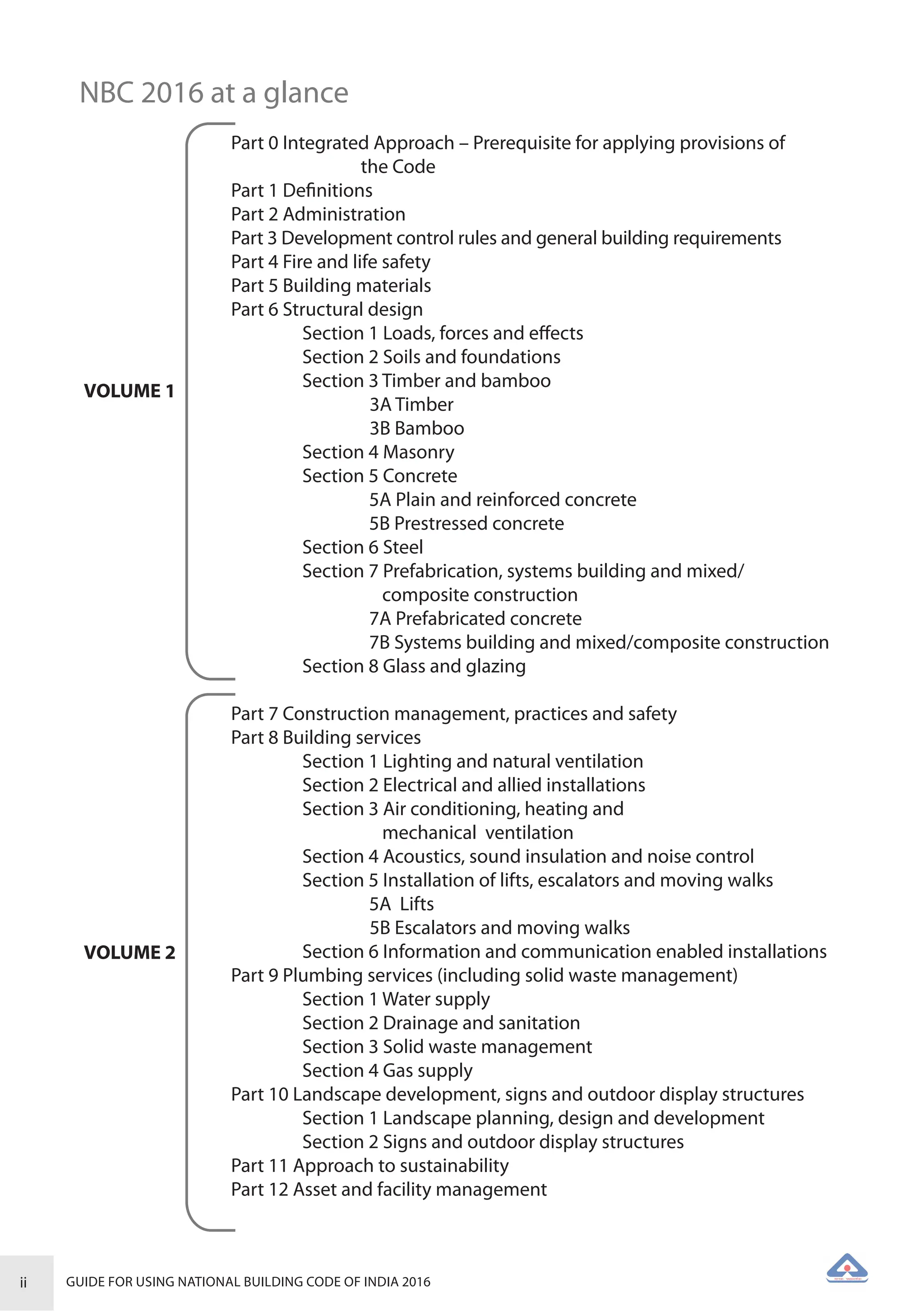
