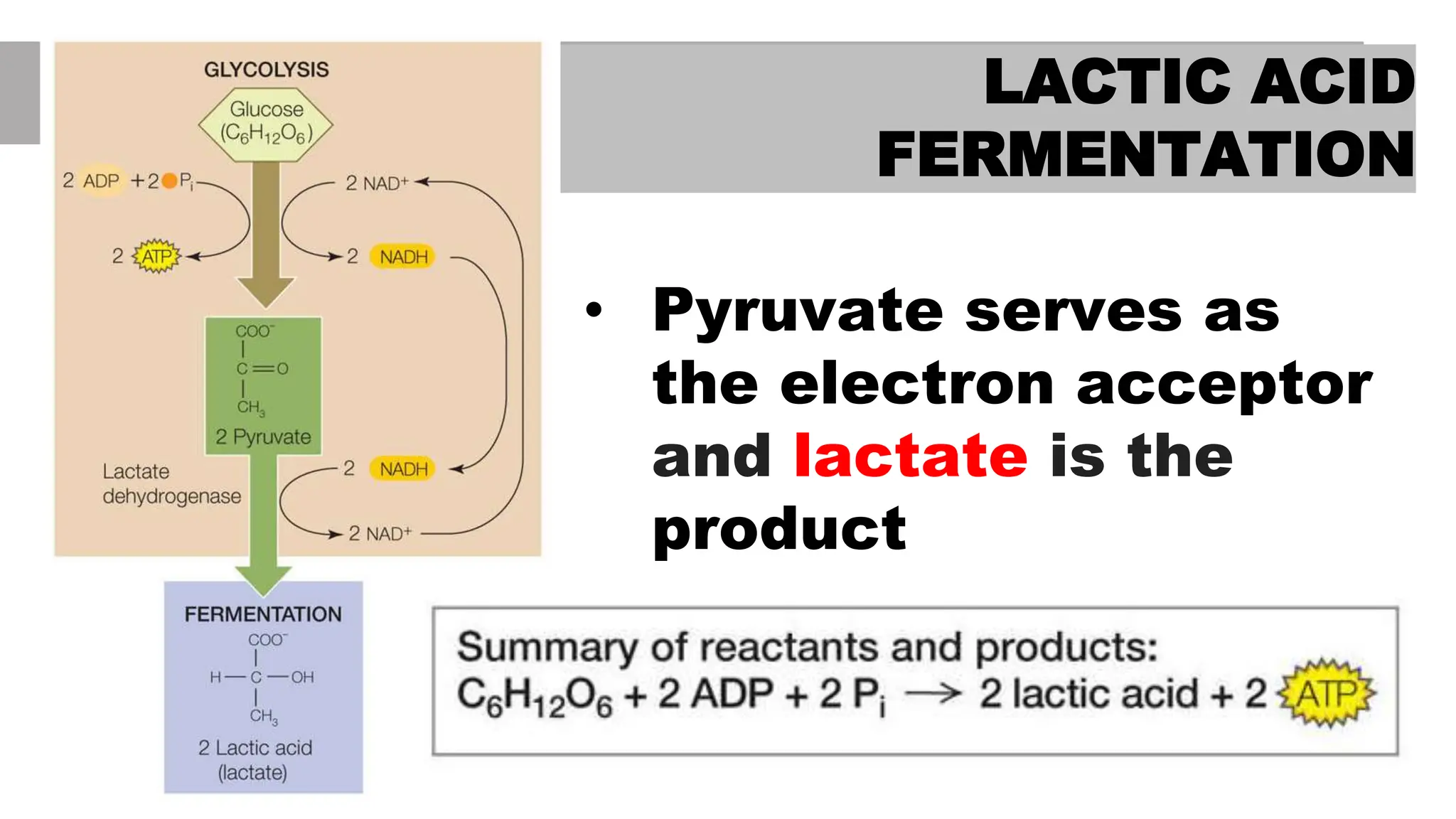
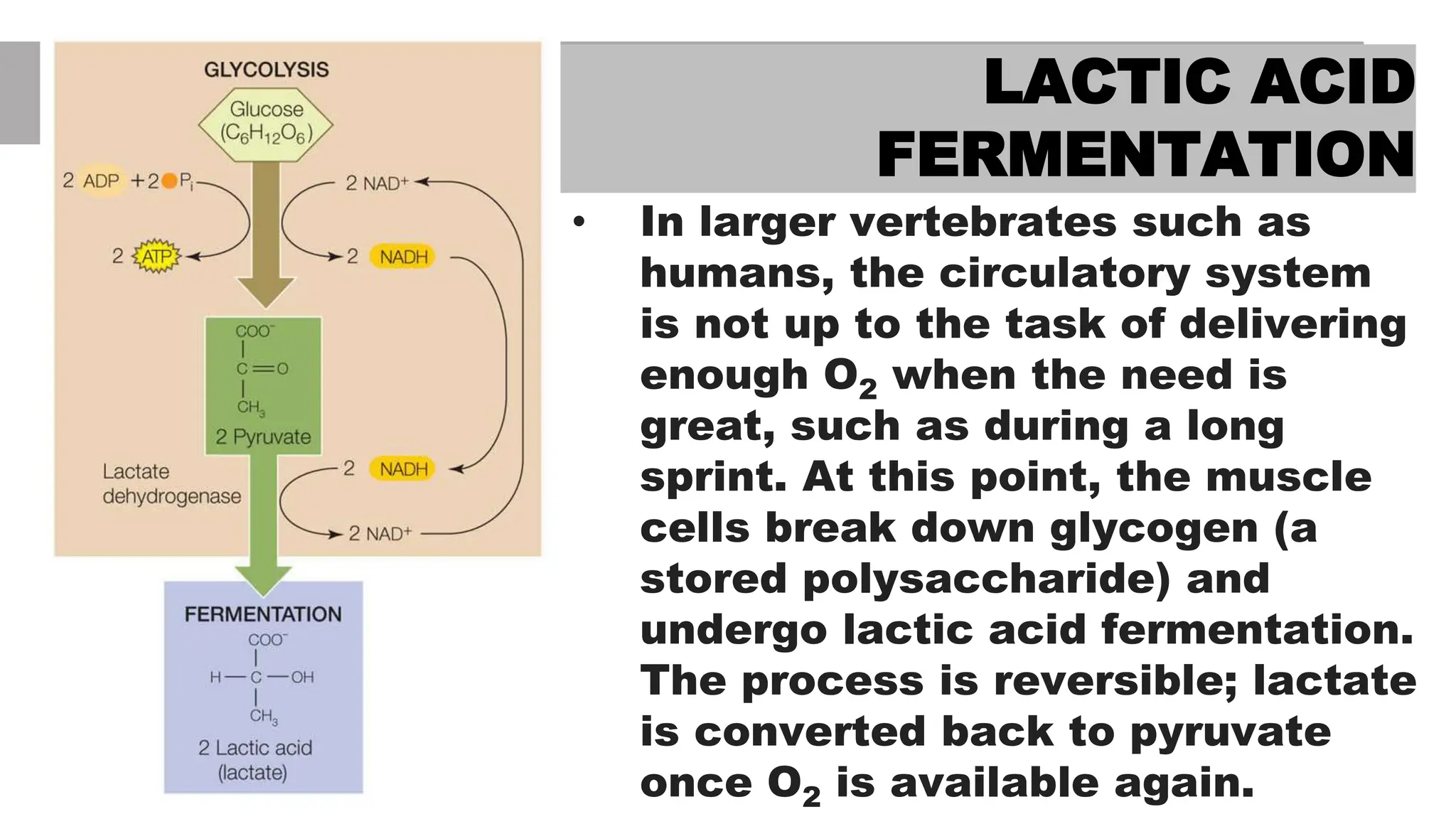
Cellular respiration is the metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose to produce ATP. There are two types of cellular respiration: aerobic respiration, which requires oxygen, and anaerobic respiration, which does not. In aerobic respiration, oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, while in anaerobic respiration other molecules like pyruvate or acetaldehyde accept electrons in place of oxygen. Two types of anaerobic respiration are lactic acid fermentation, where pyruvate is the electron acceptor producing lactic acid, and alcoholic fermentation where acetaldehyde accepts electrons producing alcohol and carbon dioxide.