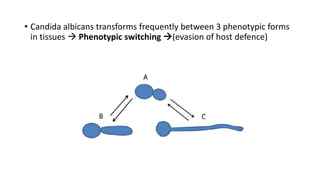
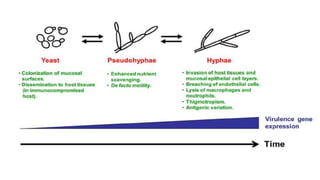
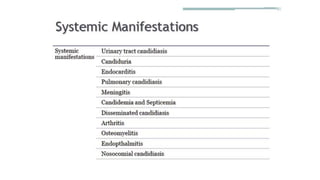
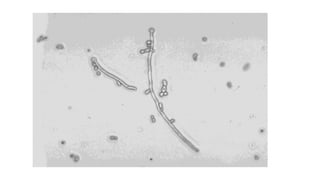
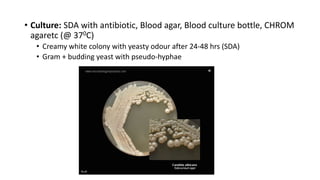
This document discusses Candida, a fungal pathogen that can cause various infections in humans. It notes that Candida albicans is the most common Candida species causing infection. It identifies several risk factors that increase the risk of Candida infection, including extremes of age, pregnancy, HIV infection, steroid/cytotoxic drug therapy, malignancy, and broad spectrum antibiotic use. The document outlines several types of Candida infections, including mucosal and cutaneous candidiasis. It also describes methods for laboratory diagnosis of Candida infections through microscopy, culture, and other tests. Treatment generally involves the use of antifungal azole drugs or amphotericin B.