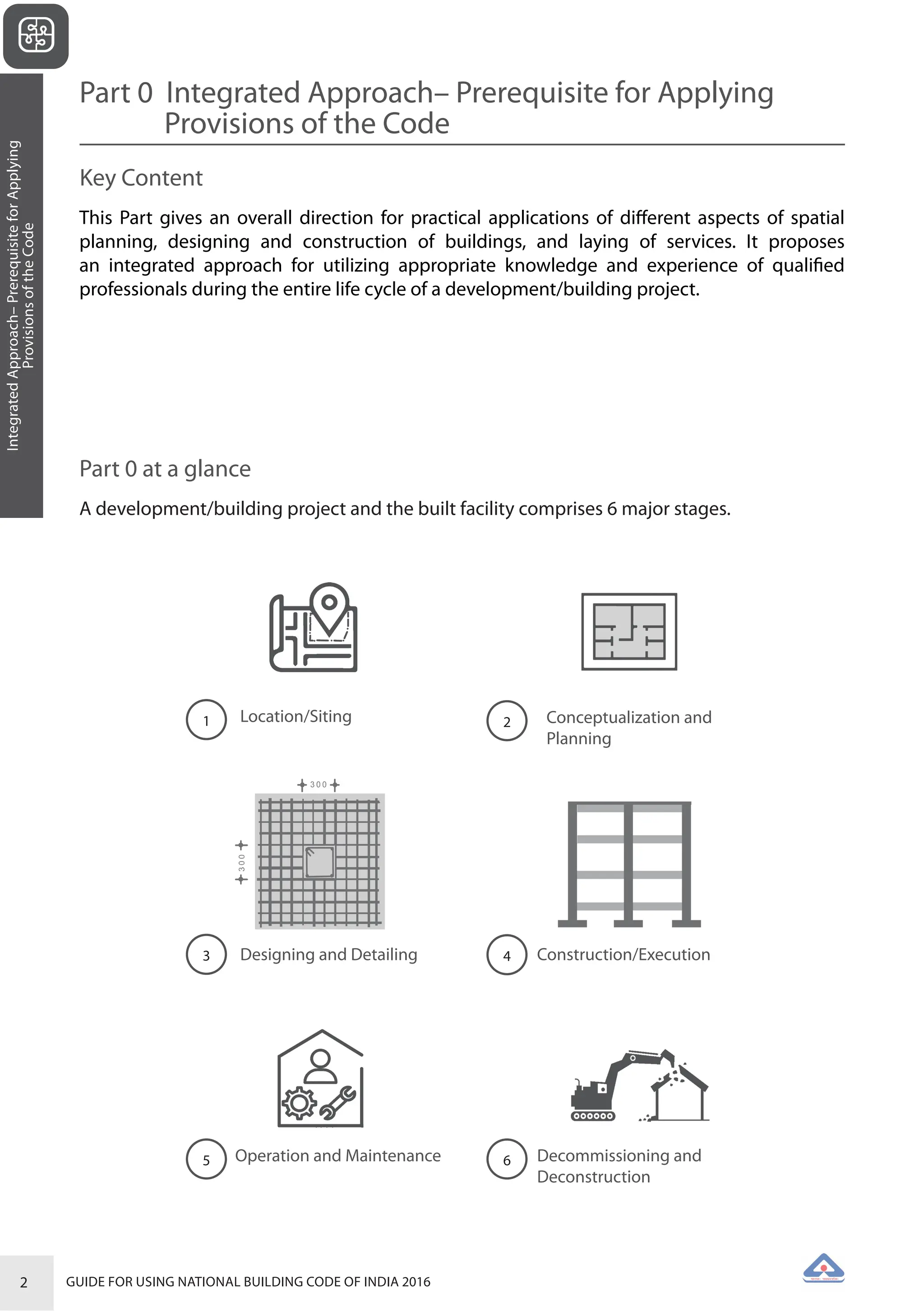
