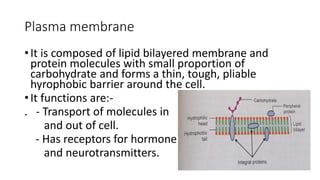
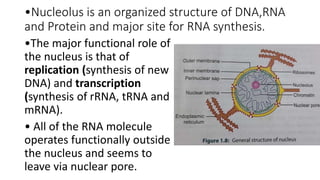
The document provides an overview of the cell as the fundamental unit of life, detailing its three main components: the plasma membrane, cytoplasm with organelles, and the nucleus. Key organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and peroxisomes are described along with their functions in protein synthesis, energy production, and waste digestion. Additionally, the nucleus is highlighted as the control center containing DNA and involved in replication and transcription processes.