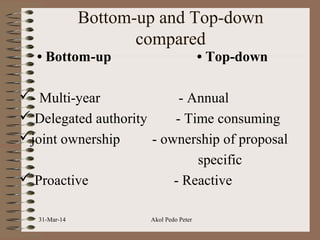
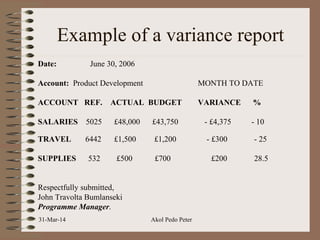
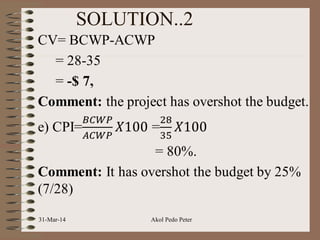
The document discusses budgeting, including definitions, significance, approaches, types of budgets, and the budgetary process. It outlines three common budgeting approaches - top-down, bottom-up, and iterative budgeting - and compares their merits and demerits. The document also discusses features of an effective budget, linking budgets to project activities through earned value analysis, and measures for budgetary control.