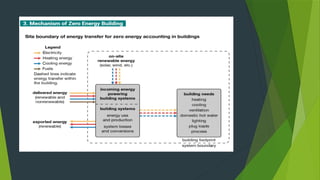
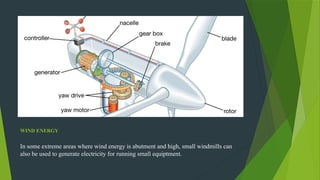
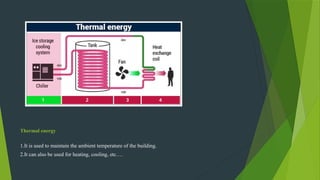
A zero energy building (ZEB) generates more energy than it consumes, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and reliance on fuels. Key approaches to ZEB include passive solar design, energy simulation, and renewable energy generation methods such as solar cells and wind turbines. ZEB can be applied in various settings, offering advantages like reduced living expenses and environmental compatibility, although it faces challenges due to a lack of skilled designers and limited solar energy availability in certain areas.
















![References
[1] P.Torcellini,S. Pless, M. Deru, D. Crawley, Zero Energy Buildings: A Critical Look at The
Definition, in: ACEEE Summer Stud, Pacific Grove, California, USA, 2006
[2] Sami A. Al-Sanea , M.F. Zedan, S.N. Al-Hussain. Effect of thermal mass on performance
of insulated building walls and the concept of energy savings potential,2011,
www.elsevier.com/ locate/apenergy
[3] M. Noguchi, A. Athienitis, V. Delisle, J. Ayoub, B. Berneche, Net Zero Energy Homes of
the Future: A Case Study of the ÉcoTerraTM House in Canada, in: Renewable Energy
Congress, Glasgow, Scotland, July, 2008.
[4] T.V. Esbensen, V. Korsgaard, Dimensioning of the solar heating system in the zero energy
house in Denmark, Solar Energy 19 (2) (1977) 195–199.
[5] A.J. Marszal, et al., Zero Energy Building – A review of definitions and calculation
methodologies, Energy Buildings (2011), doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2010.12.022](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cppimp203-240924022846-1d8c90cb/85/Capstone-project-planning-Zero-energy-building-21-320.jpg)