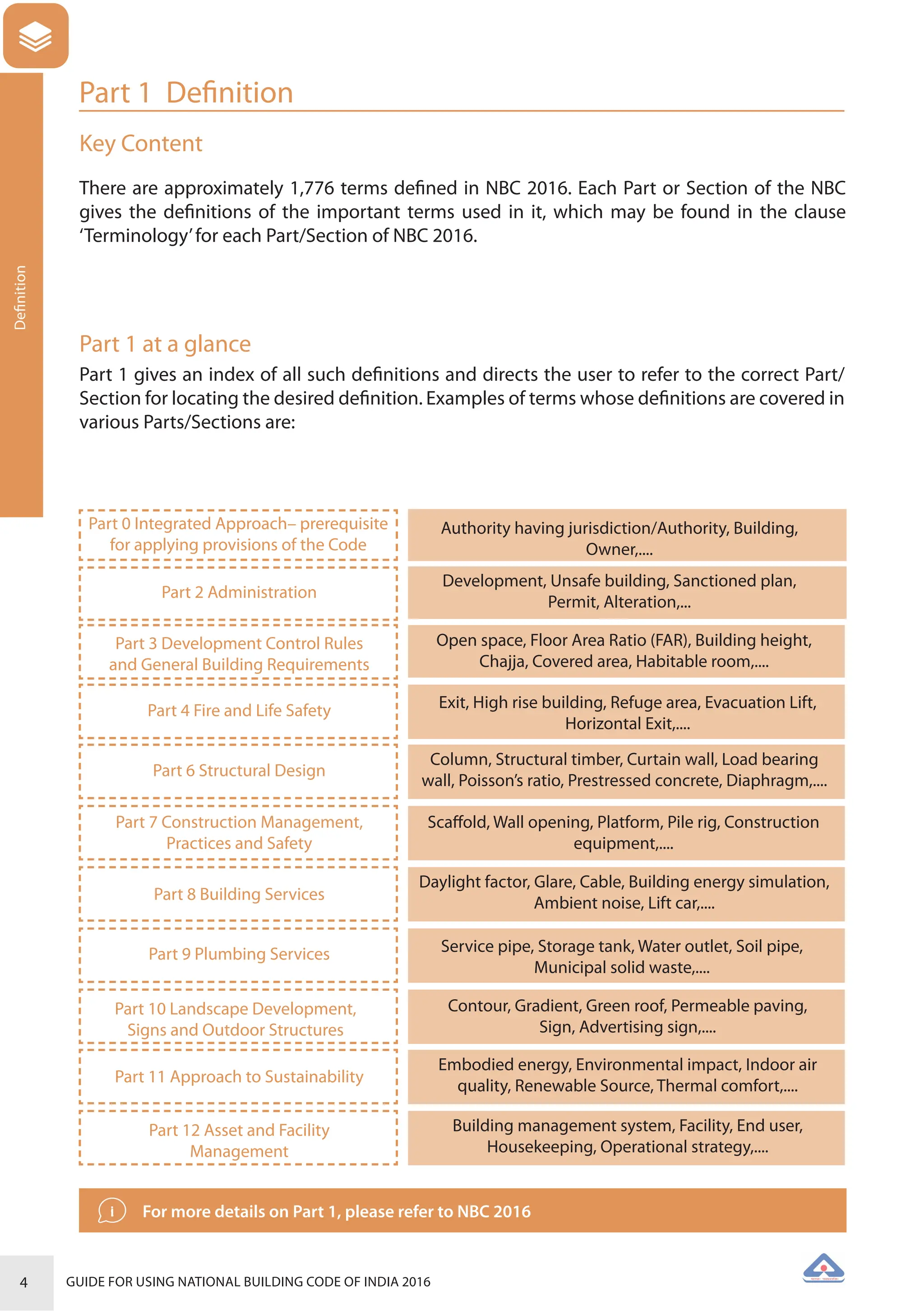
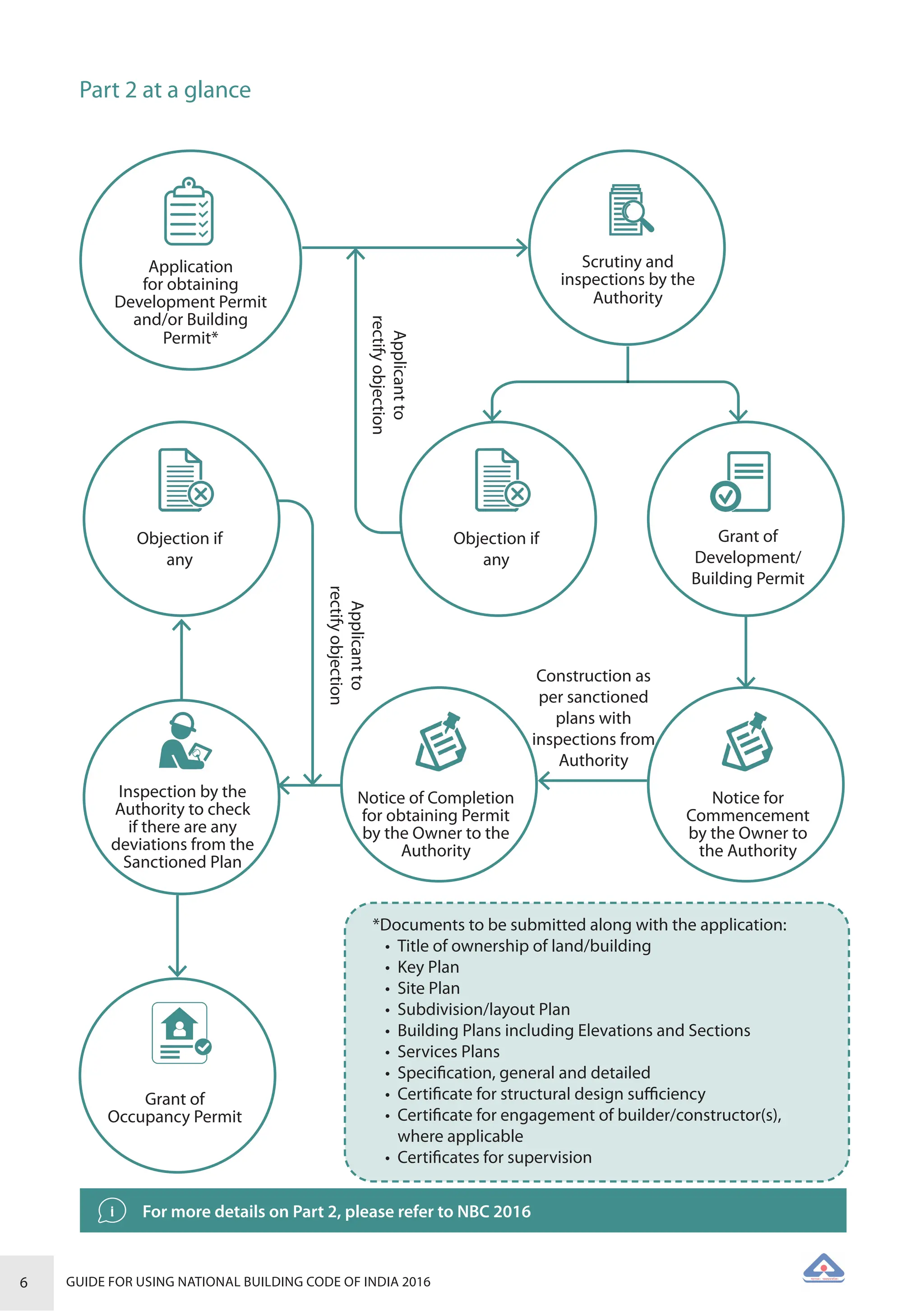
