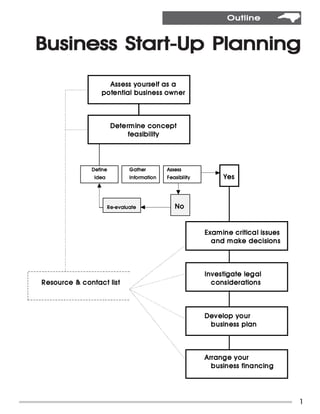
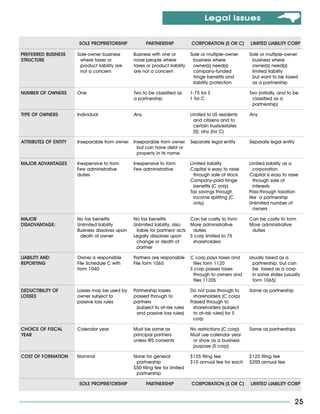
This document is a guide for starting a small business in North Carolina. It covers topics such as assessing your potential as a business owner, determining the feasibility of your business concept, examining critical issues and decisions, developing a business plan, arranging financing, and understanding legal and regulatory requirements. The guide provides information on these topics to help new entrepreneurs start and run a successful small business.