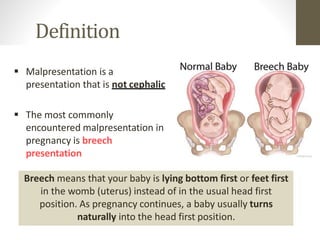
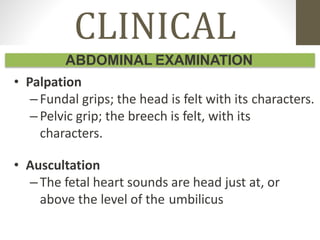
This document provides information on breech presentation during pregnancy. It defines breech as when a baby is lying bottom or feet first instead of head first. Breech occurs in 3-4% of term pregnancies and up to 25% of preterm pregnancies before 28 weeks. There are three types of breech positions: frank, complete, and footling. Breech can be diagnosed through abdominal palpation, vaginal examination, or ultrasound. Management options include external cephalic version to manually turn the baby, vaginal breech delivery if certain criteria are met, or caesarean section.