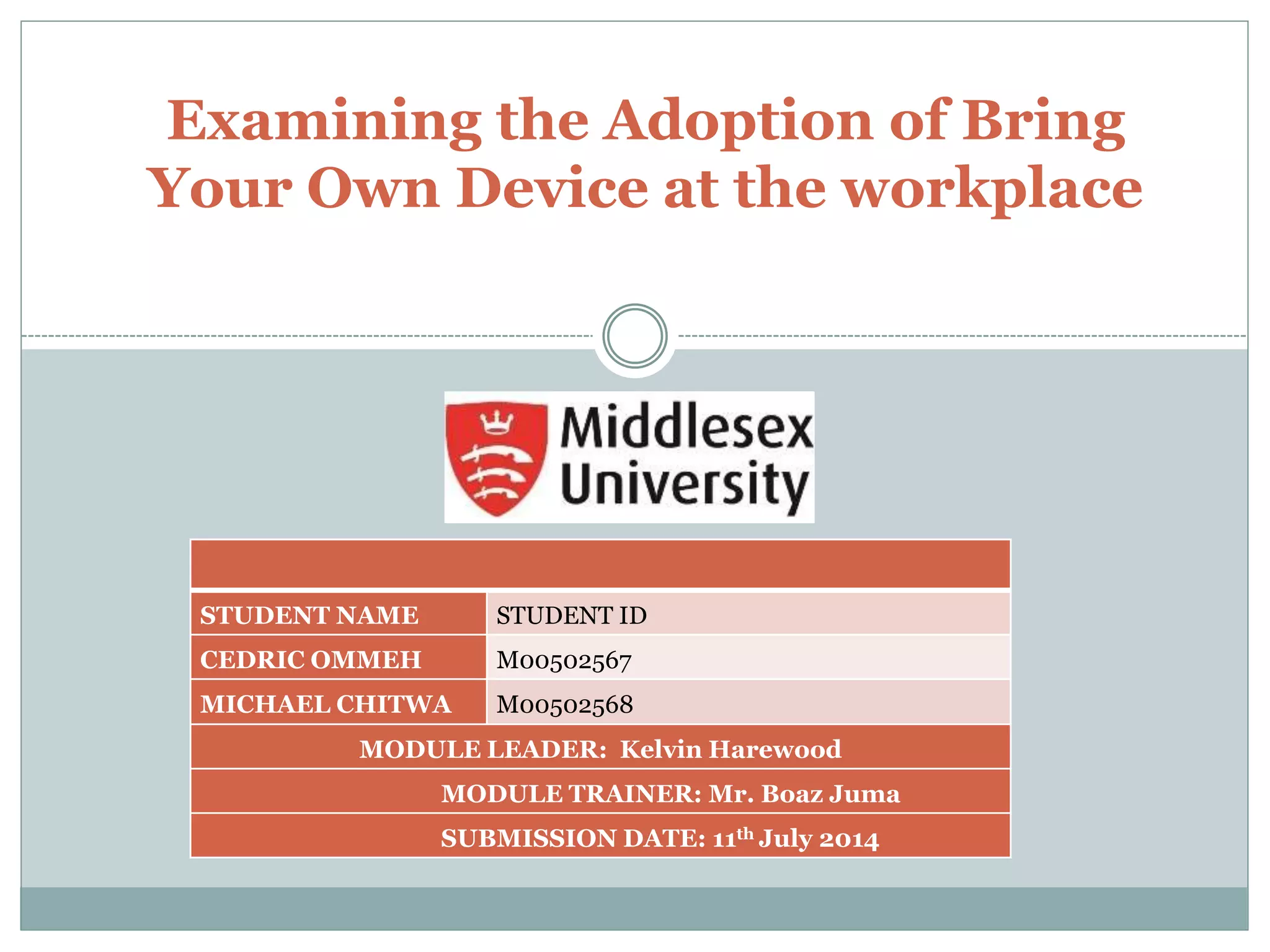
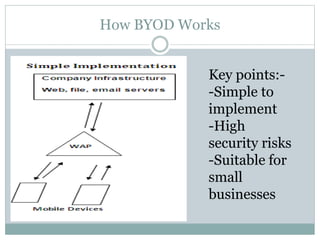
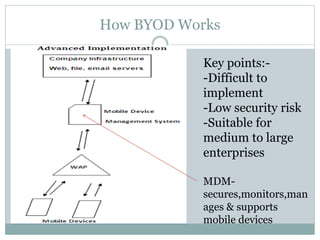
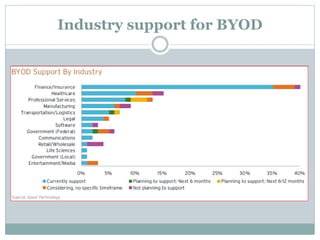
The document discusses the concept of Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) in the workplace, highlighting its definition, adoption drivers, and associated challenges. It outlines benefits such as increased flexibility, productivity, and employee satisfaction, while also addressing security risks, privacy issues, and costs. Ultimately, it concludes that despite challenges, BYOD is beneficial for organizations and may evolve into a broader technology adoption trend.