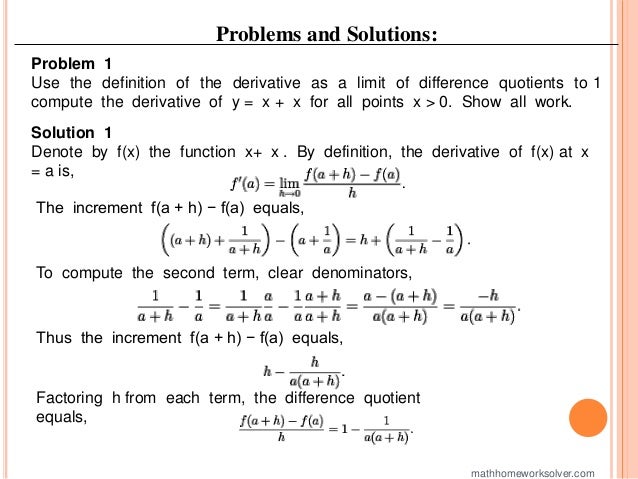
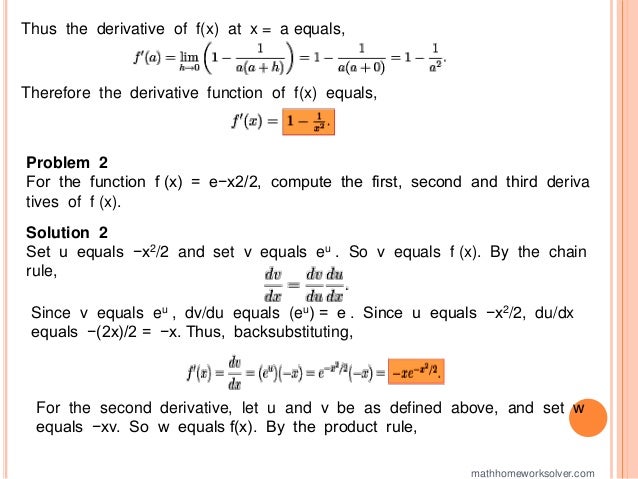
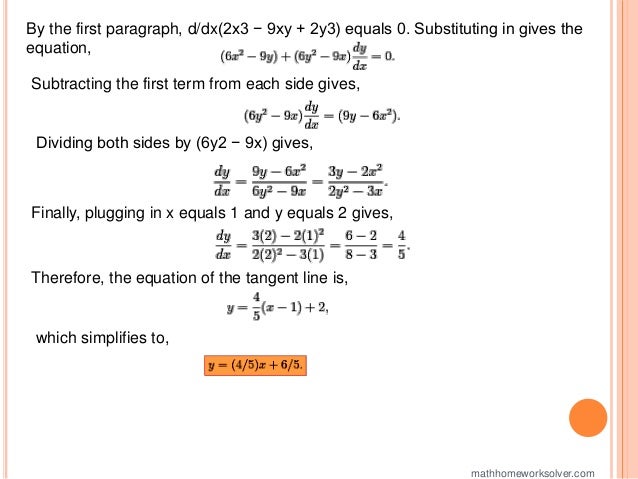
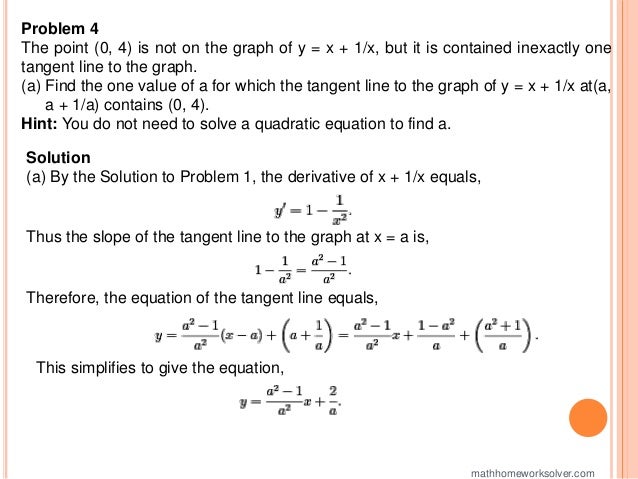
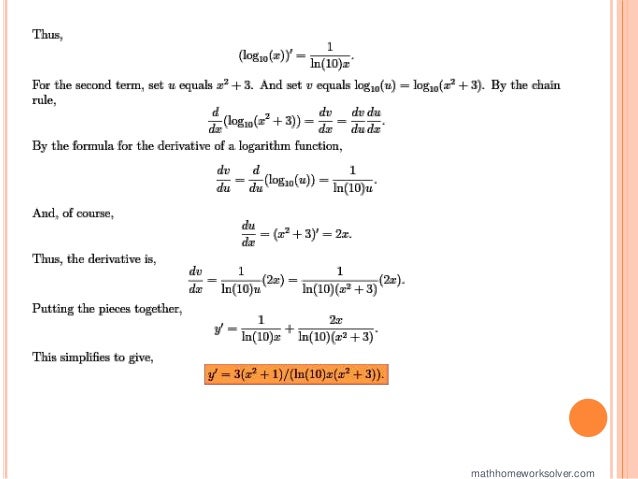
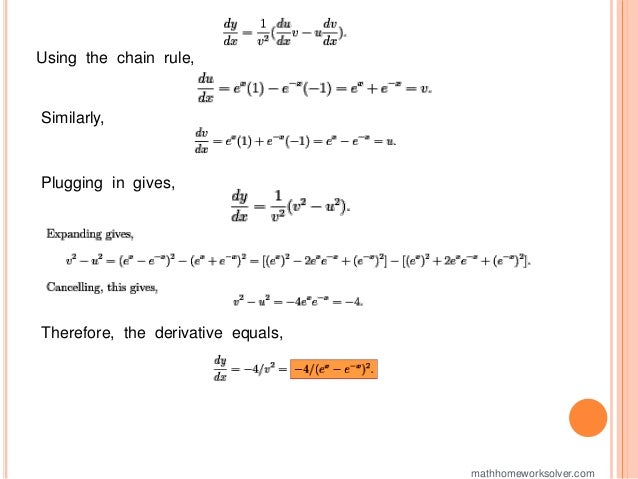The document provides detailed solutions to a variety of calculus problems, including computing derivatives using limits, implicit differentiation, and solving for tangent lines. It also includes explanations for finding derivatives of specific functions and presents problems related to an automobile crash test scenario. Additionally, the document addresses an extra credit challenge involving polynomial forms of nth derivatives.