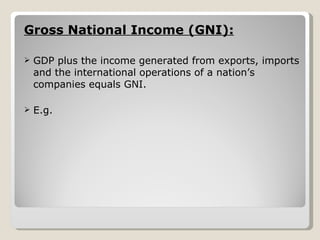
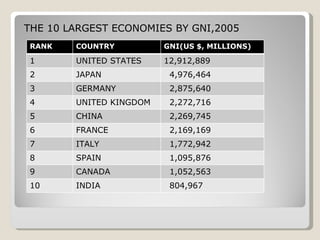
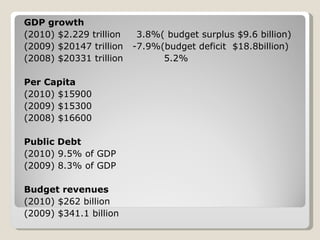
The document discusses key economic factors and statistics for Brazil, Russia, India, and China (BRIC). It notes that together the BRIC countries account for over a quarter of the world's land area and 40% of the global population. Specifically, it provides GDP, GNI, per capita income, labor force participation, and other data for each country. It also summarizes predictions that China and India will be dominant global suppliers of manufactured goods and services while Brazil and Russia will be important raw material suppliers.