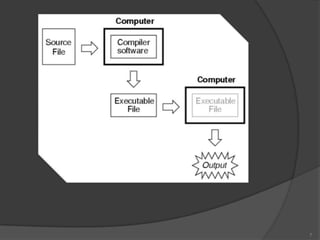
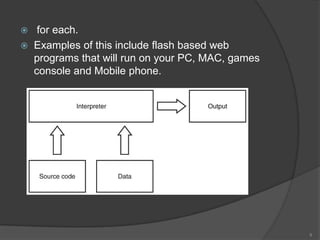
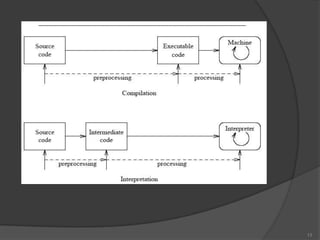
The document discusses three computer language translators: compilers, interpreters, and assemblers. [1] A compiler translates high-level code into machine code for faster execution, while an interpreter executes code line-by-line which is slower but allows for quicker testing. [2] An assembler directly translates assembly language instructions into machine code through a 1:1 mapping of mnemonics to instructions. [3] Compilers produce standalone executable programs while interpreters are useful for learning and debugging through a read-check-execute loop.