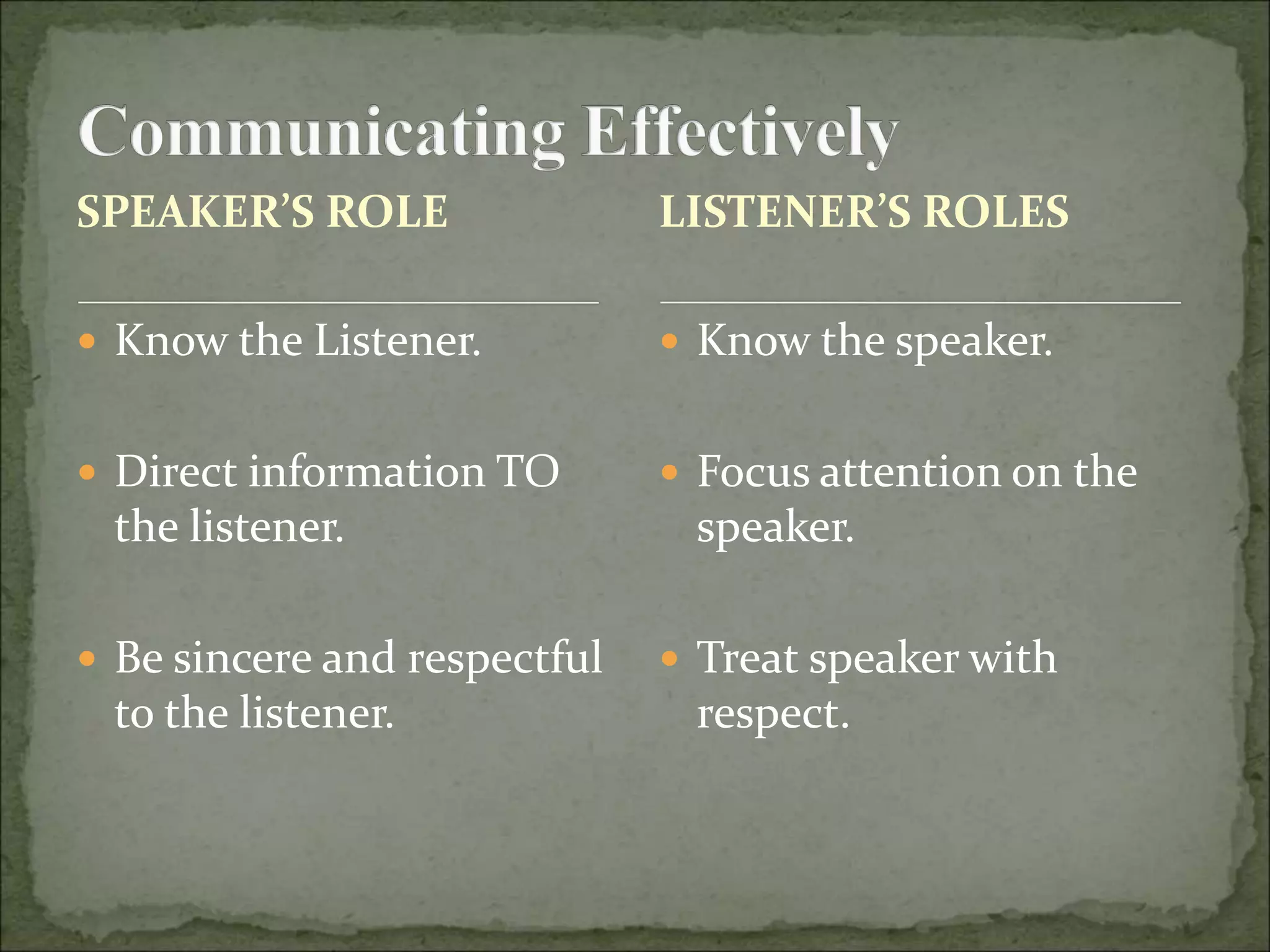
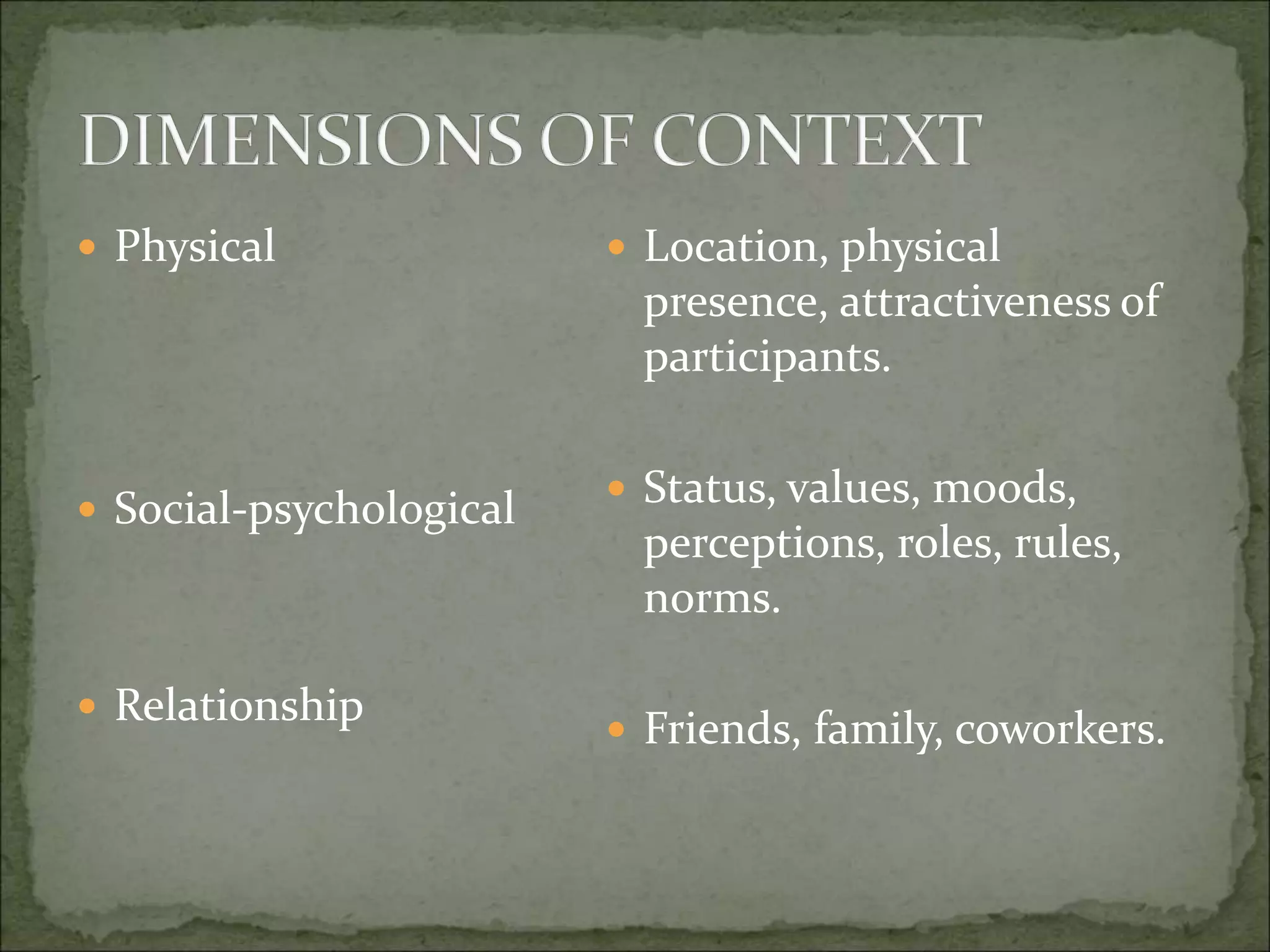
This document discusses several key aspects of communication and meaning. It explains that meaning depends on context, including the situation and accompanying behaviors. Meaning exists in the heads of individuals and can change with experience or differ between people. Misunderstandings are unavoidable but can be anticipated. Effective communication requires understanding the audience, their perspectives, and the relationship between speakers and listeners.