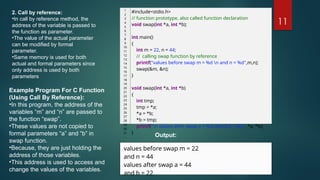
The document explains the concept of functions in the C programming language, including their definition, types, and the importance of structuring programs using functions. It details standard library functions, user-defined functions, and the benefits of using functions such as reusability and improved readability. Additionally, it illustrates function declaration, calling methods (call by value and call by reference), and provides example code snippets for clarity.