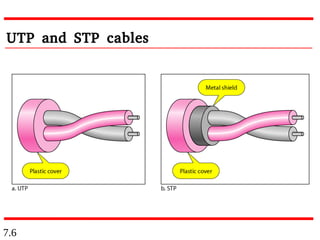
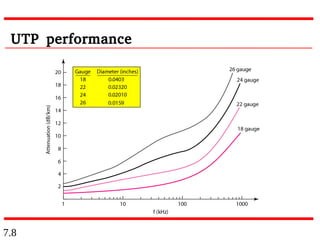
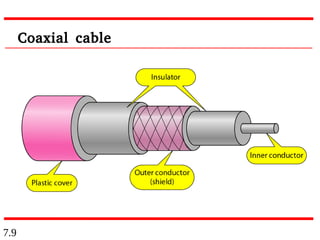
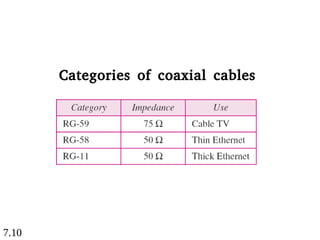
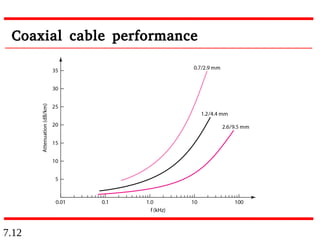
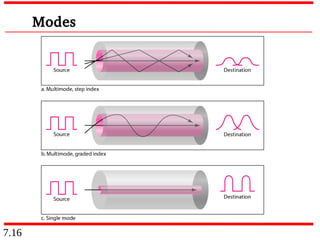
This document discusses different types of transmission media, including guided and unguided media. Guided media uses physical conduits like twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable to transmit signals. Unguided or wireless media transmits electromagnetic waves without a physical conductor, using radio waves, microwaves, or infrared signals. It provides details on the characteristics and applications of different guided and wireless transmission technologies.