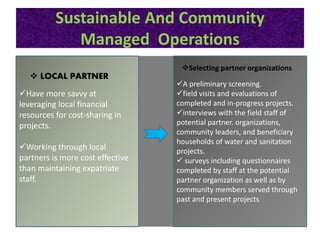
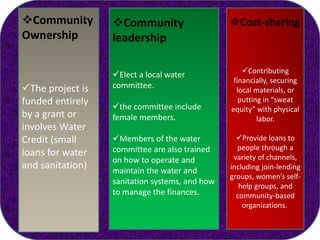
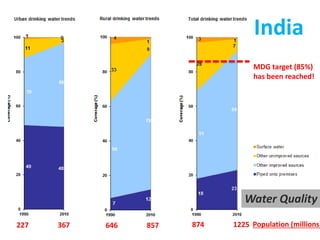
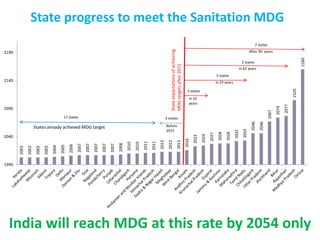
The document discusses challenges with access to clean water and sanitation in India. Over 780 million people in India lack access to an improved water source and more than 600 million practice open defecation. While India has met the Millennium Development Goal for access to water, it is not on track to meet the sanitation target. The document outlines strategies used in India for sustainable and community-managed water and sanitation services, including selecting local partners, gaining community ownership, obtaining cost-sharing from communities, using appropriate technologies, and addressing sanitation and hygiene issues through training. If trends continue, India is estimated to meet the sanitation MDG goal by 2054.