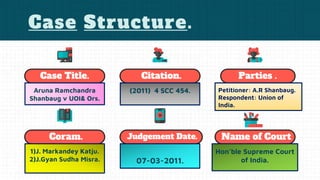
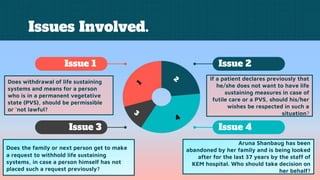
The case of Aruna Ramchandra Shanbaug v. Union of India involved the debate over passive euthanasia for a woman in a permanent vegetative state, with the Supreme Court ruling against her request for termination of life support. The court determined that she was not brain dead and that the responsibility for her care lay with the hospital staff, hence any decision to withdraw life-sustaining treatment was unlawful. The judgment highlighted the complexity of the right to die and clarified guidelines for euthanasia within the framework of the Indian Constitution's Article 21.