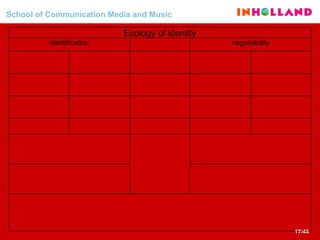
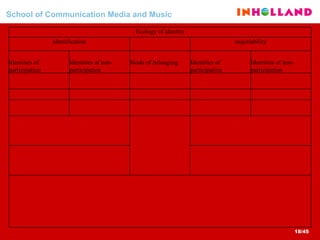
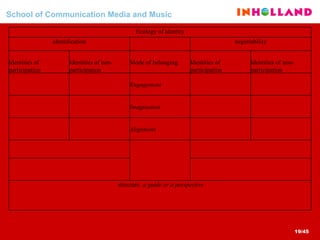
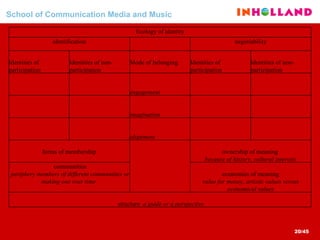
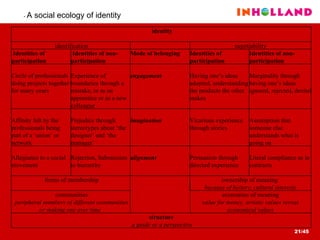
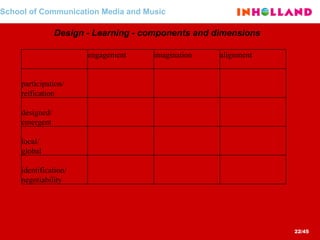
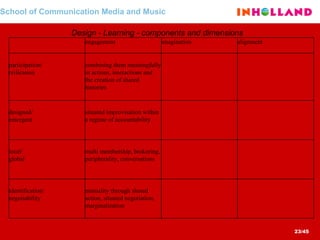
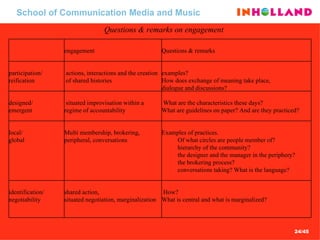
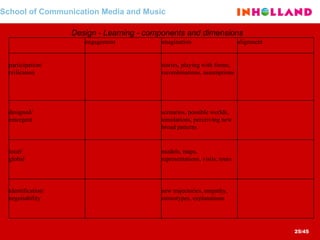
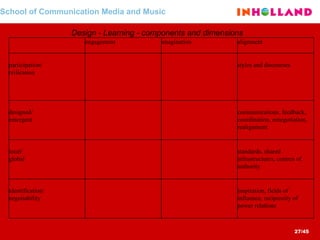
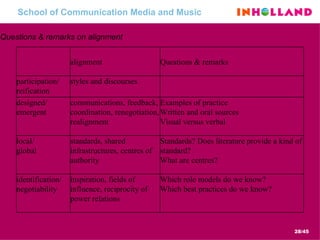
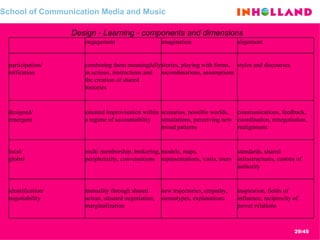
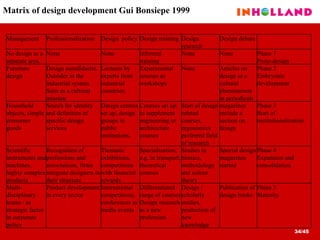
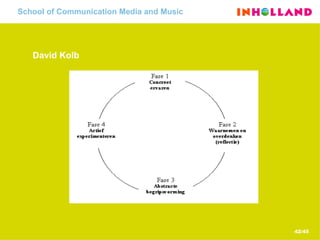
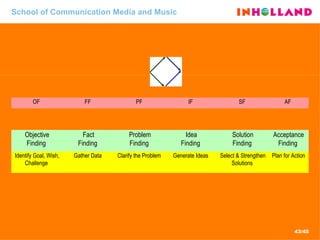
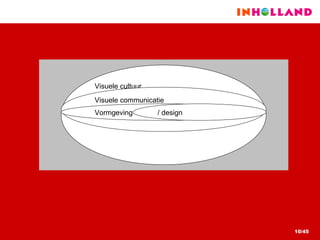
The document discusses visual communication, design, and communities of practice around these fields. It addresses questions around what practices and communities exist, who is involved, and definitions of key terms like visual culture, visual communication, and design. It also examines identities, participation, and learning within communities of practice, looking at components like identification, imagination, and engagement.











![Definitions design Traffic in two directions: creative and analytic thinking. As applied creativity, as problem solving, as learning, as a social process, as play 1] Designed by men. Non-verbal communication. Design gives functional and emotional values to a product. [2] A plan to arrange elements in such a way that a specific aim will be reached best. [3] [1] Dorst, Understanding design, 2003 [2] Van Thiel and Michels: De basis van design management, 1998 [3] Eames in Laurel: Design research, 2003](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbrdlecturerotterdam-090305061211-phpapp02/85/Cbrd-Lecture-Rotterdam-13-320.jpg)
![School of Communication Media and Music Definitions of design Design [4] as art Design as problem solving Design as a creative act Design as a group of related professions Design as industry Design as a process What is the relationship of design with economy and culture? [4] Rachel Cooper, Mike Press, The Design Agenda , 1999](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cbrdlecturerotterdam-090305061211-phpapp02/85/Cbrd-Lecture-Rotterdam-14-320.jpg)