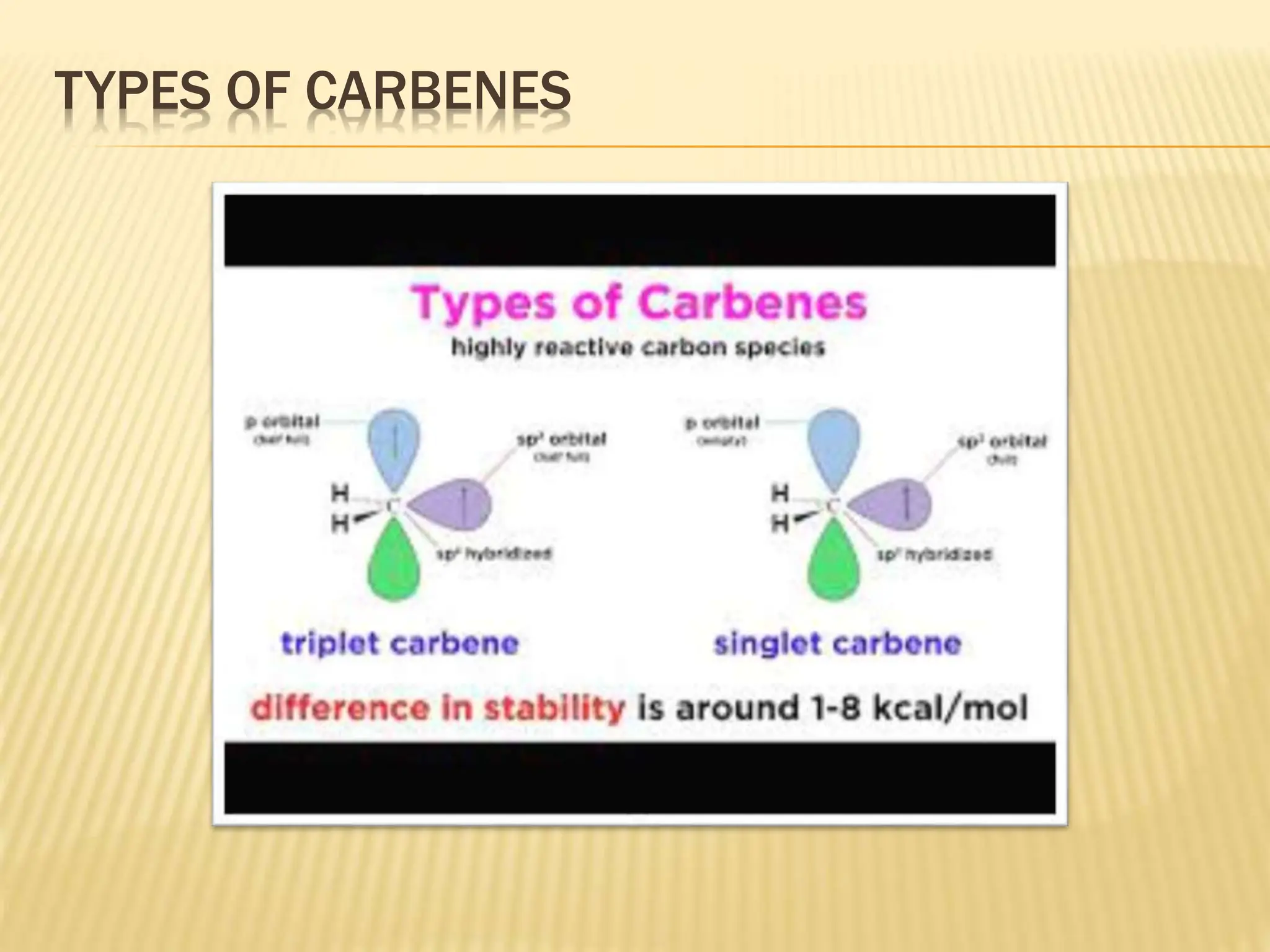
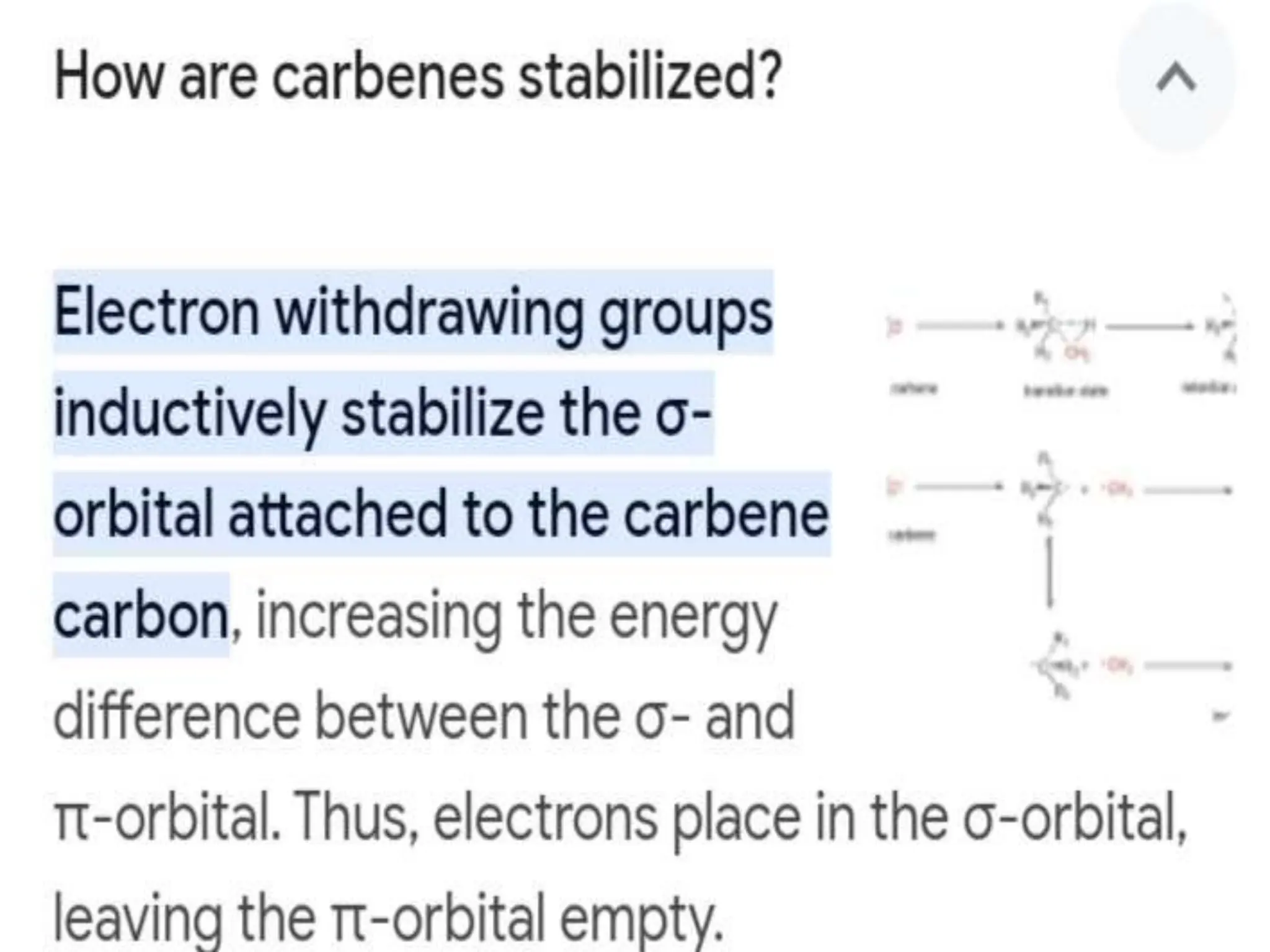
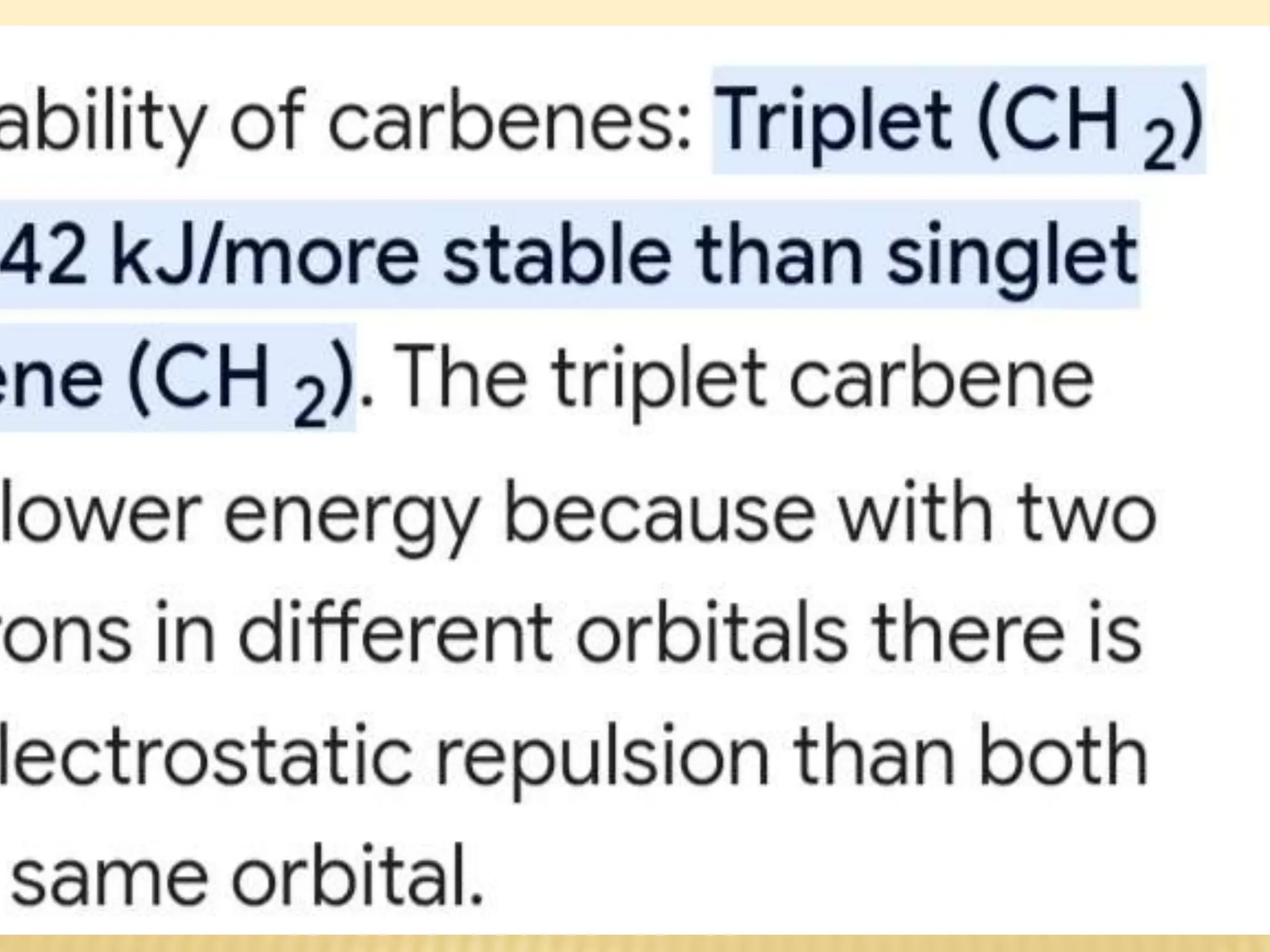
