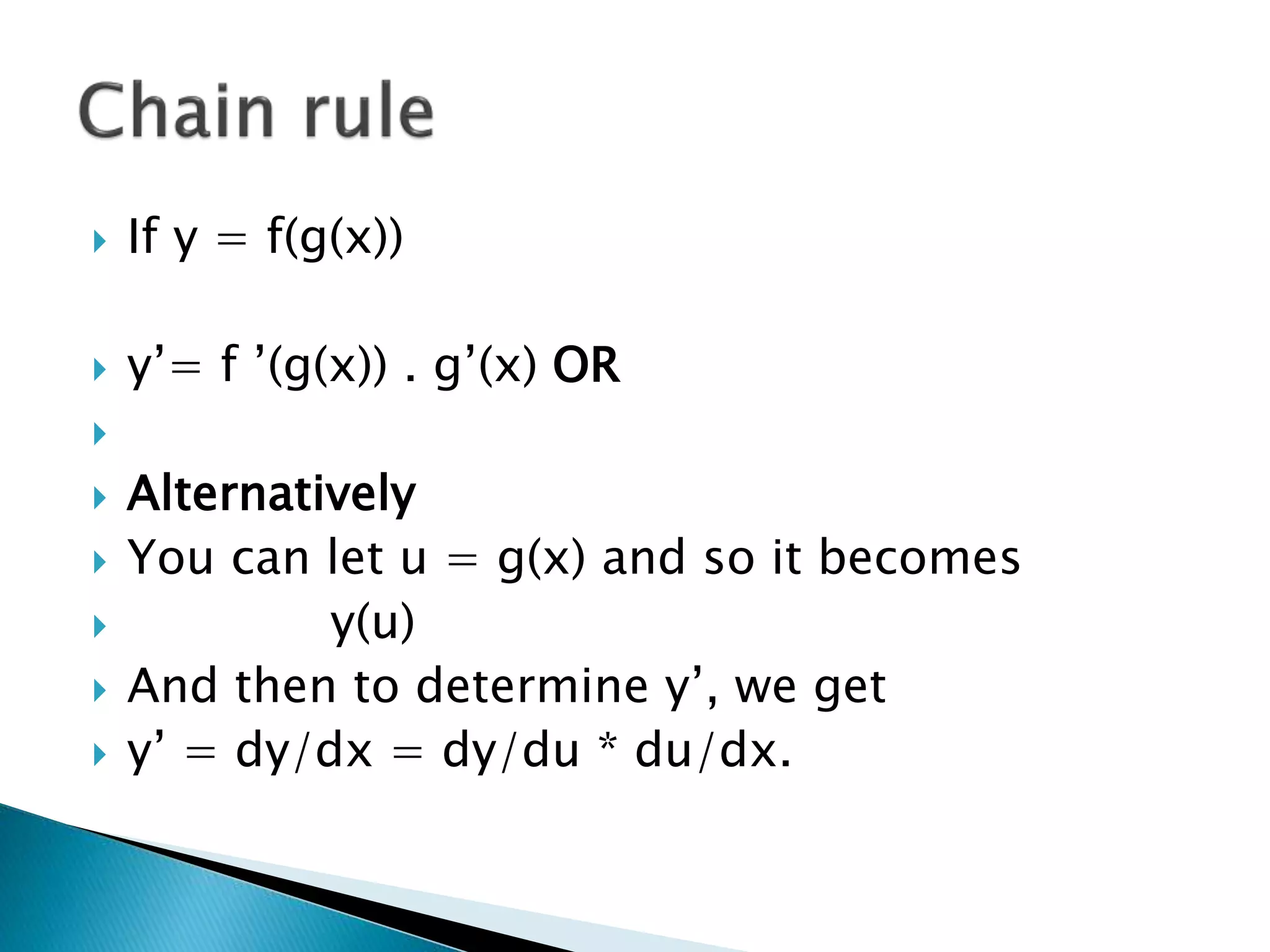
The chain rule deals with functions within functions and describes how to take the derivative. It states that if y = f(g(x)), then y' = f'(g(x)) * g'(x). Alternatively, it can be written as letting u = g(x), so y(u) and then taking dy/dx = dy/du * du/dx. Examples are worked out, such as finding the derivative of y = (2x + 5)2 and y = 5/(3x-5)3.