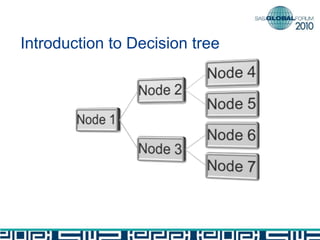
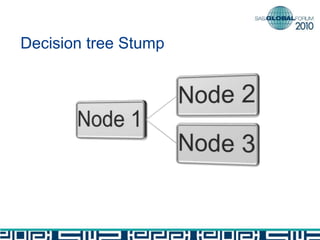
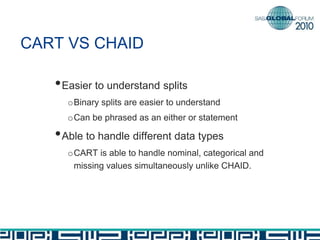
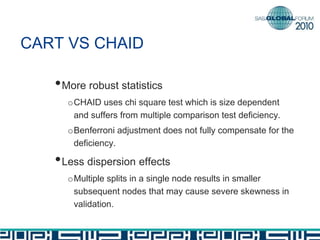
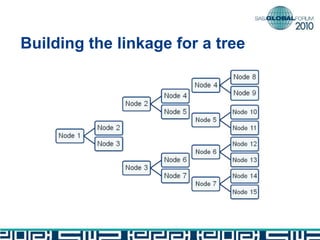
The document discusses building decision tree stumps from full decision trees. It introduces decision trees and defines a decision tree stump. It compares the CART and CHAID algorithms, noting CART handles different data types better and uses more robust statistics. It discusses splitting criteria like Gini impurity and building a SAS macro to create a decision tree stump by recursively splitting on the variable with the maximum Gini decrease. Finally, it notes decision tree stumps can be linked to build a full decision tree.