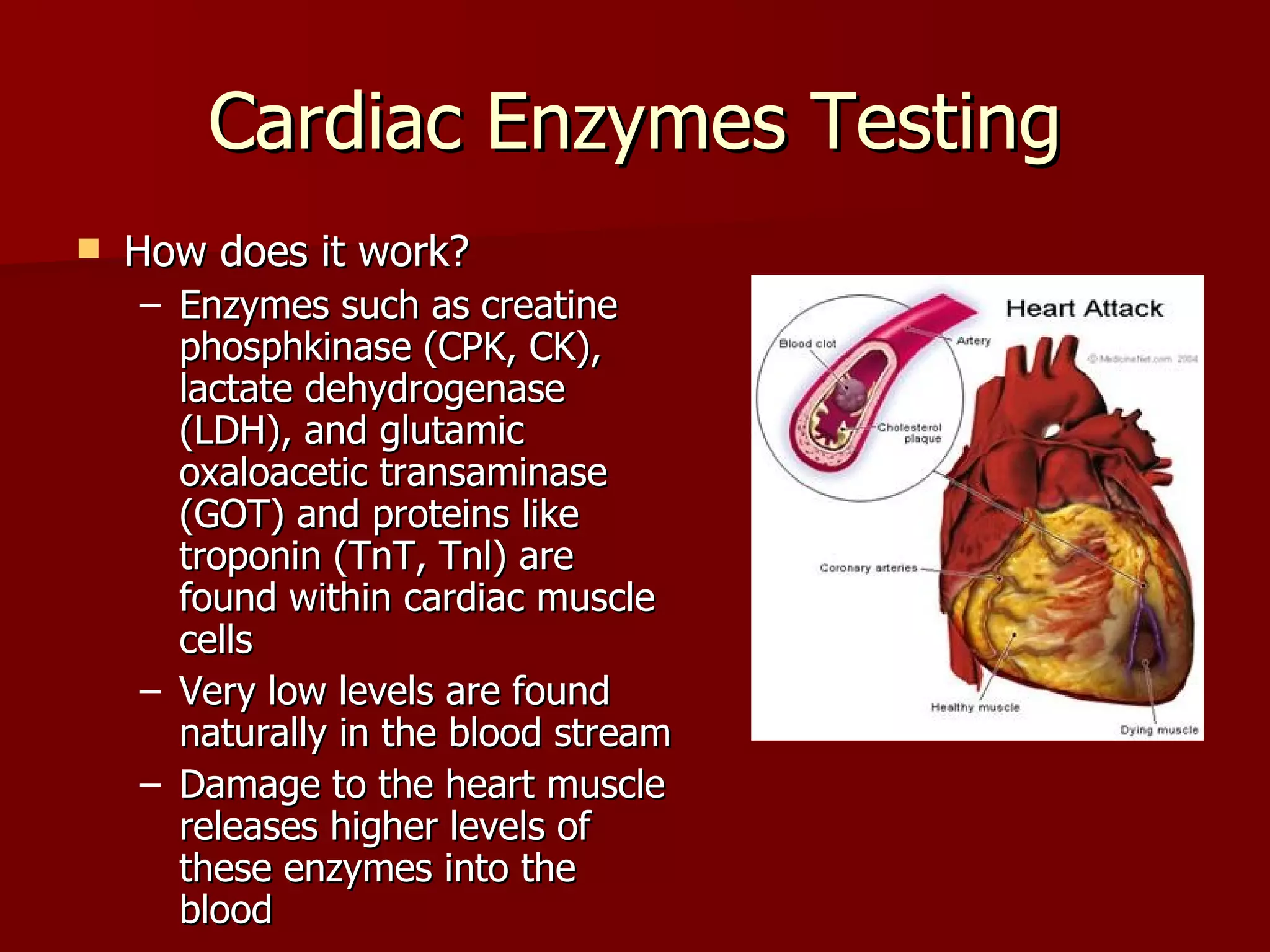
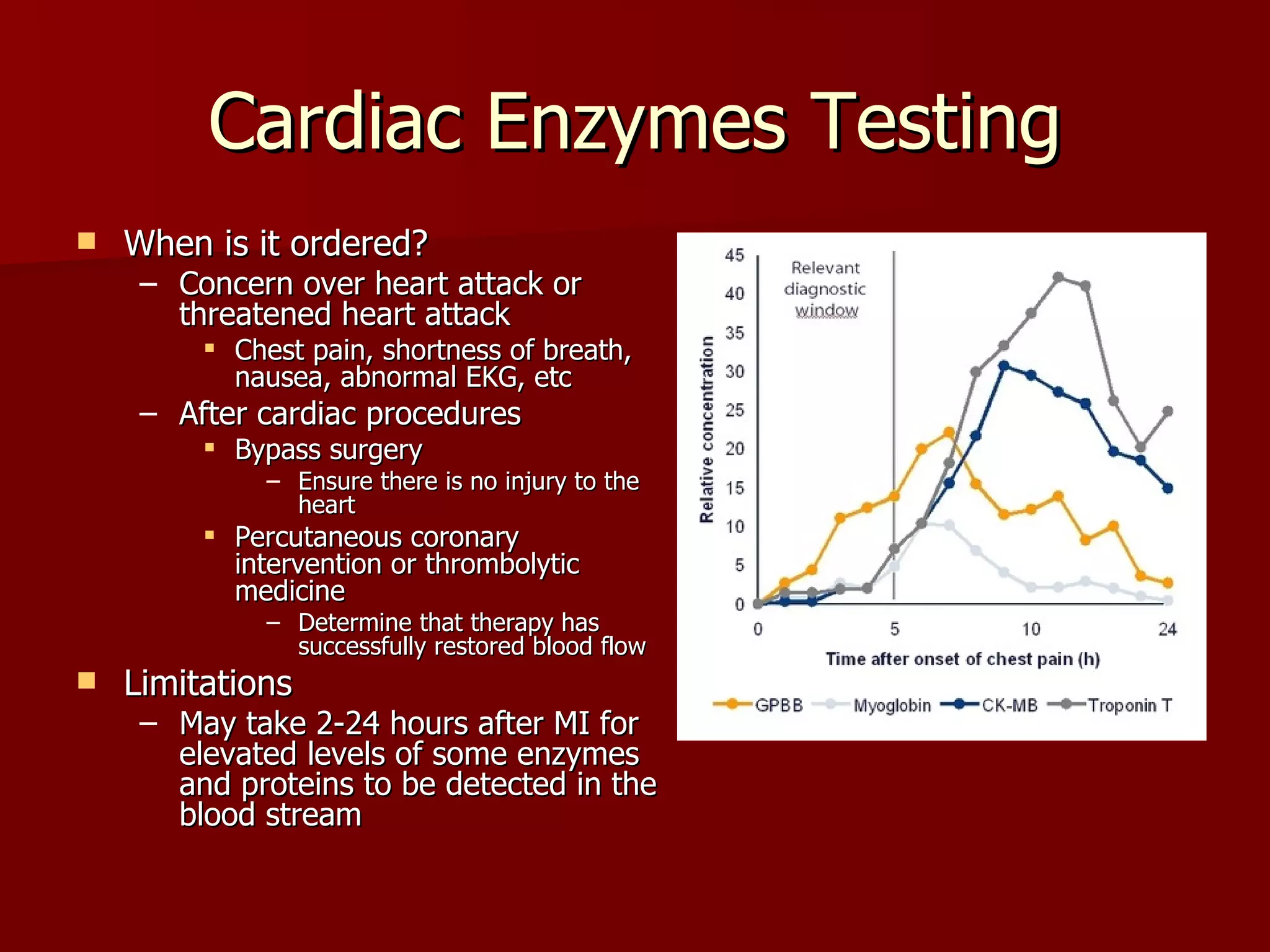
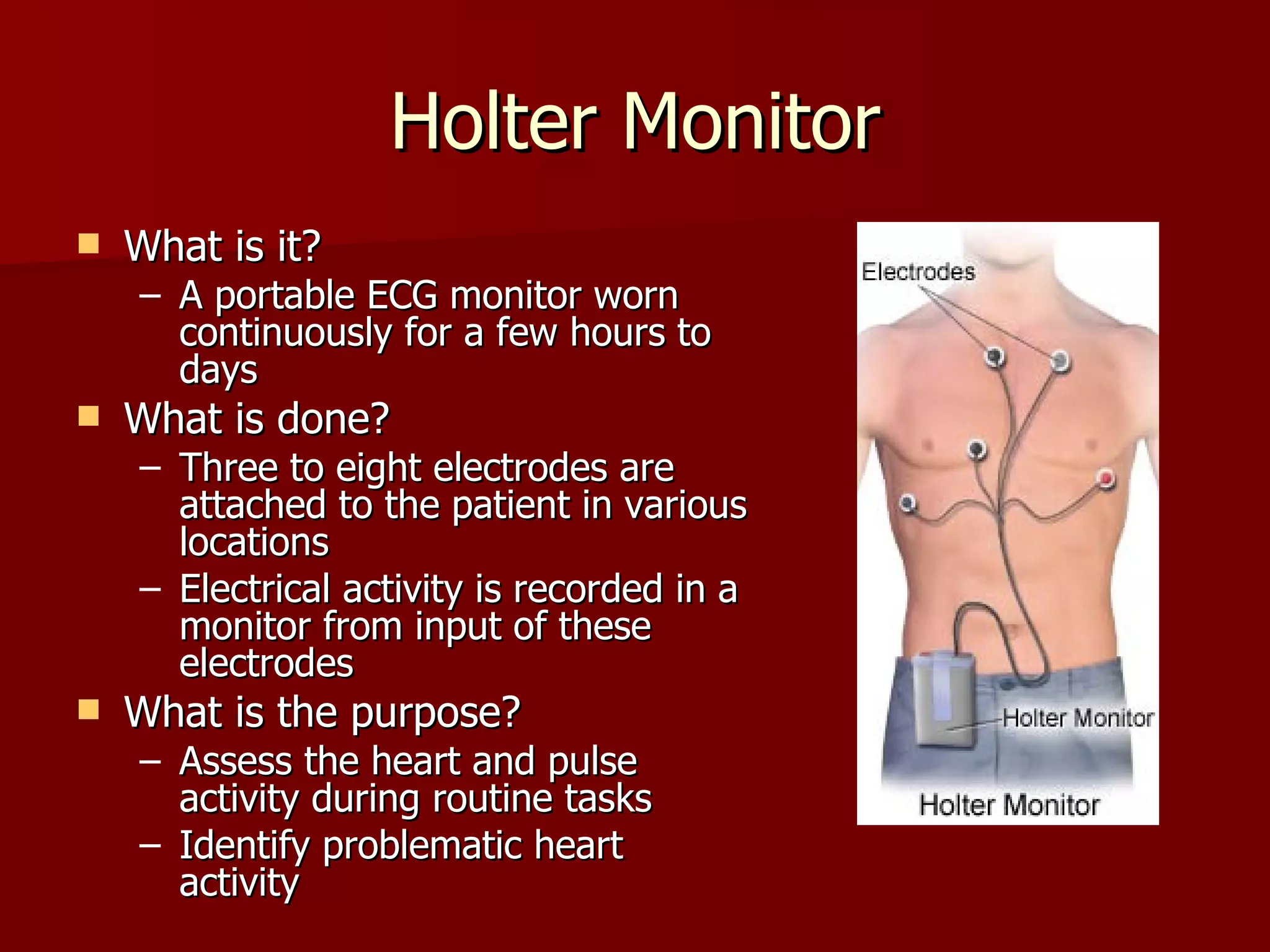
