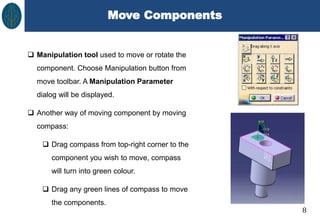
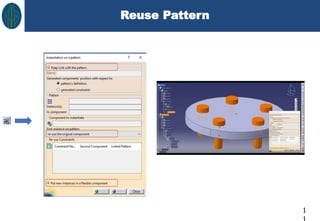
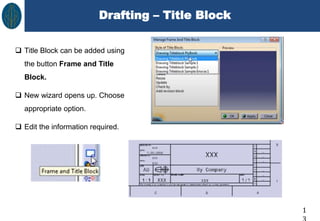
This document discusses CATIA V5 assembly modeling. It describes assembly modeling as creating designs from two or more components assembled together. There are two main approaches: bottom-up assembly, where components are created separately and then assembled, and top-down assembly, where components are created directly within the assembly. The document outlines how to create new products, insert existing components, move components, and apply constraints to restrict component movement in CATIA V5 assembly design.