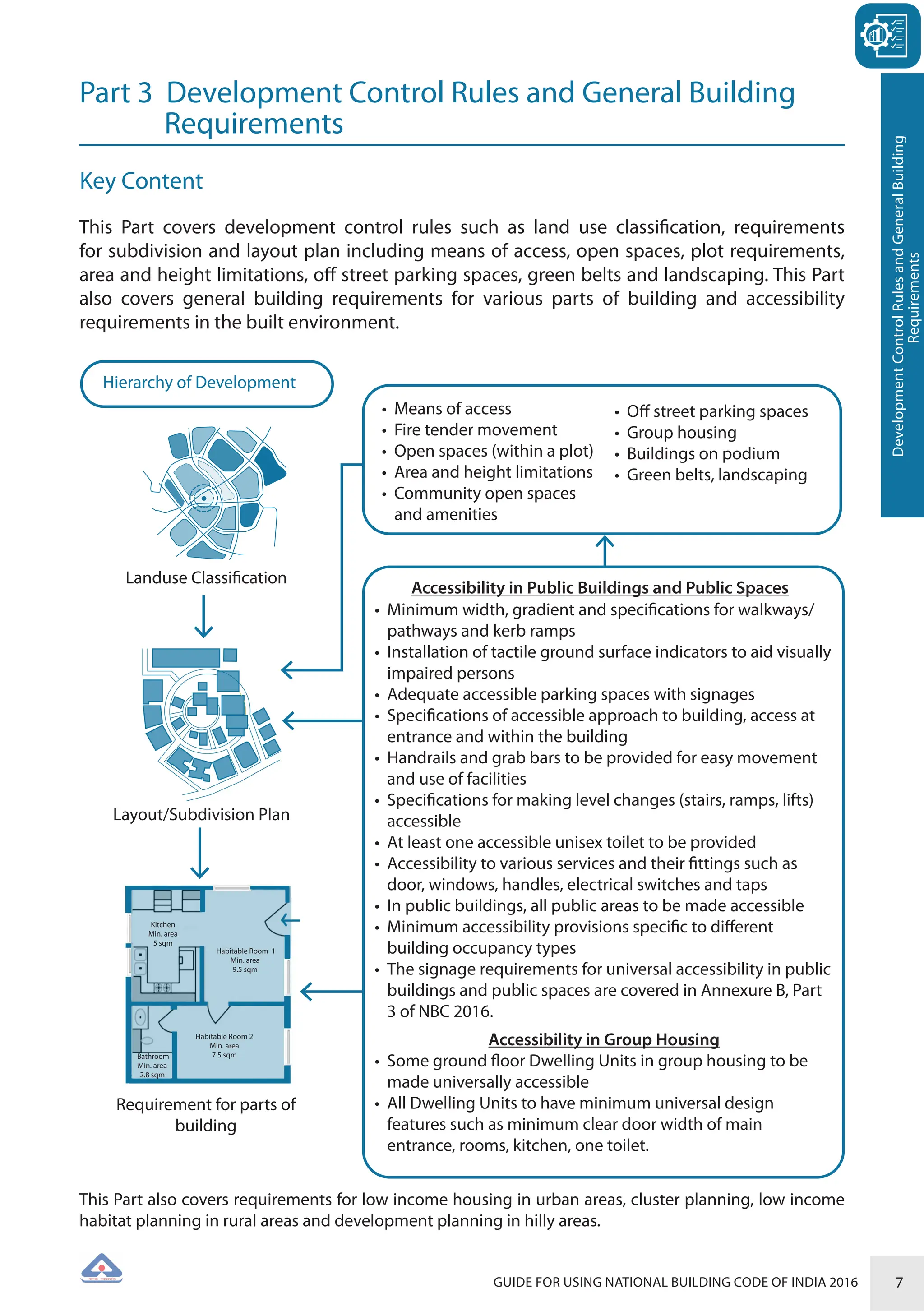
