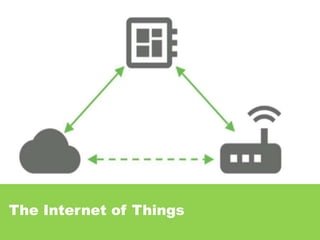
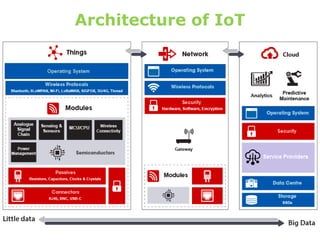
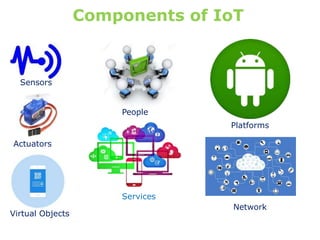
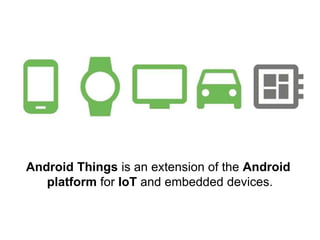
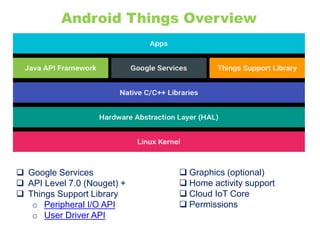
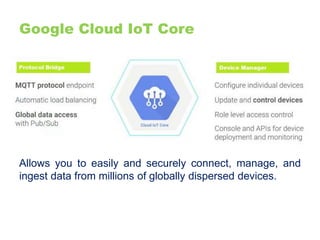
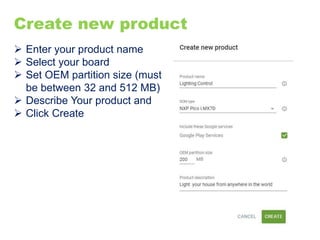
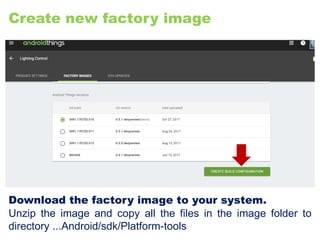
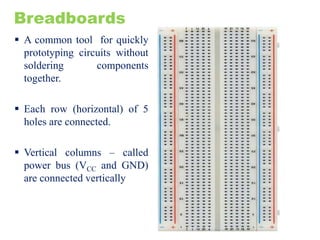
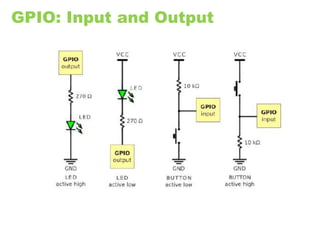
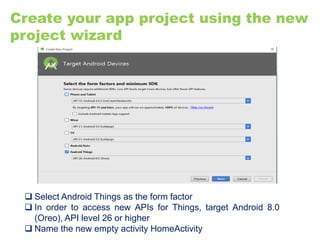
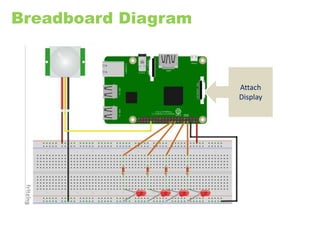
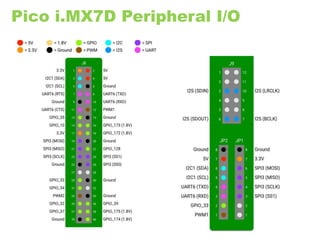
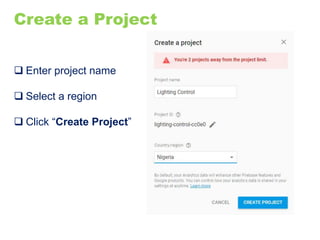
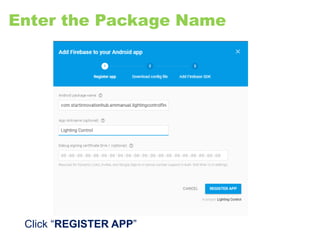
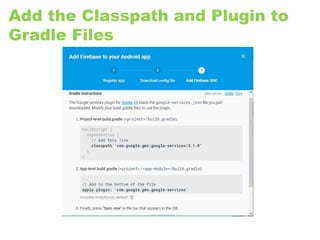
The document provides an overview of the Internet of Things (IoT) architecture and components, detailing various use cases and projects such as smart street lighting and home automation. It discusses the Android Things platform, its requirements, and how to create applications using Android Studio while integrating Firebase for remote monitoring and control. It also covers basic electronics and peripheral connections needed for IoT projects, along with links to resources for further development.