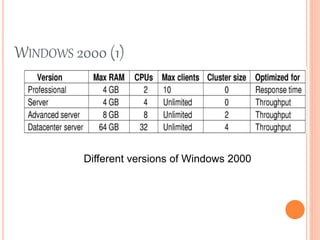
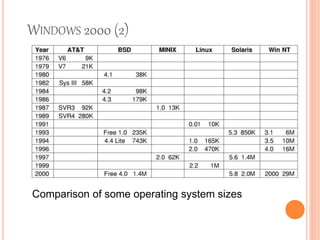
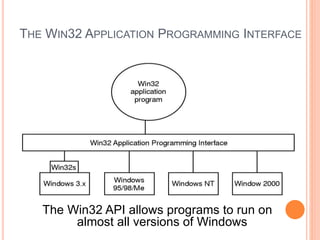
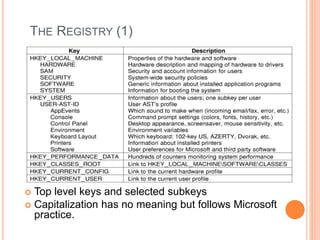
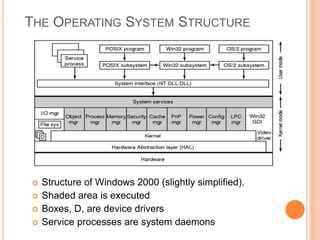
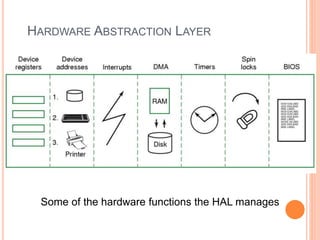
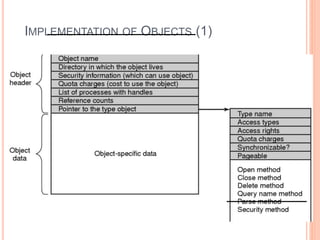
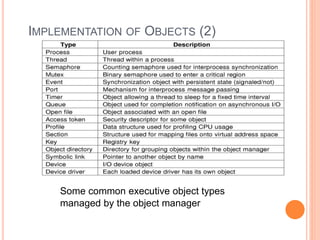
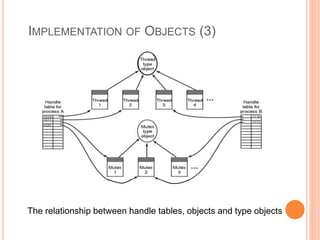
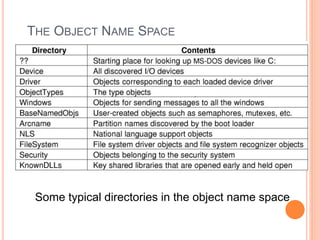
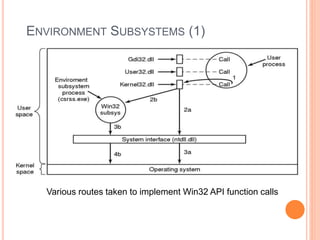
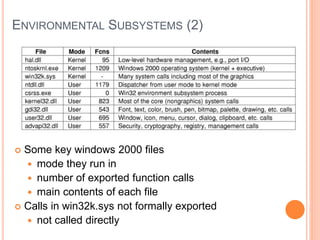
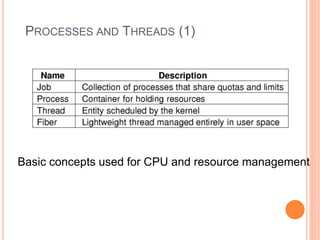
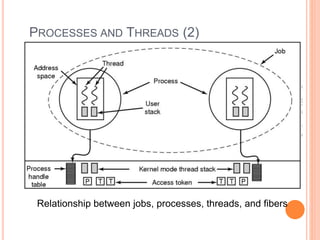
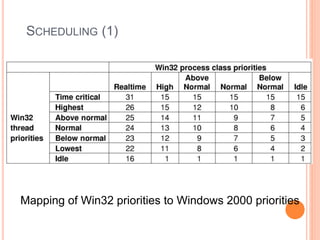
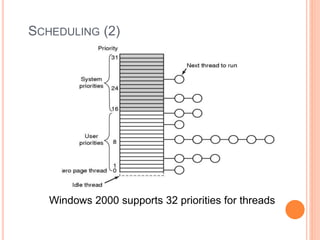
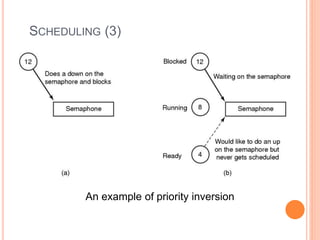
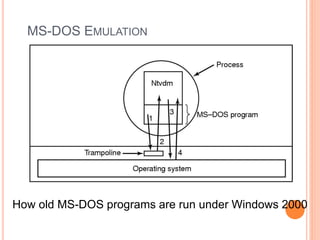
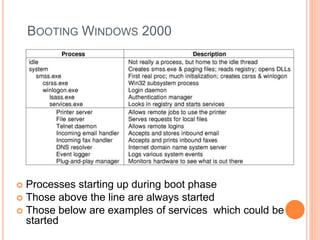
