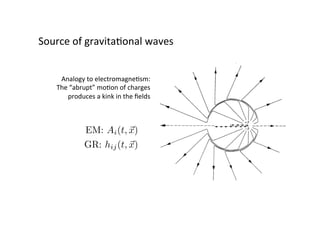
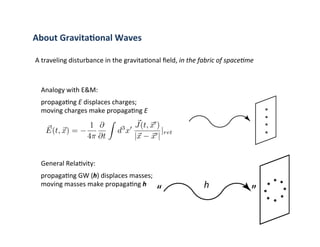
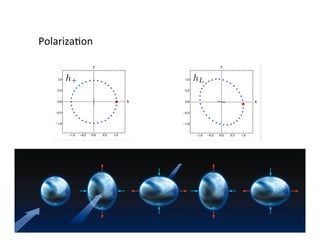
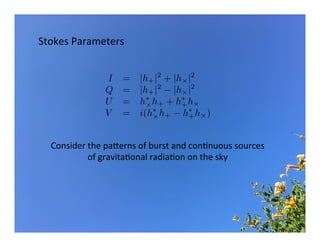
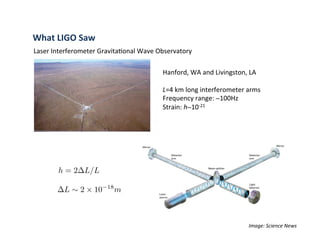
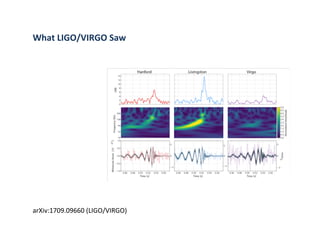
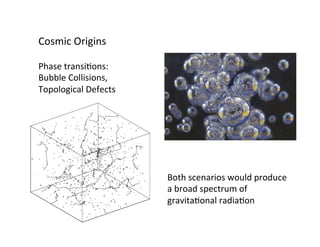
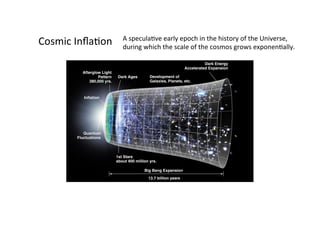
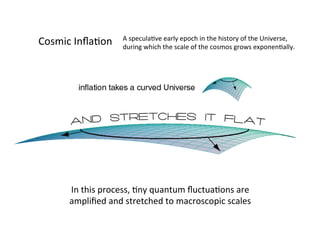
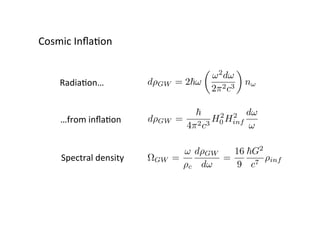
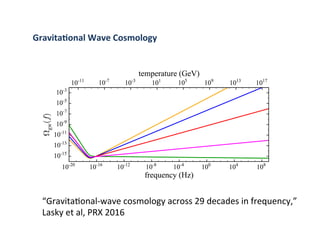
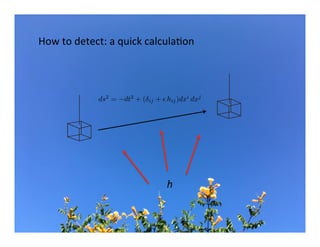
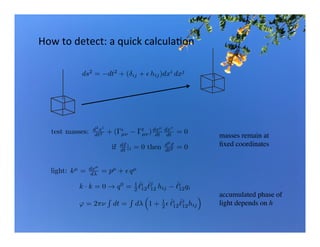
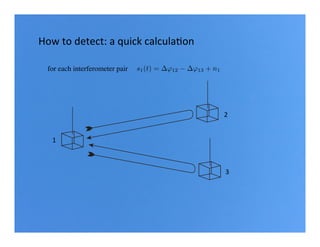
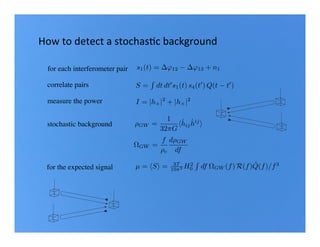
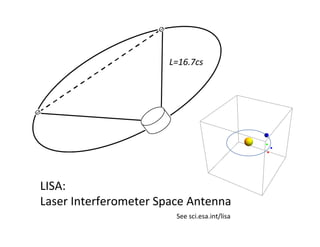
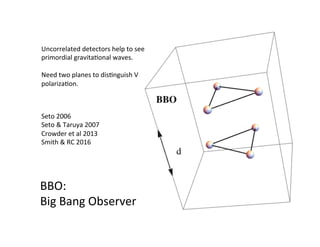
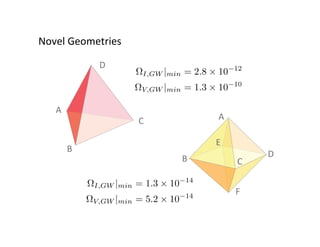