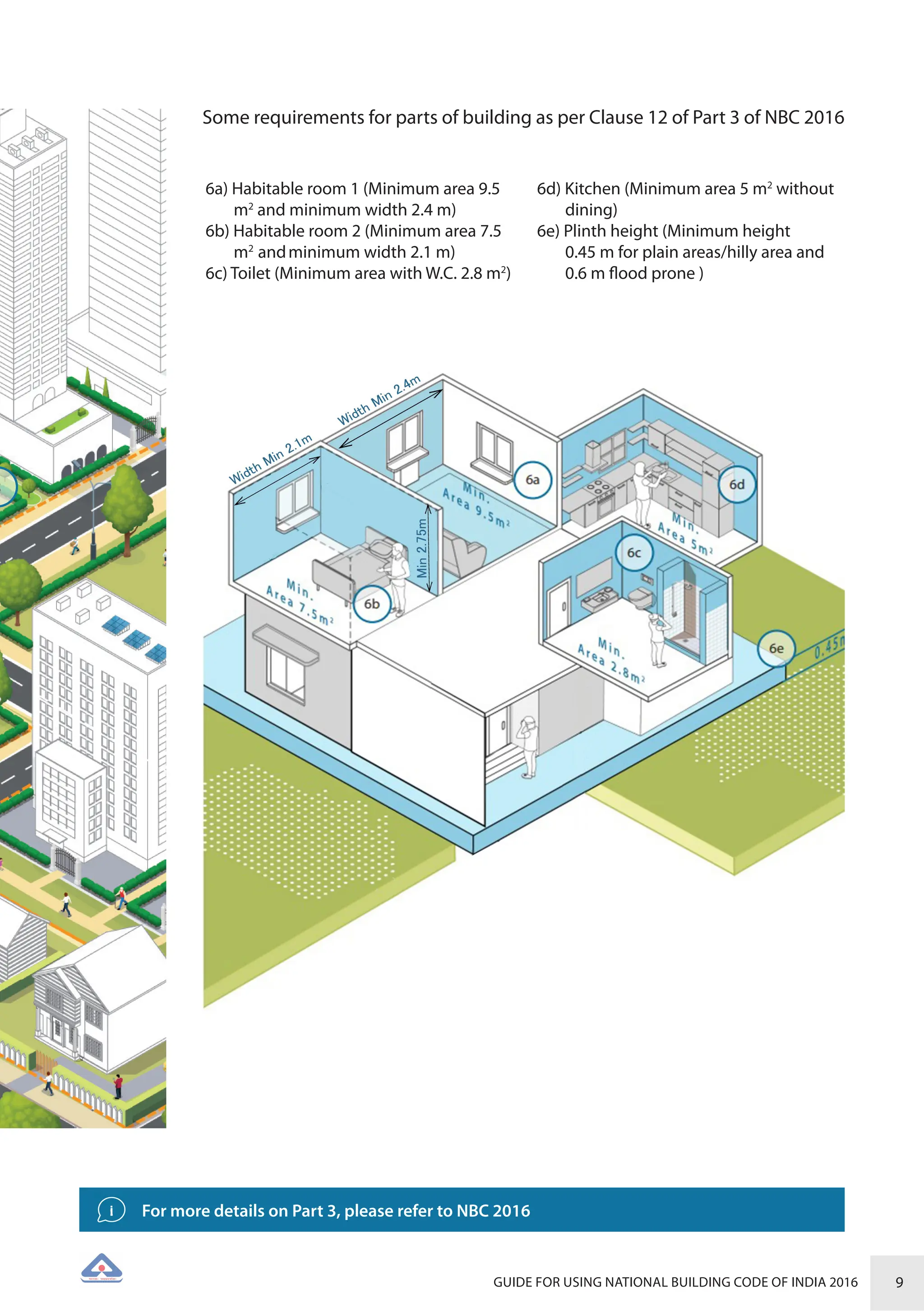