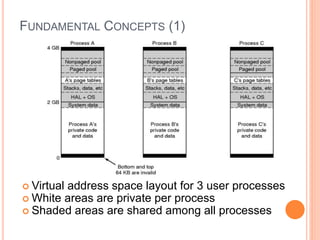
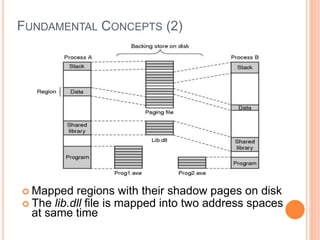
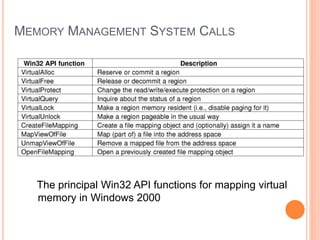
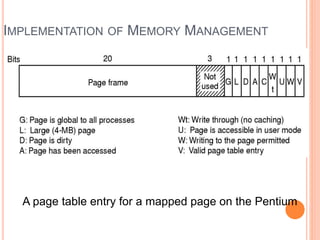
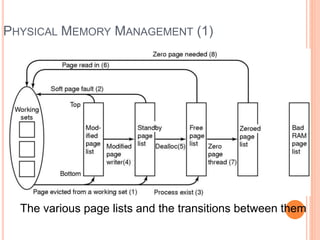
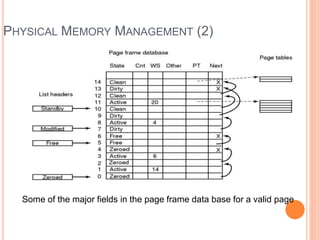
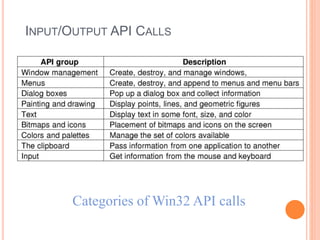
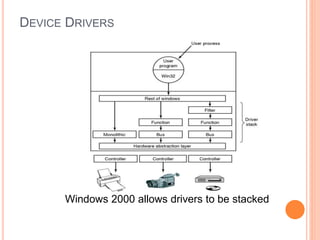
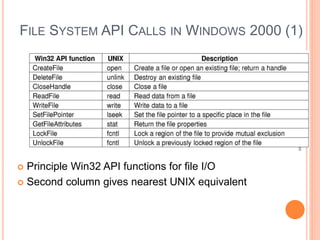
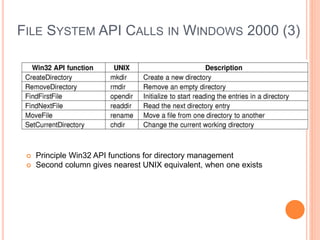
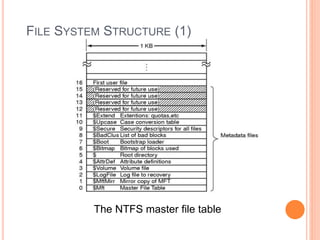
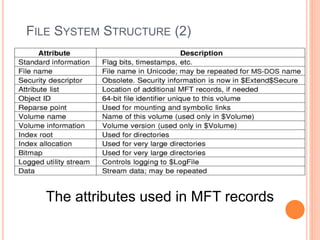
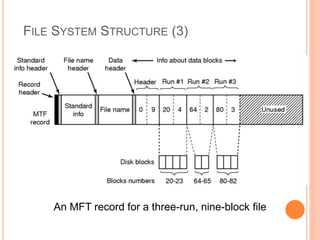
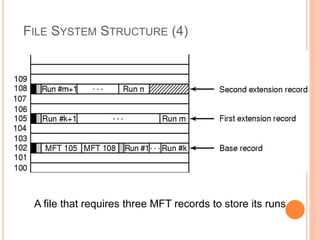
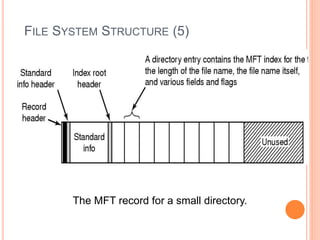
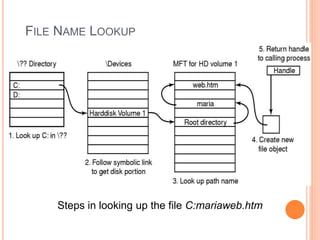
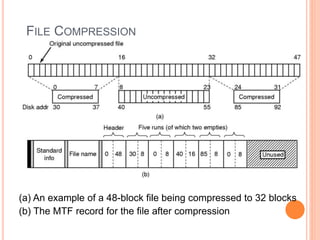
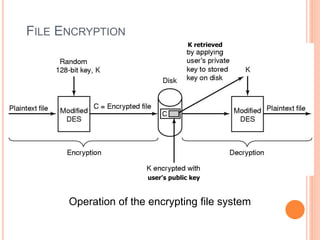
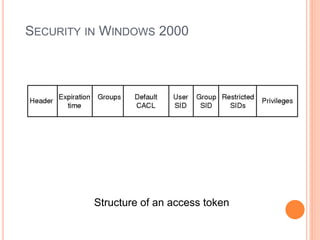
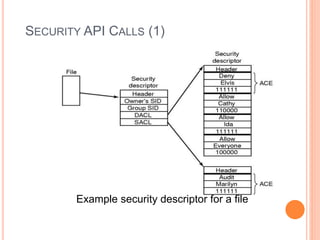
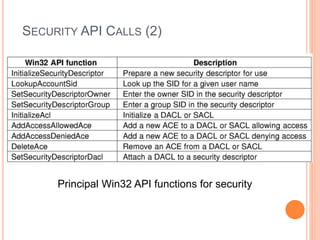
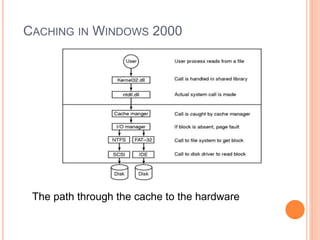
Windows 2000 includes different versions and has a larger operating system size than other versions. It uses the Win32 API to allow program compatibility across Windows versions and manages objects through handle tables. Memory management involves virtual address spaces that are shared and private to processes, as well as page tables that map pages between physical and virtual memory. File I/O, directory management, and file searches use API calls that interface with the NTFS file system which stores metadata and file data in MFT records. Security in Windows 2000 uses access tokens to control permissions through security API functions.