Embed presentation
Download to read offline



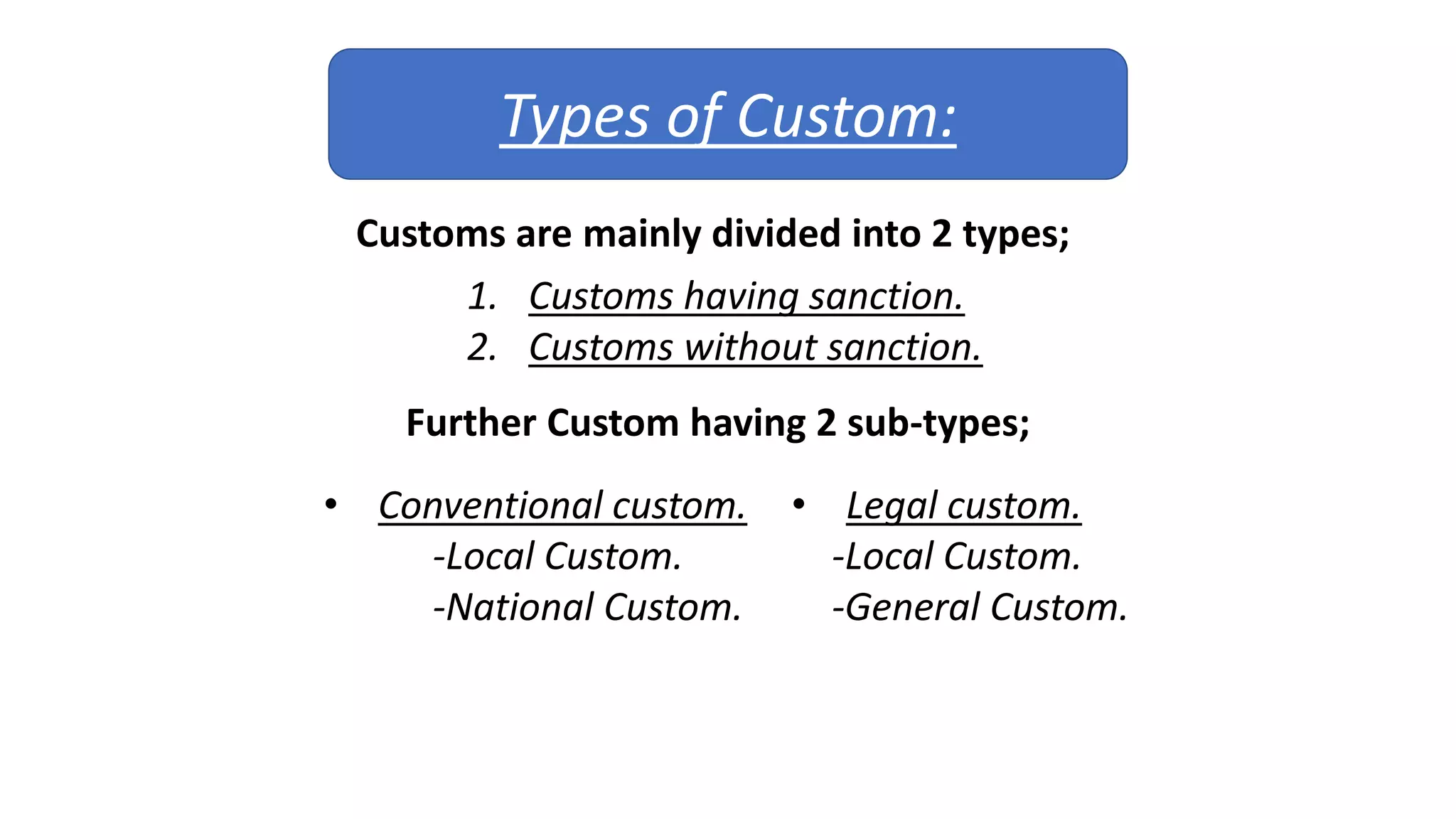

Custom is considered the oldest form of law making and an important source of law. In primitive societies, people's lives were regulated by customs that developed according to circumstances. Some jurists believe customs originated from common practices that became necessary over time through repetition and imitation. Customs are divided into those with legal sanction and those without. For a custom to be valid as law, it must be reasonable, consistent, compulsory, continuous over time, and certain.




