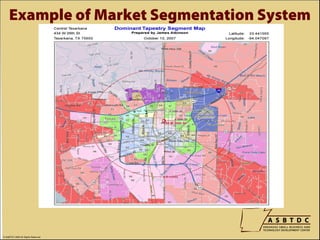
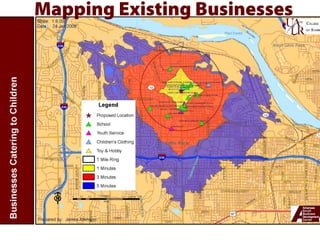
This document provides an overview of how to write an effective business plan in 3 to 5 concise points or sections. It recommends including products/services, market analysis, industry overview, operations, and budgets. Market research tools are suggested to define the target customer and location. The presentation stresses that the plan should clarify thinking and identify benchmarks to evaluate business progress. Financial projections and supporting documents are also important for obtaining financing.