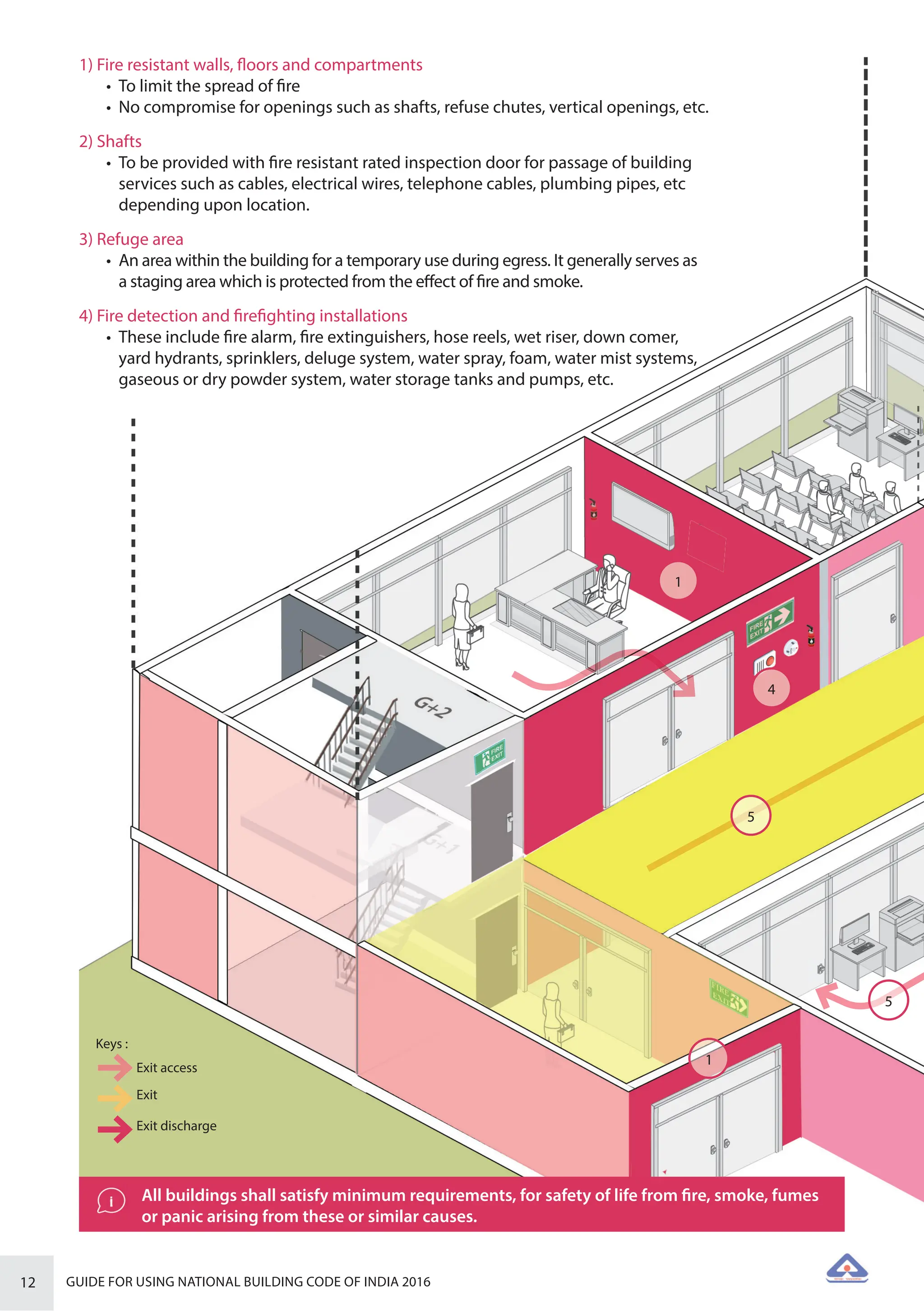
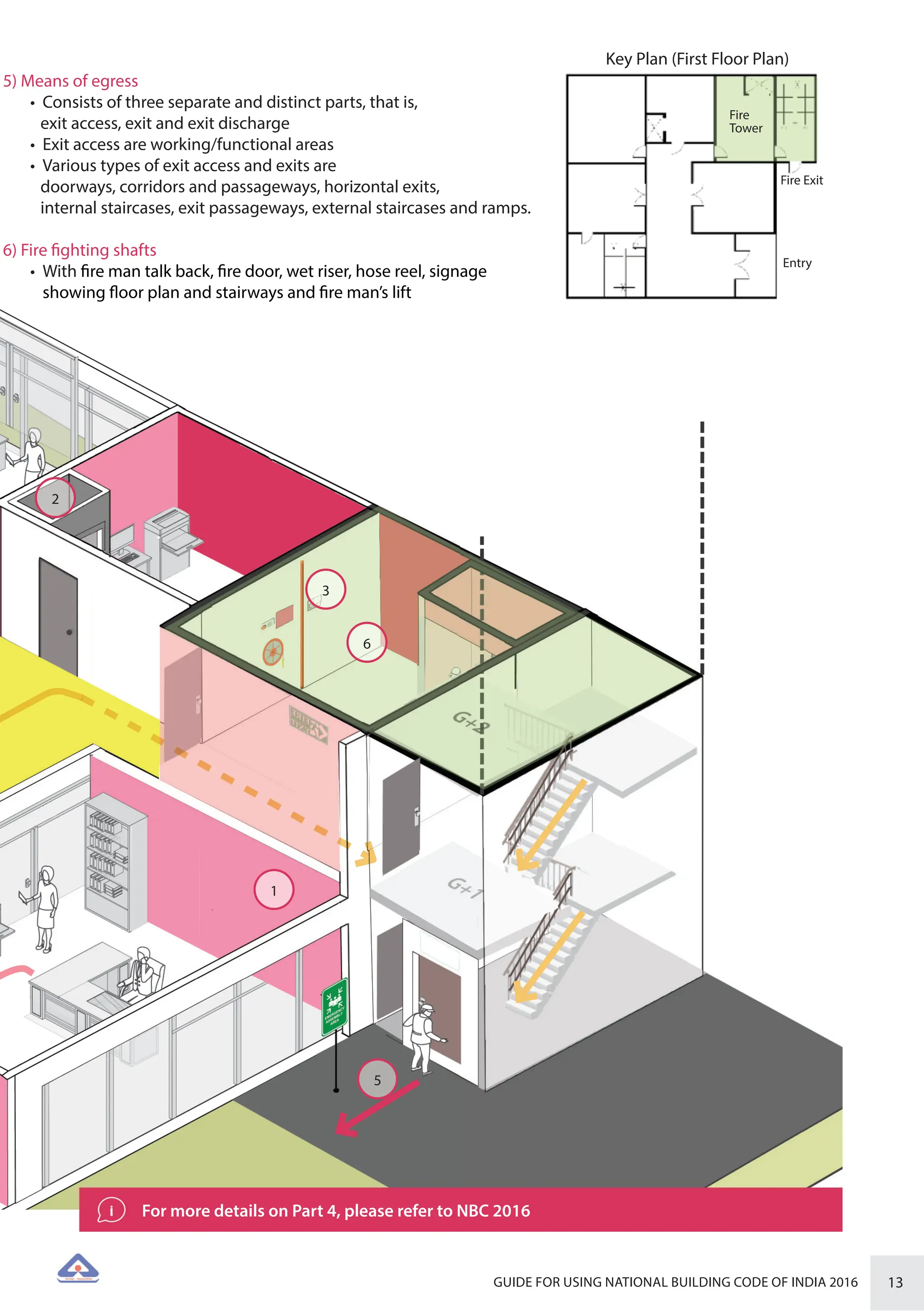
