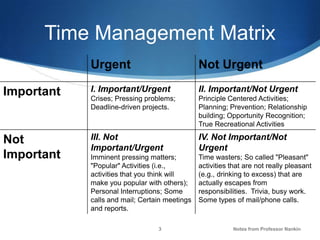
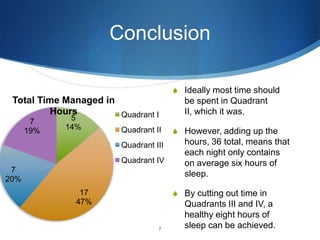
The document is a report analyzing the author's time management over two days using a time management matrix. It includes an introduction to time management and the matrix. The matrix divides time into important/urgent, important/not urgent, not important/urgent, and not important/not urgent. Charts show the author spent most time on important schoolwork, with some reductions in last minute work and distractions from day one to two. The conclusion notes the benefits of focusing more on important tasks and less on urgent or distracting activities to allow for sufficient sleep.