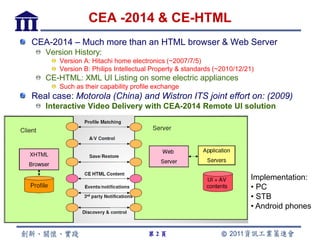
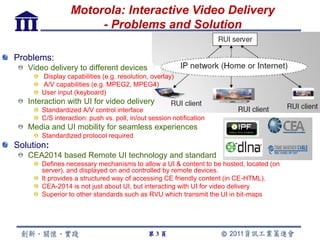
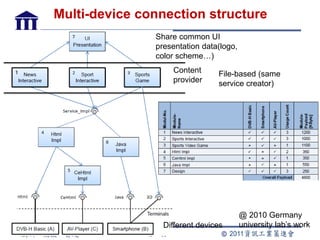
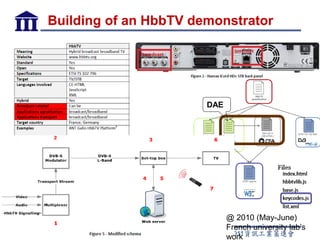
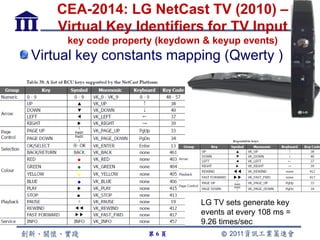
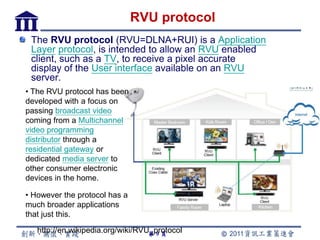
CE-HTML provides a standardized structure for virtual keyboards and remote user interfaces on consumer electronics. It has been implemented on devices like set-top boxes, smartphones, and smart TVs from manufacturers like Motorola, Philips, and LG. Protocols like CEA-2014 and NotifSocket enable dynamic updates and event handling for remote user interfaces across multiple connected devices.