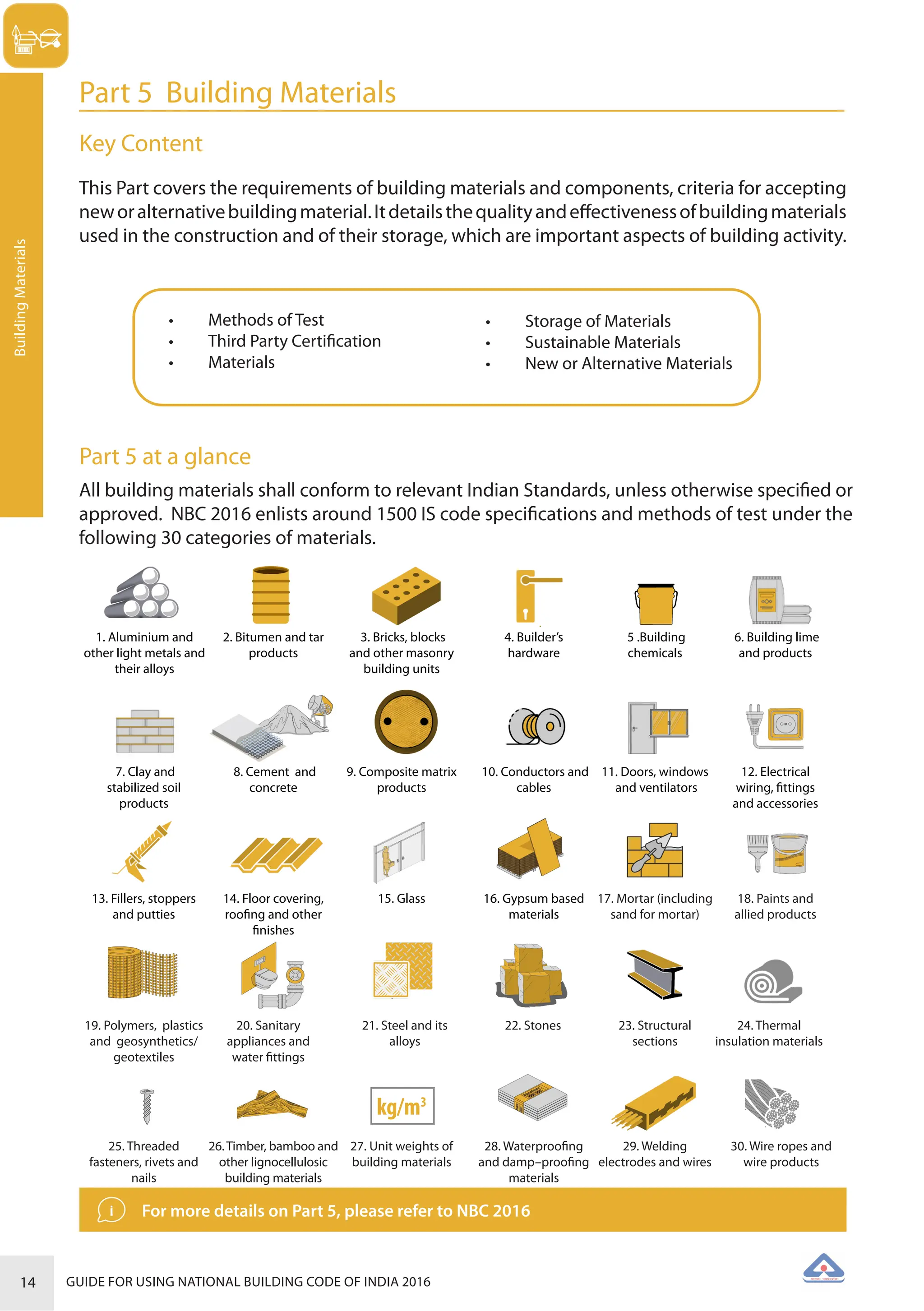
