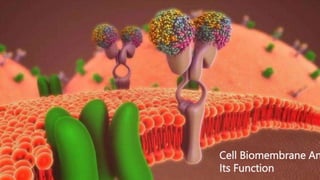
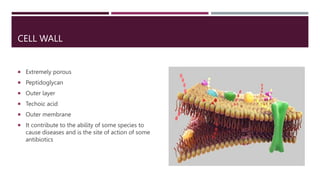
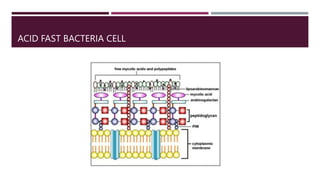
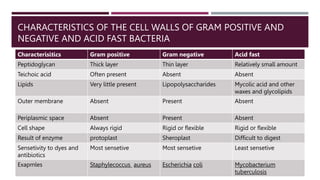
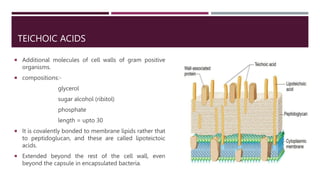
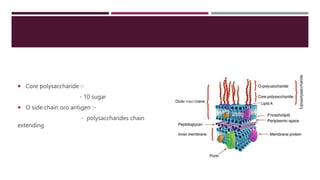
This document discusses the structure and composition of bacterial cell walls. It describes three main types of cell walls: gram positive, gram negative, and acid-fast. Gram positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer and teichoic acids. Gram negative bacteria have a thin peptidoglycan layer, an outer membrane, and lipopolysaccharides including lipid A and core polysaccharides in their outer membrane. Acid-fast bacteria like Mycobacterium tuberculosis have a cell wall with mycolic acids and waxes that makes them resistant to acid-fast staining. The cell wall structure contributes to differences in bacterial shape, sensitivity to antibiotics and dyes, and ability to cause disease.