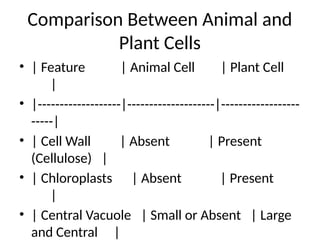
The document provides a comprehensive overview of cell structure, distinguishing between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, and detailing components of animal and plant cells. Key organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and chloroplasts are discussed, along with their functions. It emphasizes the significance of studying cells for advancements in various scientific fields.