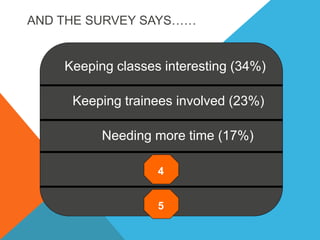
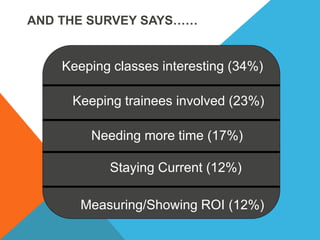
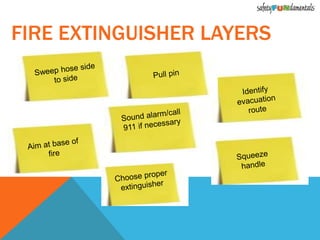
The document discusses various challenges faced by safety trainers, including keeping classes interesting and engaging trainees effectively. It emphasizes the importance of interactive and accelerated learning techniques to enhance knowledge retention and behavior change in trainees. Additionally, it highlights the role of positive emotions, physical activities, and diverse learning methods in creating a more effective training environment.