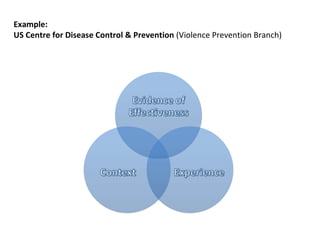
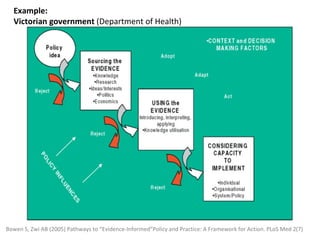
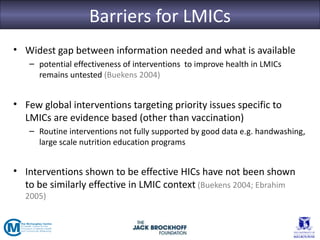
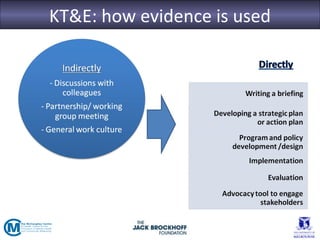
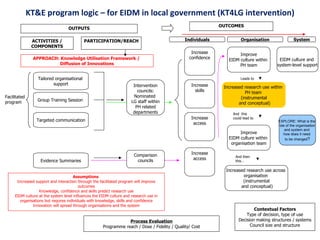
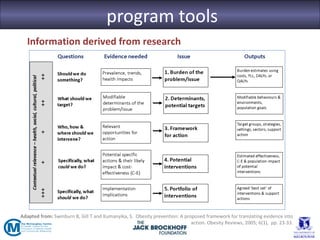
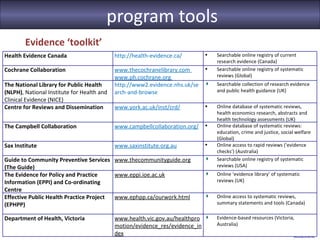
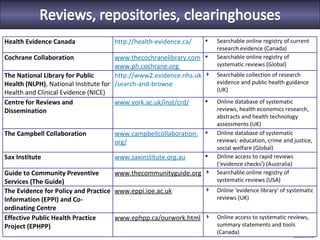
The seminar focused on bridging the gap between research and practice in public health, emphasizing the importance of evidence-informed decision-making. It discussed strategies such as knowledge brokering and training to improve the integration of research findings into policy and practice. Barriers to evidence use were identified, including lack of access and trust, particularly in low- and middle-income countries where effective interventions remain untested.