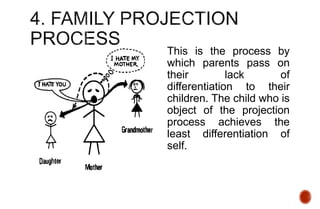
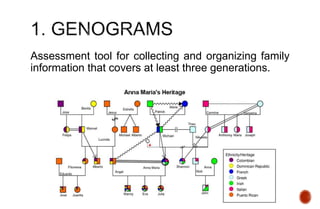
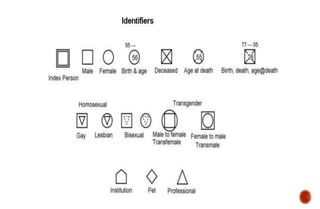
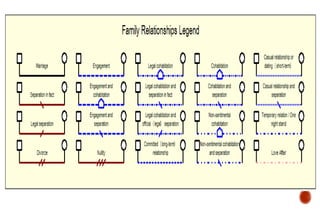
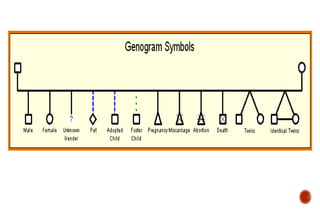
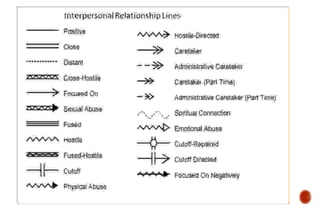
The document discusses the concept of differentiation within family systems, highlighting its impact on relationships and emotional stability. It explores how unresolved emotional issues can be passed down through generations, leading to increased anxiety and fusion among family members. The assessment tool outlined aims to enhance differentiation, reduce reactivity, and facilitate healthier communication within families across multiple generations.