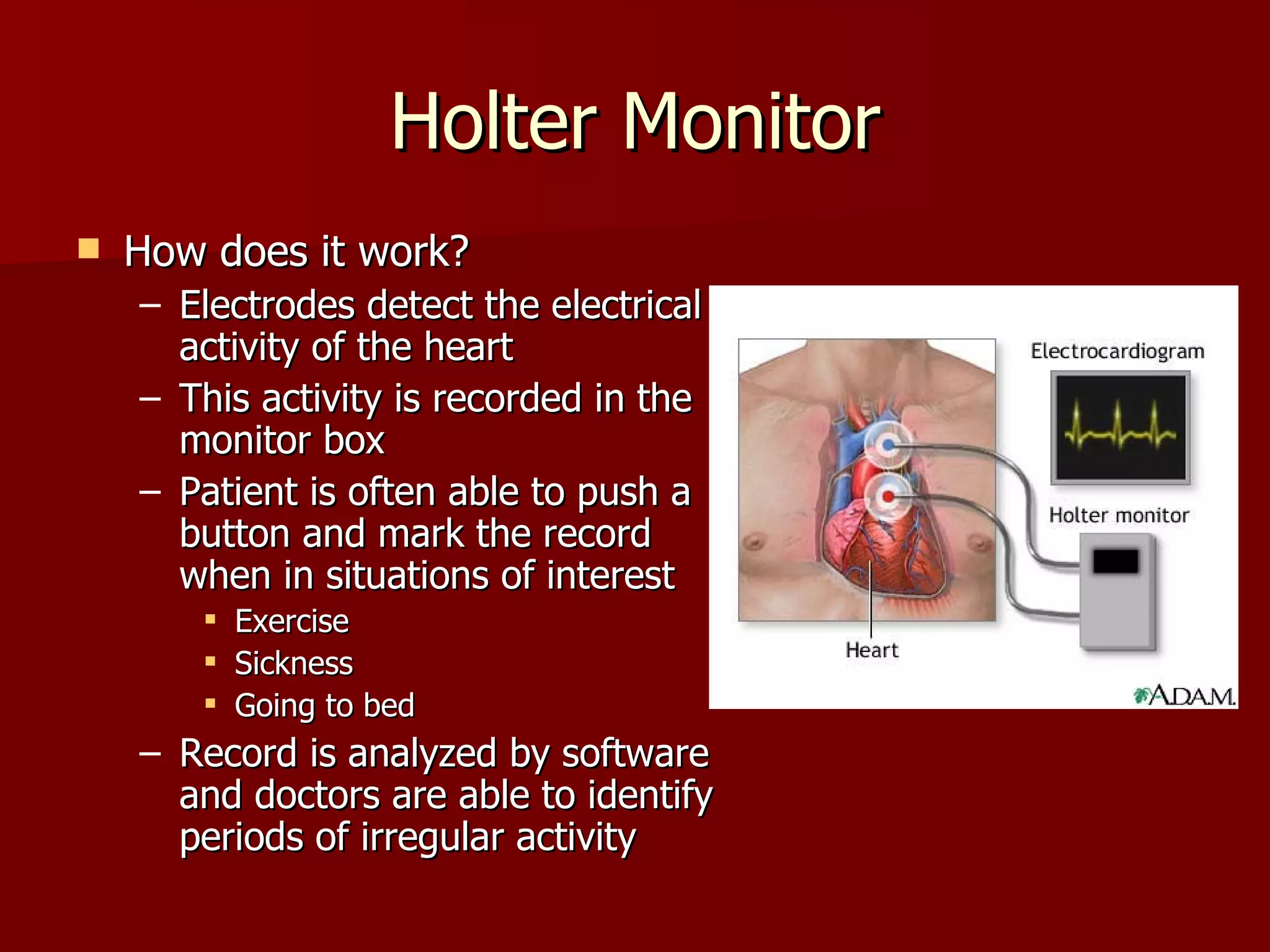
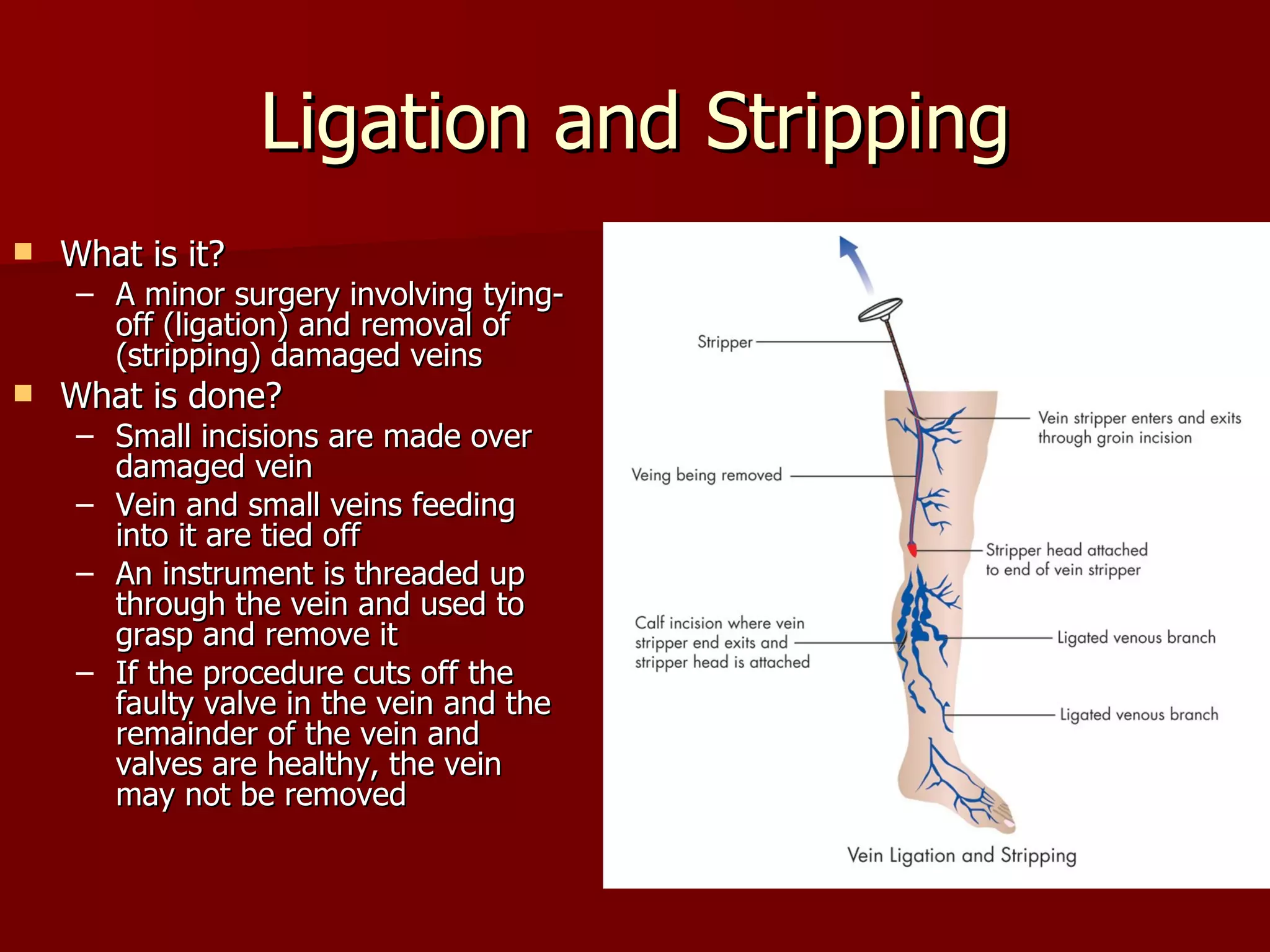
