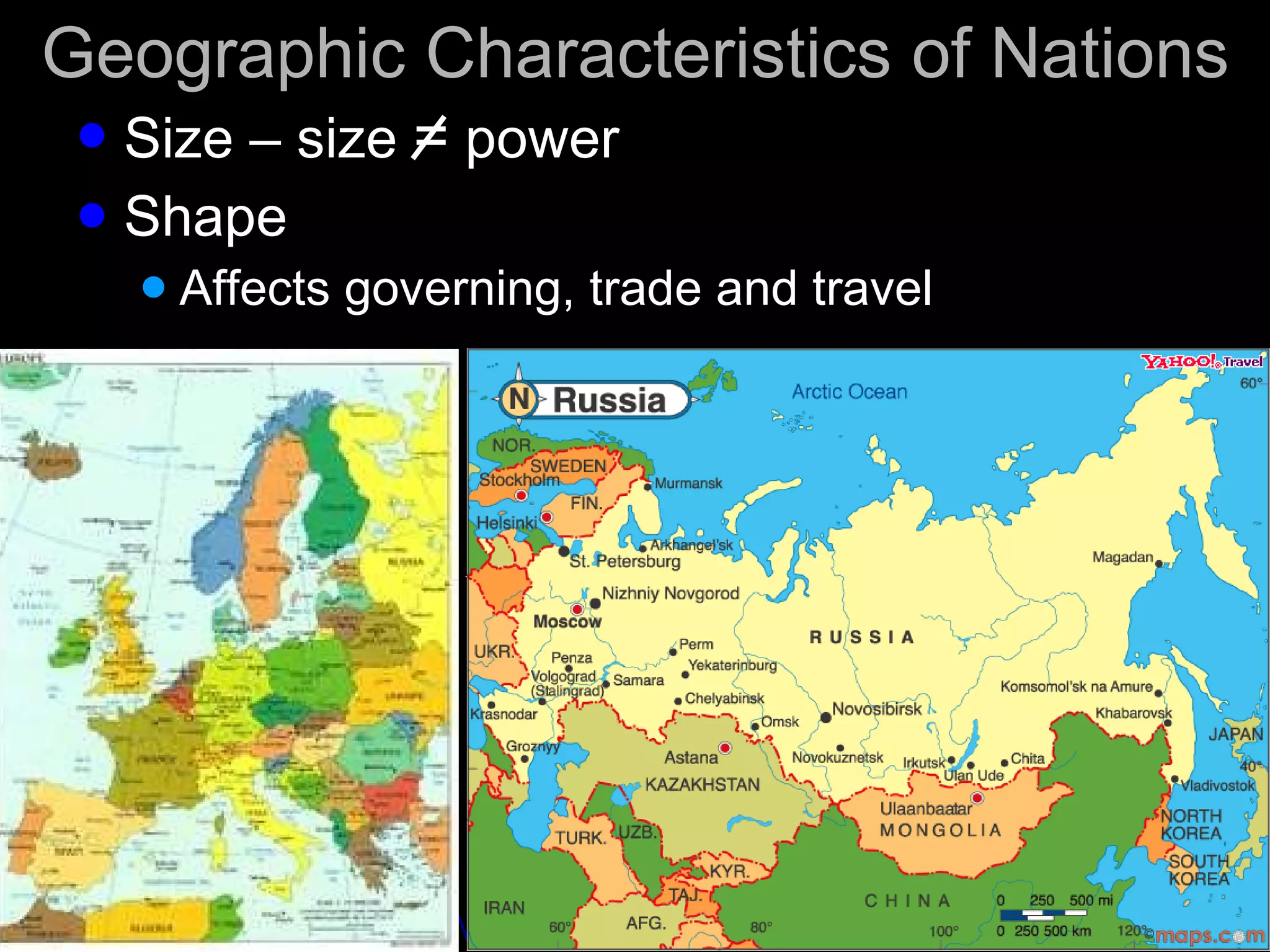
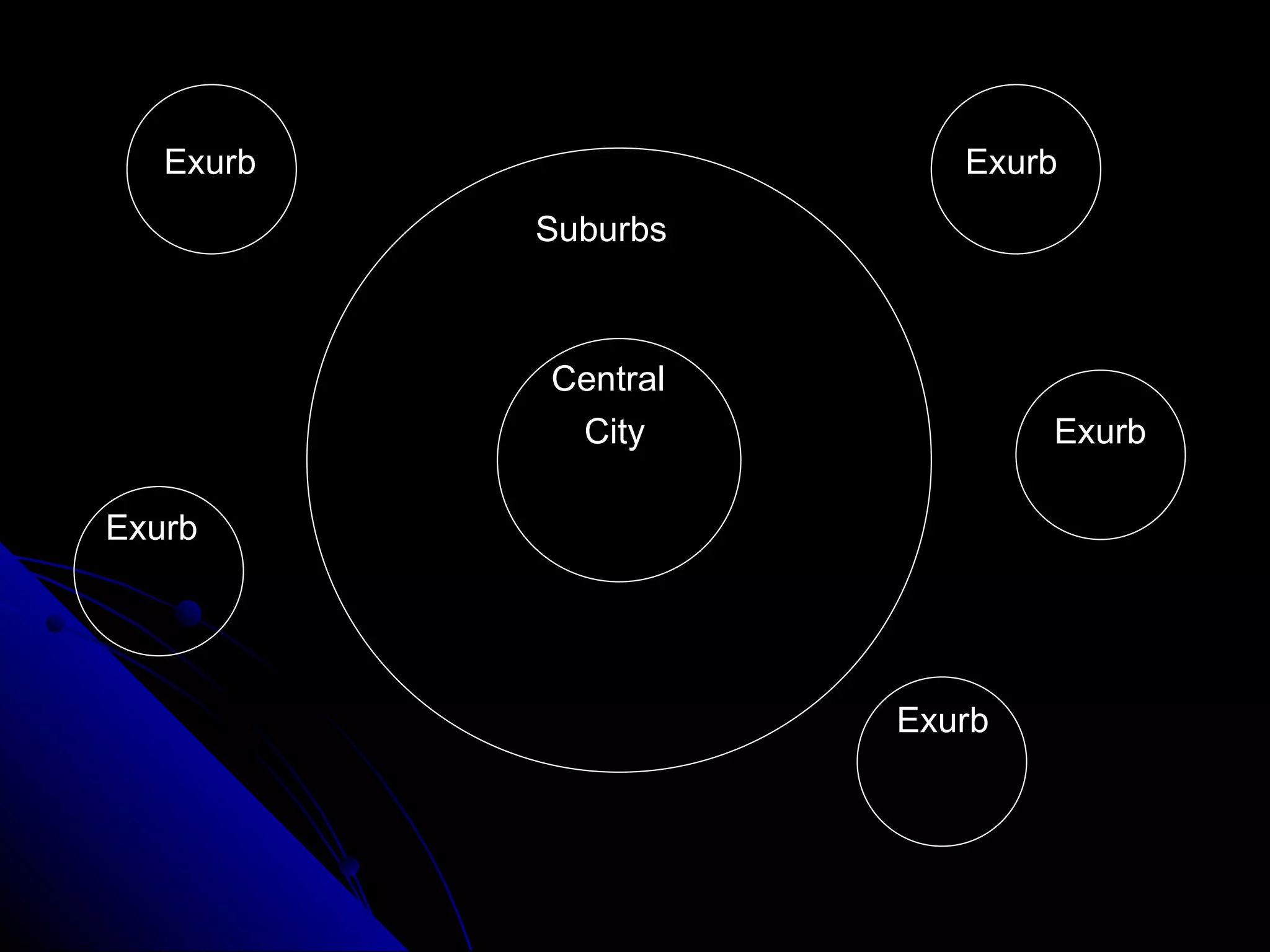
The document discusses political geography, defining states and nations, and various types of government, including democracy, monarchy, dictatorship, and communism. It also covers geographic characteristics that affect nations, such as size, shape, location, and boundaries, alongside urban geography concepts like metropolitan areas and land use patterns. Additionally, it addresses the functions of cities in terms of business, education, entertainment, and social services.