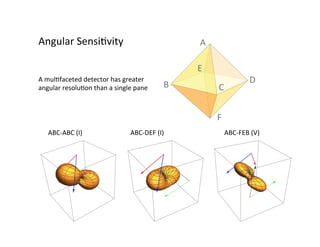
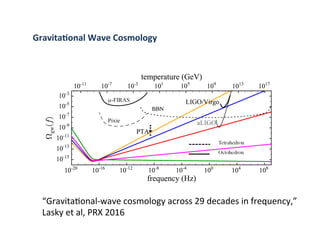
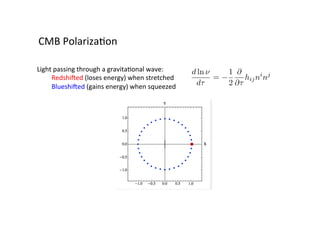
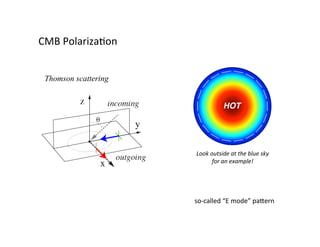
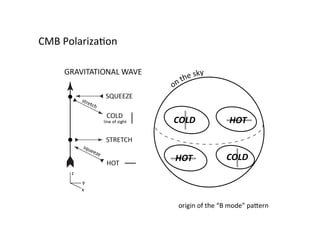
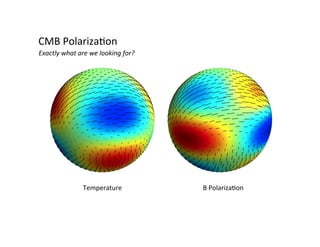
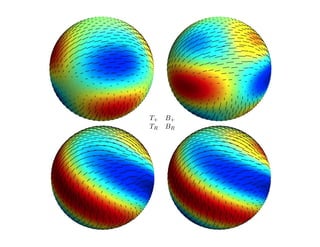
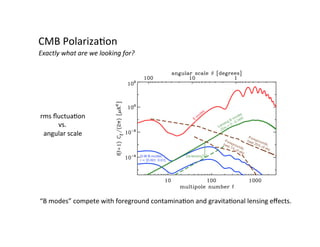
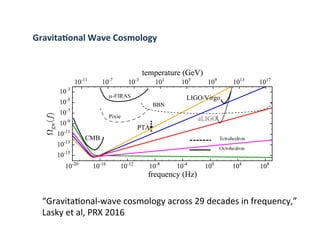
Primordial gravitational waves from inflation could be detected using the cosmic microwave background. Gravitational waves passing through the last scattering surface would induce B-mode polarization patterns in the CMB. Future experiments aim to detect these B-modes as a signature of primordial gravitational waves, which would provide insights into inflation and the very early universe.