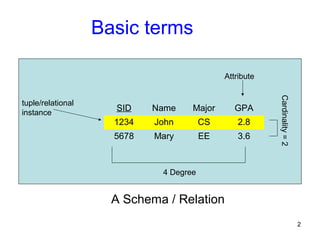
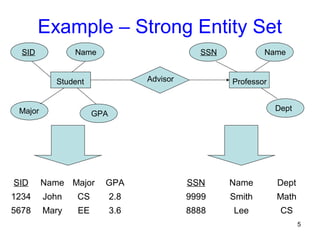
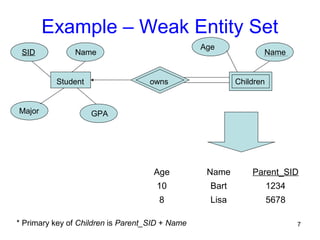
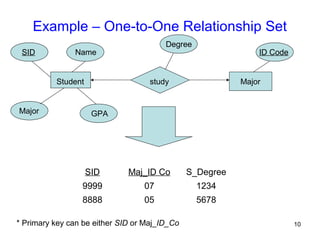
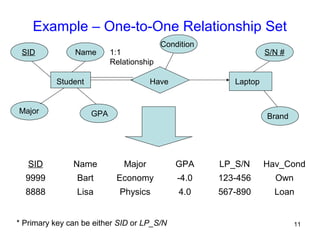
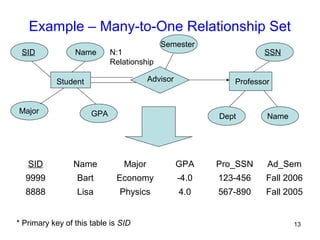
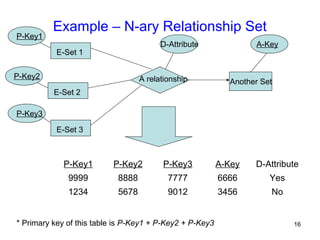
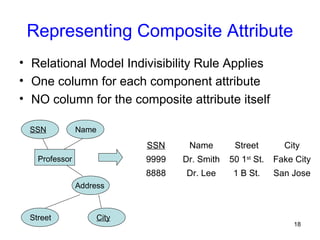
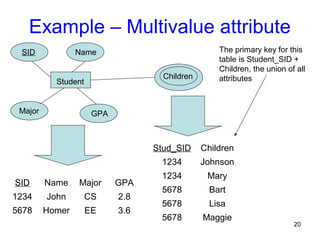
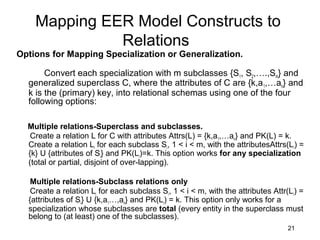
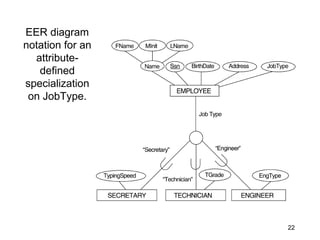
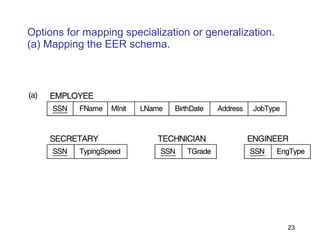
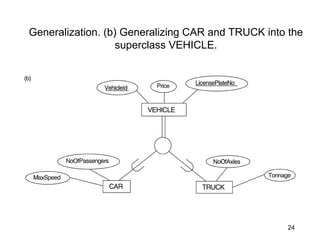
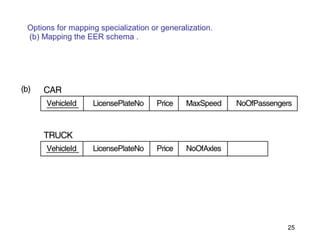
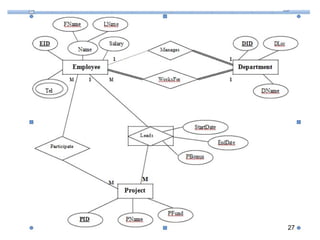
This document discusses mapping entities, relationships, and attributes from an ER diagram to tables in a relational database. It provides three rules for the mapping: 1) entity names become table names, 2) attributes become columns, and 3) relationships are mapped using foreign keys. Examples are given for mapping various model constructs like weak entities, one-to-one/many relationships, multivalued attributes, and specialization/generalization. The document also discusses options for mapping specialization hierarchies to multiple tables or a single table design.