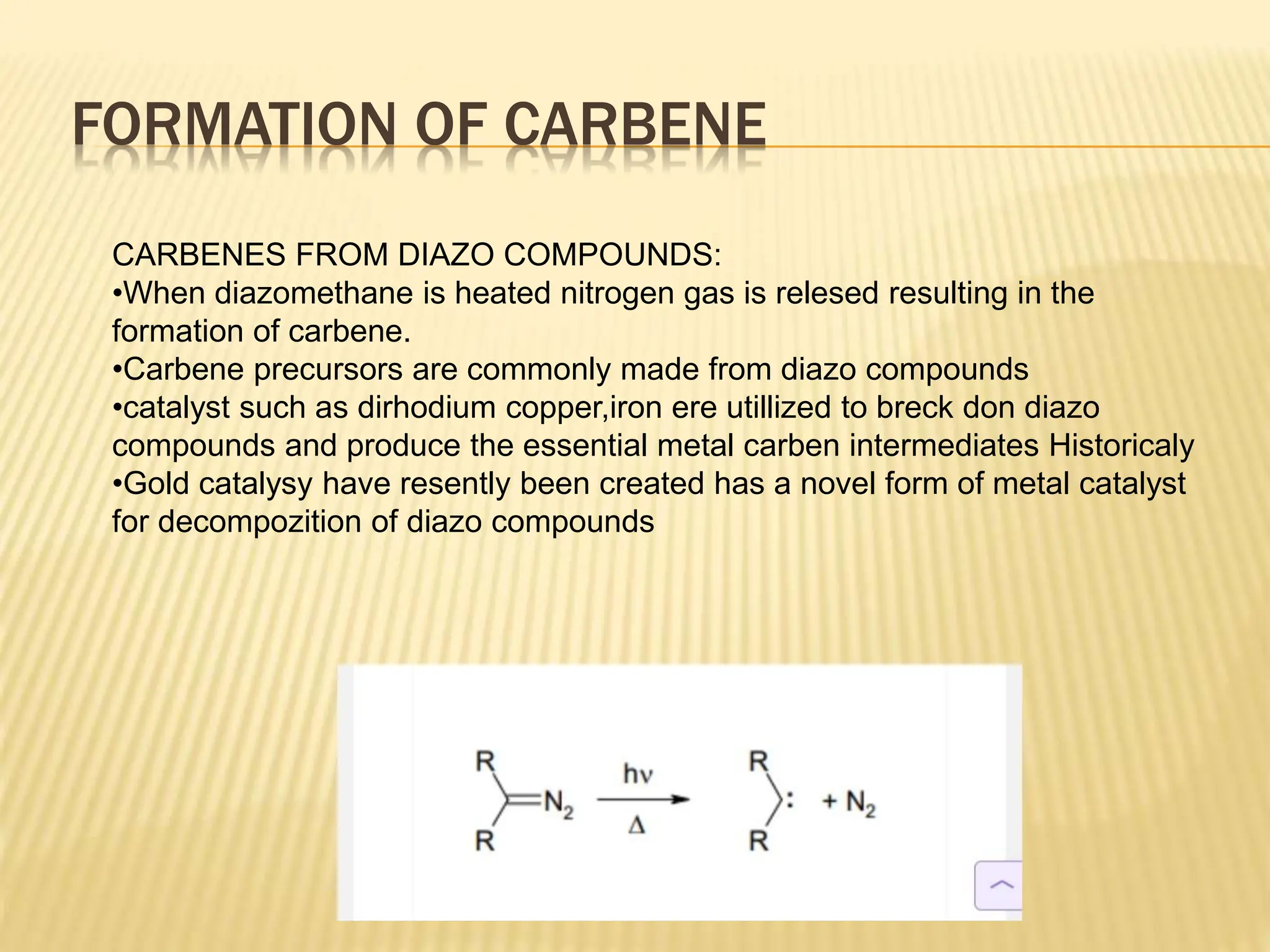
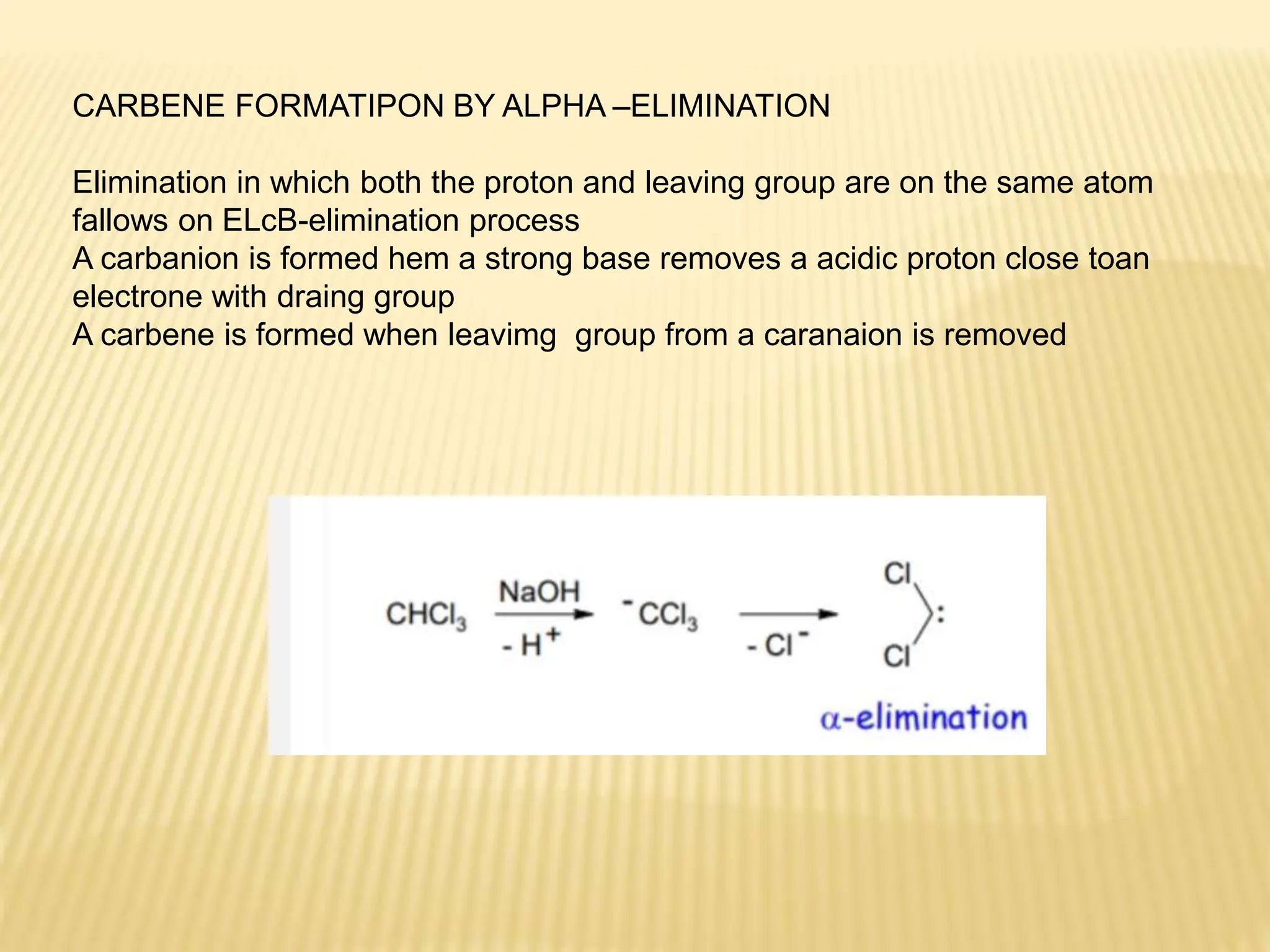
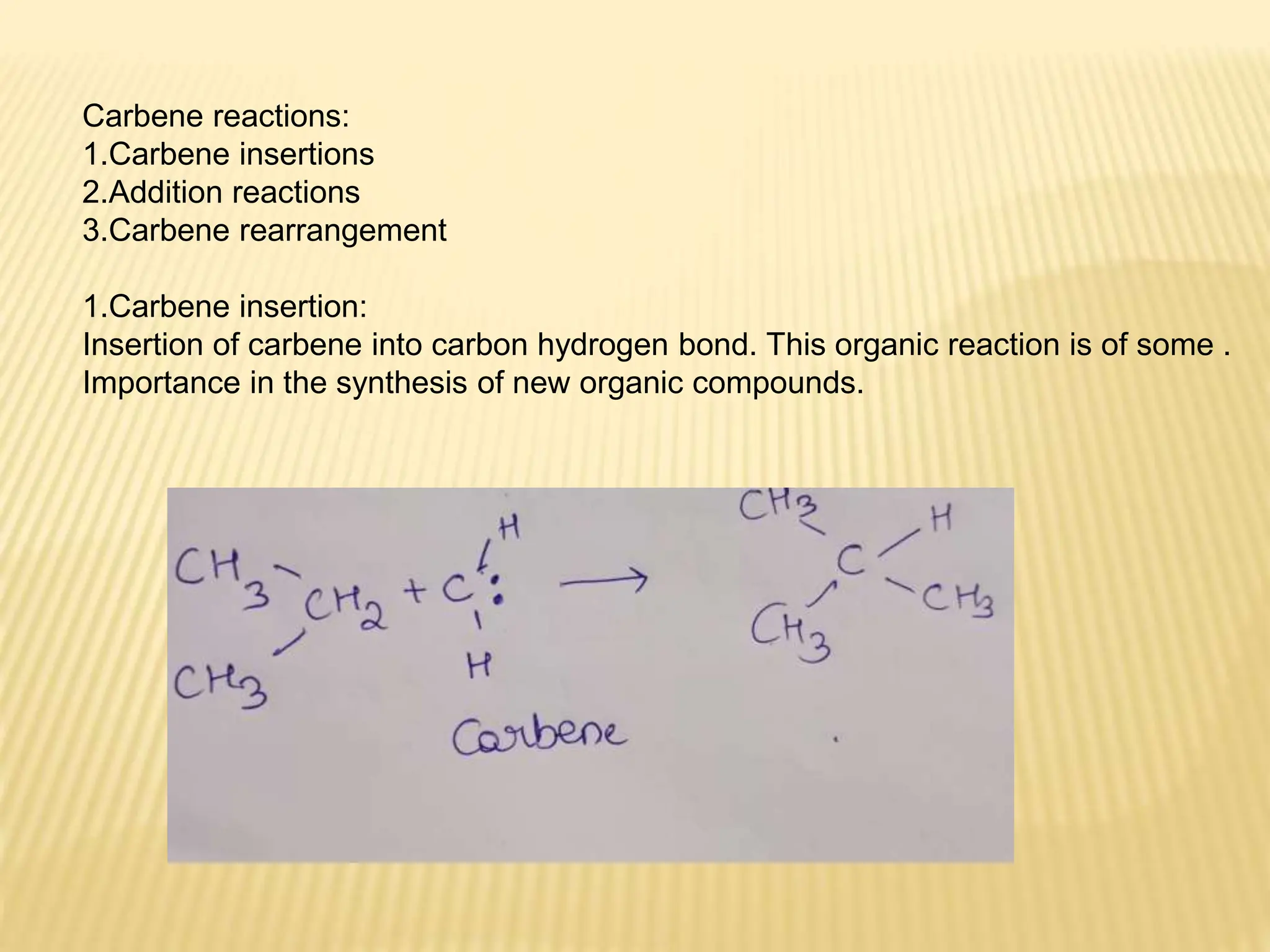