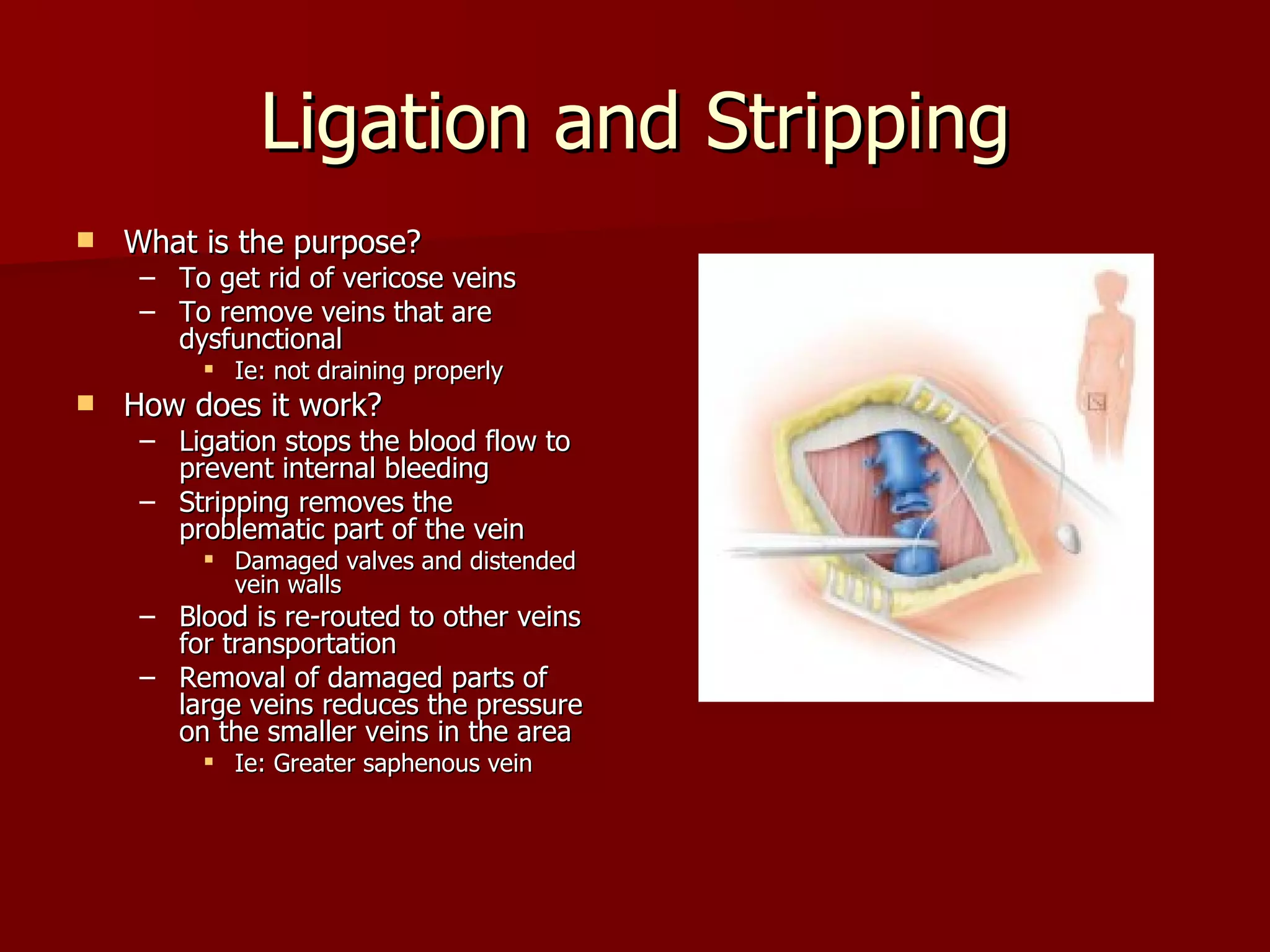
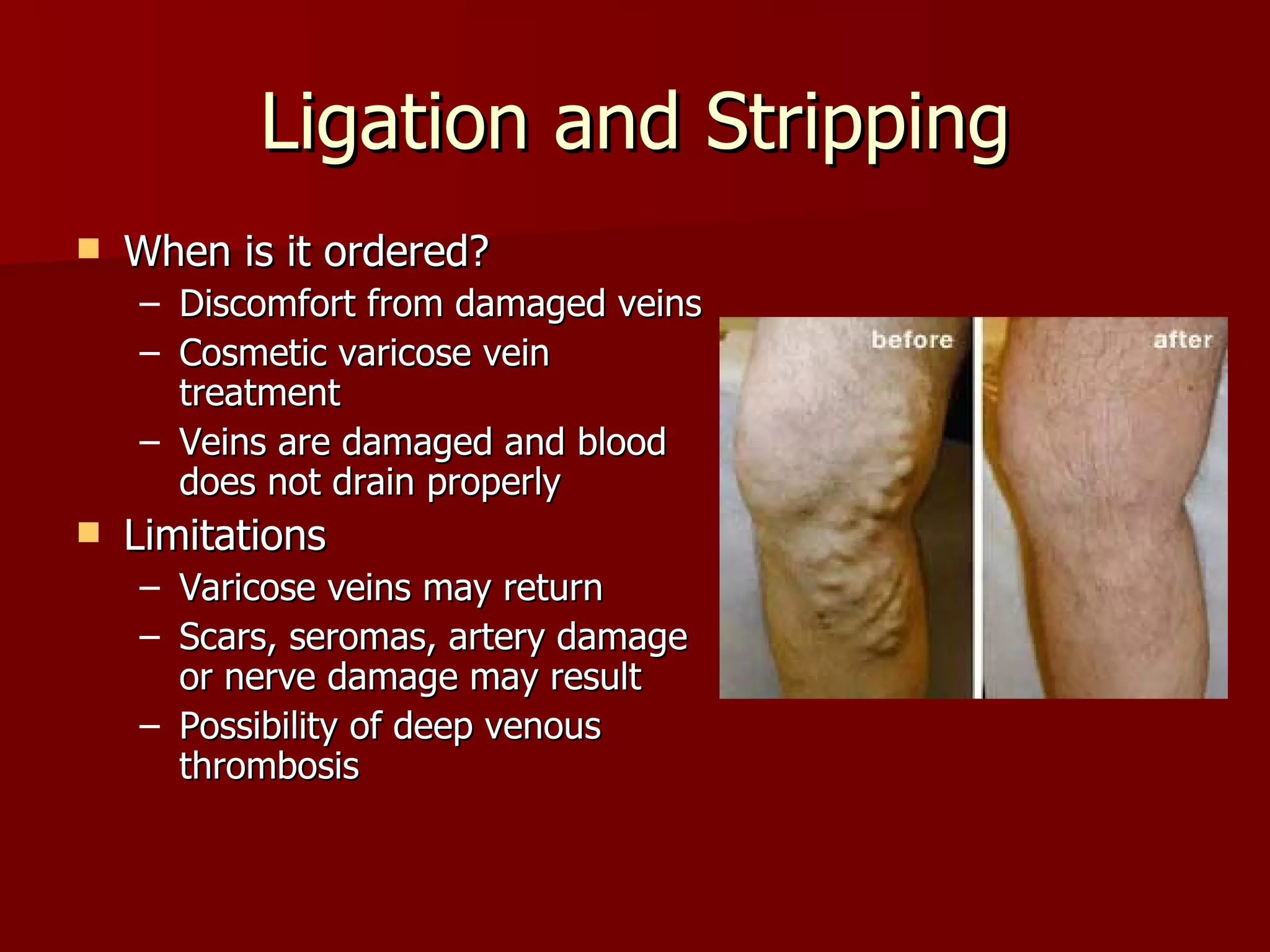
The document discusses several cardiovascular system procedures including diagnostic tests, therapeutic procedures, and minor surgeries. Cardiac enzymes testing analyzes blood levels of enzymes to detect heart muscle injury. A Holter monitor continuously records heart electrical activity over hours to days to identify arrhythmias. Ligation and stripping is a minor surgery that ties off and removes damaged veins to improve blood drainage and reduce vein pressure.