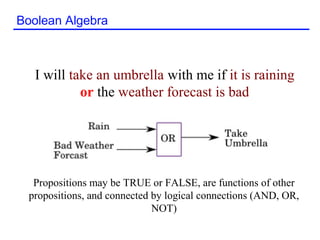
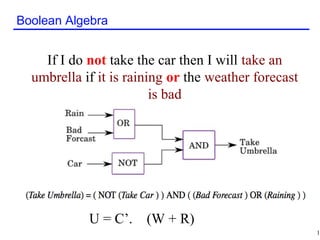
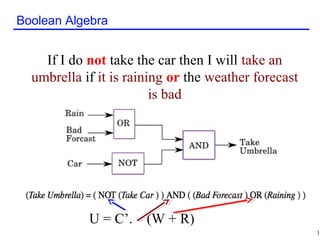
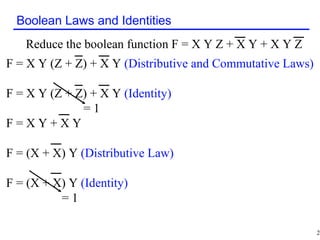
The document discusses Boolean algebra and its basic concepts. Boolean algebra uses 1 to represent True and 0 to represent False. It defines basic Boolean operations like AND, OR, and NOT. The document also shows an example of a Boolean equation to represent an "umbrella" proposition based on weather conditions. It then works through reducing a Boolean function step-by-step using Boolean identities and laws like commutative, associative, and distributive properties.