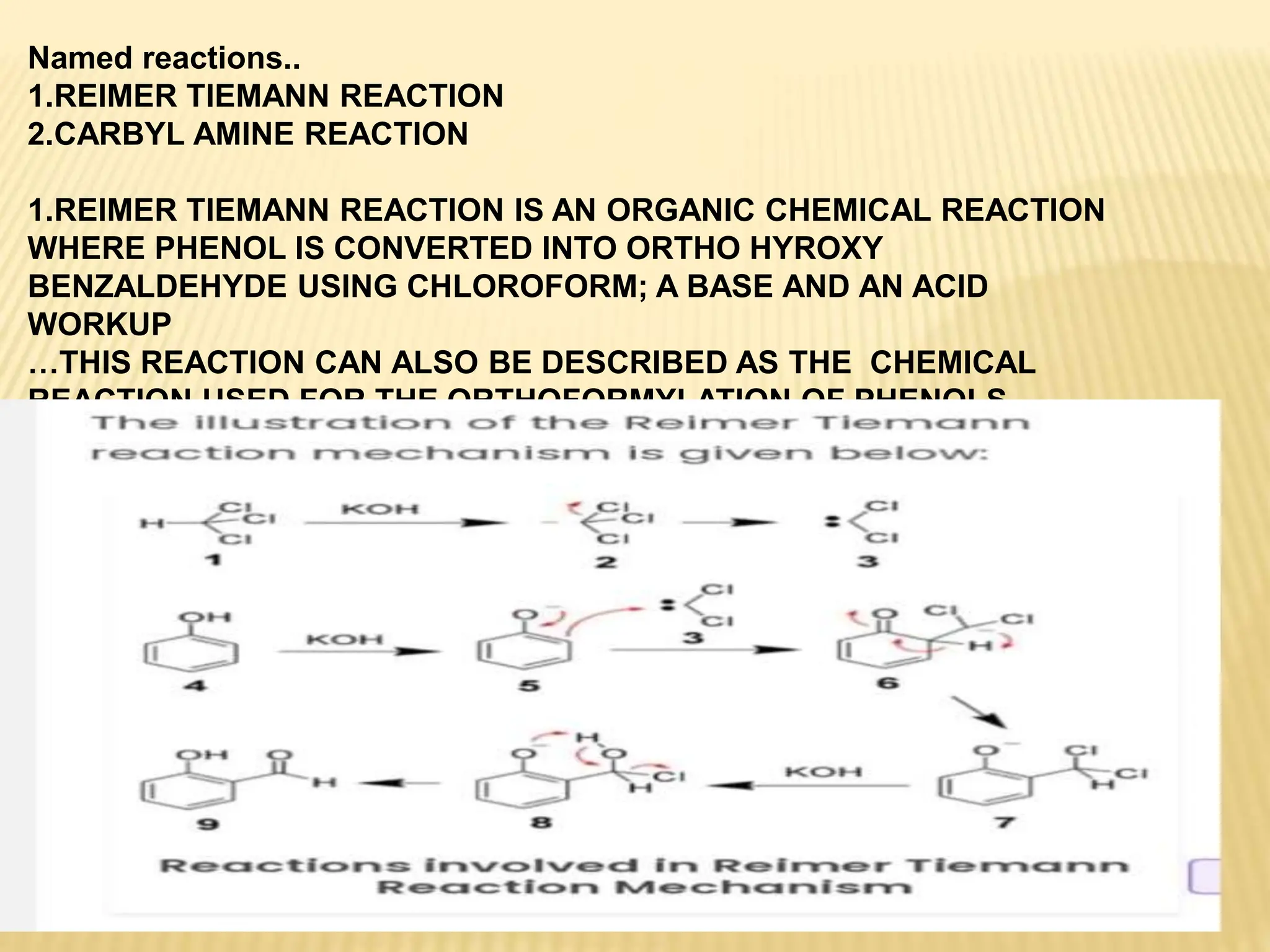
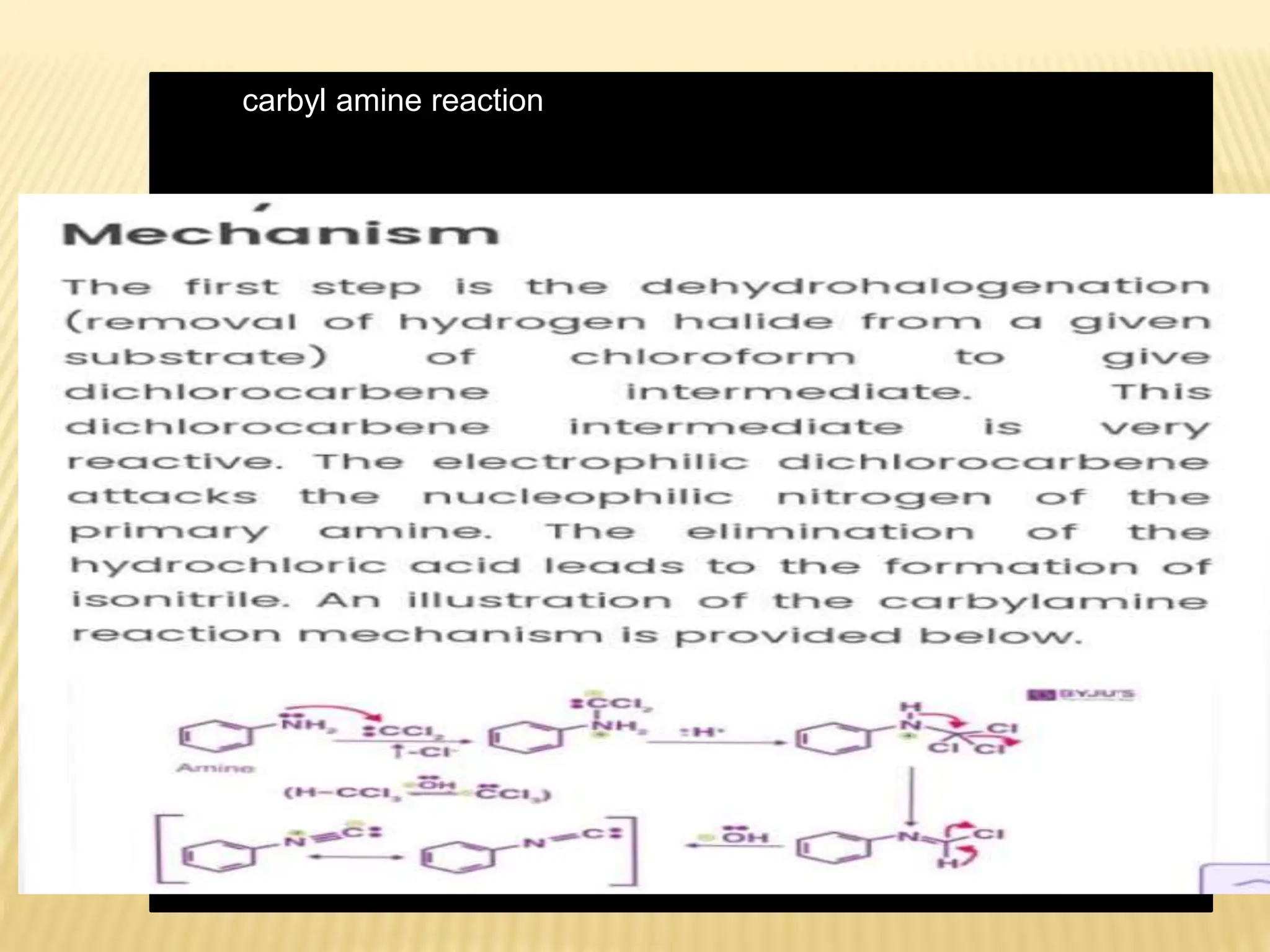
Carbenes are highly reactive molecules containing a neutral carbon atom with two unshared valence electrons. They exist in either singlet or triplet states depending on their electronic structure. Common examples include methylene, phenylmethylene, and dichlorocarbene. Carbenes are important intermediates that enable new carbon-carbon bond formation and are used in pharmaceutical catalysis. They are typically unstable but can form more stable complexes with metals. The main methods of carbene synthesis involve reactions of halogenated compounds with bases, thermal decomposition of diazo compounds, or elimination reactions involving chloroform.