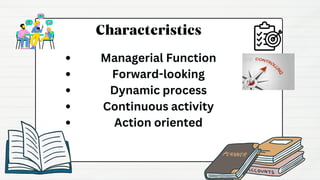
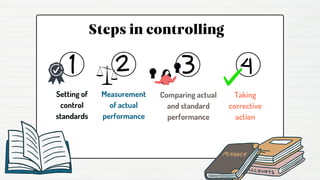
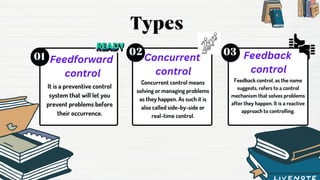
Controlling is an important management function that involves verifying tasks are performed according to plans, measuring actual performance, comparing it to standards, and taking corrective actions to achieve goals. It has objectives like ensuring organizational goals and optimal resource utilization. Advantages include minimizing errors and improving efficiency. Control can be preventive, concurrent, or feedback-based. Common techniques are budgeting, cost control, production planning, and statistical analysis. Controlling helps monitor performance but may be limited by external factors and lack standards.