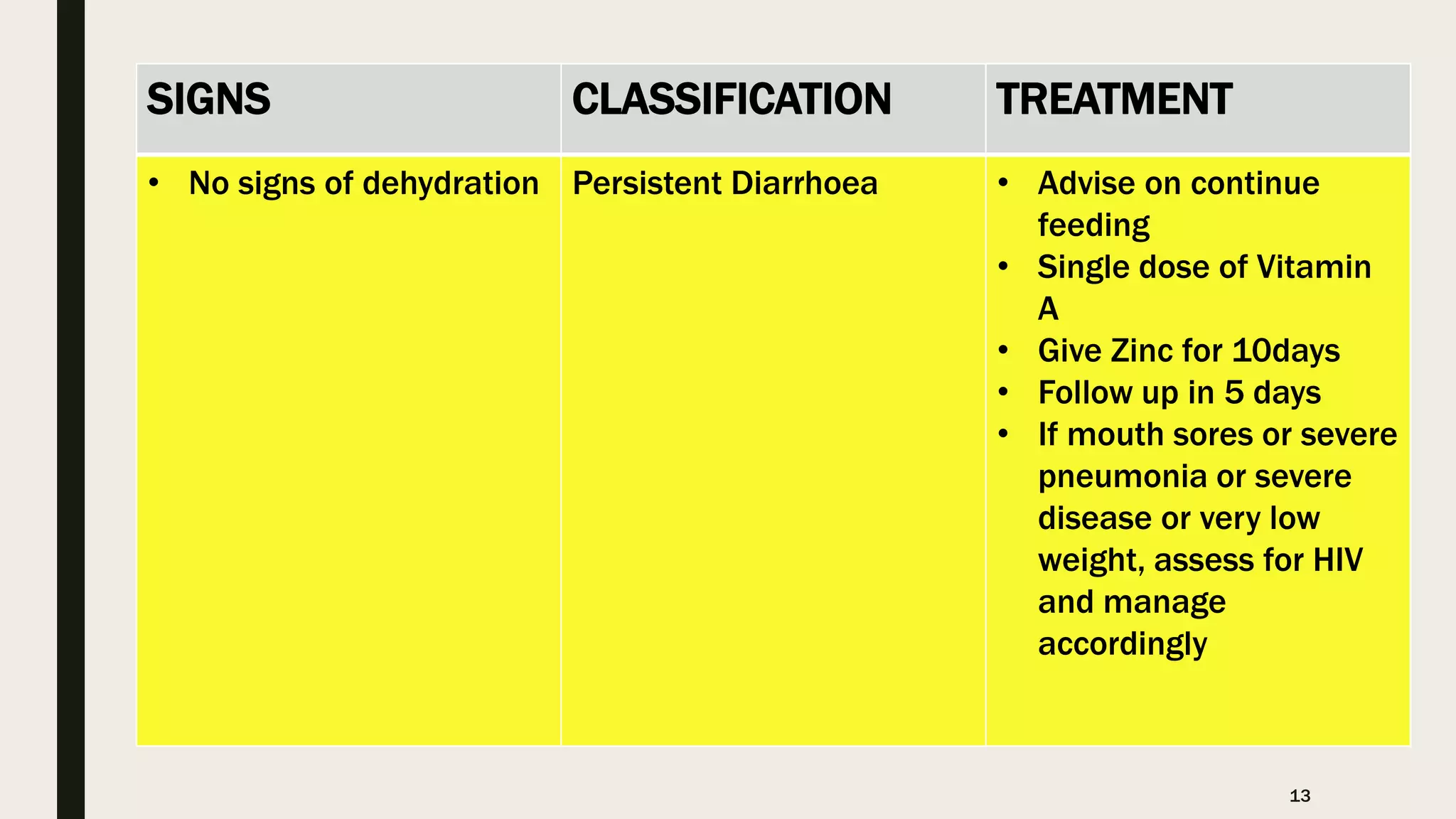
This document provides information on the 5 major childhood killer diseases (CB-IMNCI) in Nepal: pneumonia, diarrhea, measles, malaria, and malnutrition. For each disease, it lists signs, classifications, and recommended treatments according to CB-IMNCI guidelines. It describes pneumonia classifications and treatments for severe, pneumonia, and no pneumonia. For diarrhea, it outlines classifications and treatments for severe dehydration, some dehydration, no dehydration, dysentery, and persistent diarrhea. For measles, malaria, and malnutrition, it lists signs, classifications, and corresponding recommended treatments. The document aims to help participants understand and properly treat the 5 major childhood diseases according to CB-IMNCI standards.