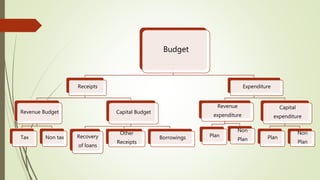
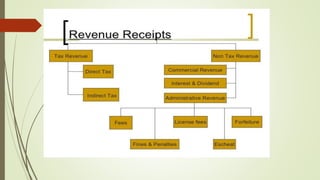
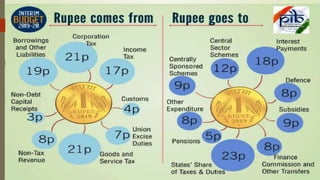
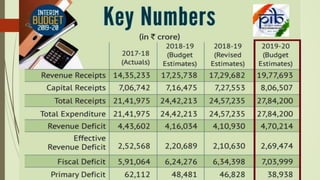
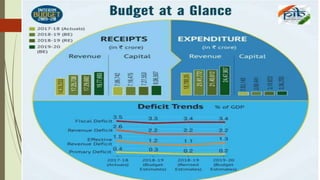
This document provides an overview of the key aspects of the 2019-2020 Union Budget of India. It discusses the meaning and types of budgets, as well as key figures from the previous, current, and upcoming fiscal years' budgets. It then summarizes some of the major policy initiatives and economic indicators highlighted in the interim budget, such as inflation reduction, banking reforms, infrastructure development, support for farmers and women, and tax proposals. The budget aims to support economic growth and development across various sectors.