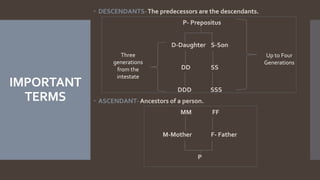
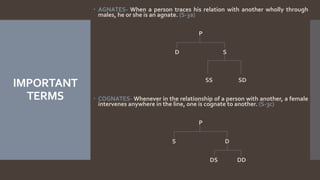
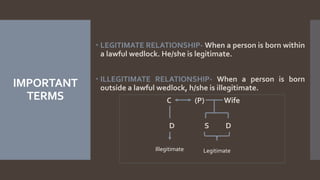
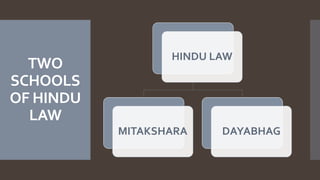
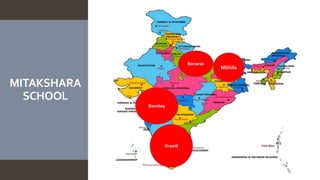
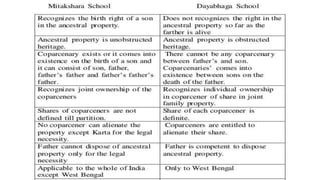
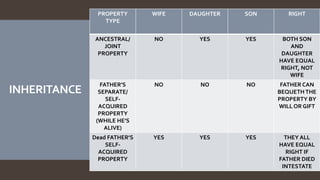
The document explains the concept of coparcenary within Hindu law, which refers to joint ownership of property limited to males who inherit by birth. It contrasts the Mitakshara and Dayabhaga schools of Hindu law in terms of property rights and inheritance, highlighting changes introduced by the Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act of 2005 that granted equal rights to daughters in coparcenary property. The amendment reformed traditional patriarchal norms, allowing women to be treated equally within the family property context, while maintaining certain existing limitations regarding maternal shares.














![CHANGES
BROUGHT BY
THE
AMENDMENT
ACTOF 2005
This amendment is based on the 17th Report
of the Law Commission dated 5th May 2005
chaired by Justice B.P. Jeewan Reddy
Mitakshara Dual mode of devolution of
Property was done away with – devolution
by either intestate or testamentary and not
by survivorship (by sons). [Section 6(3)]
Section 23 & 24 were omitted which only
gave right of dwelling to women and not
ownership and only to unmarried or deserted
wife.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coparcenary-190918041747/85/Coparcenary-in-Hindu-Law-23-320.jpg)