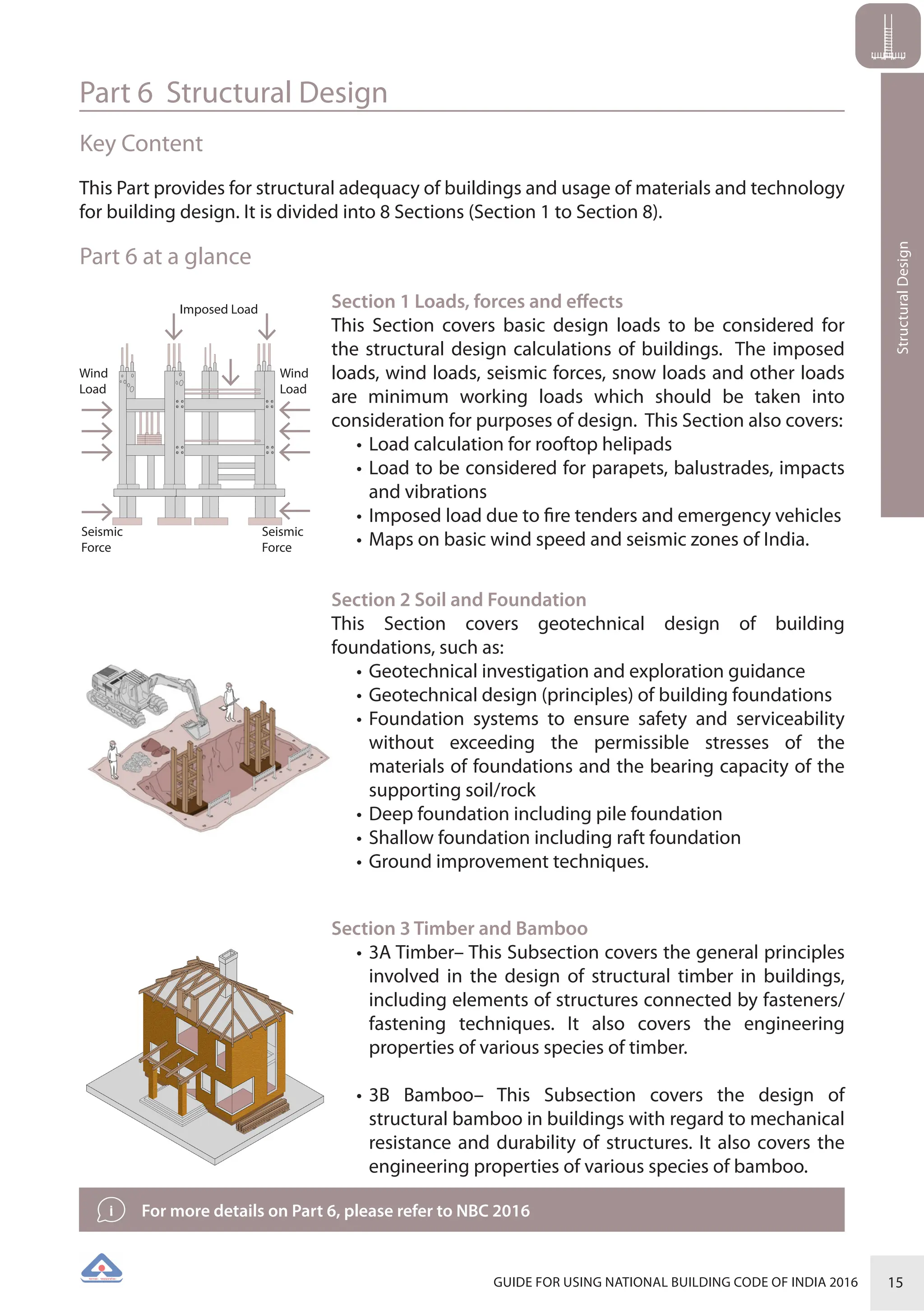
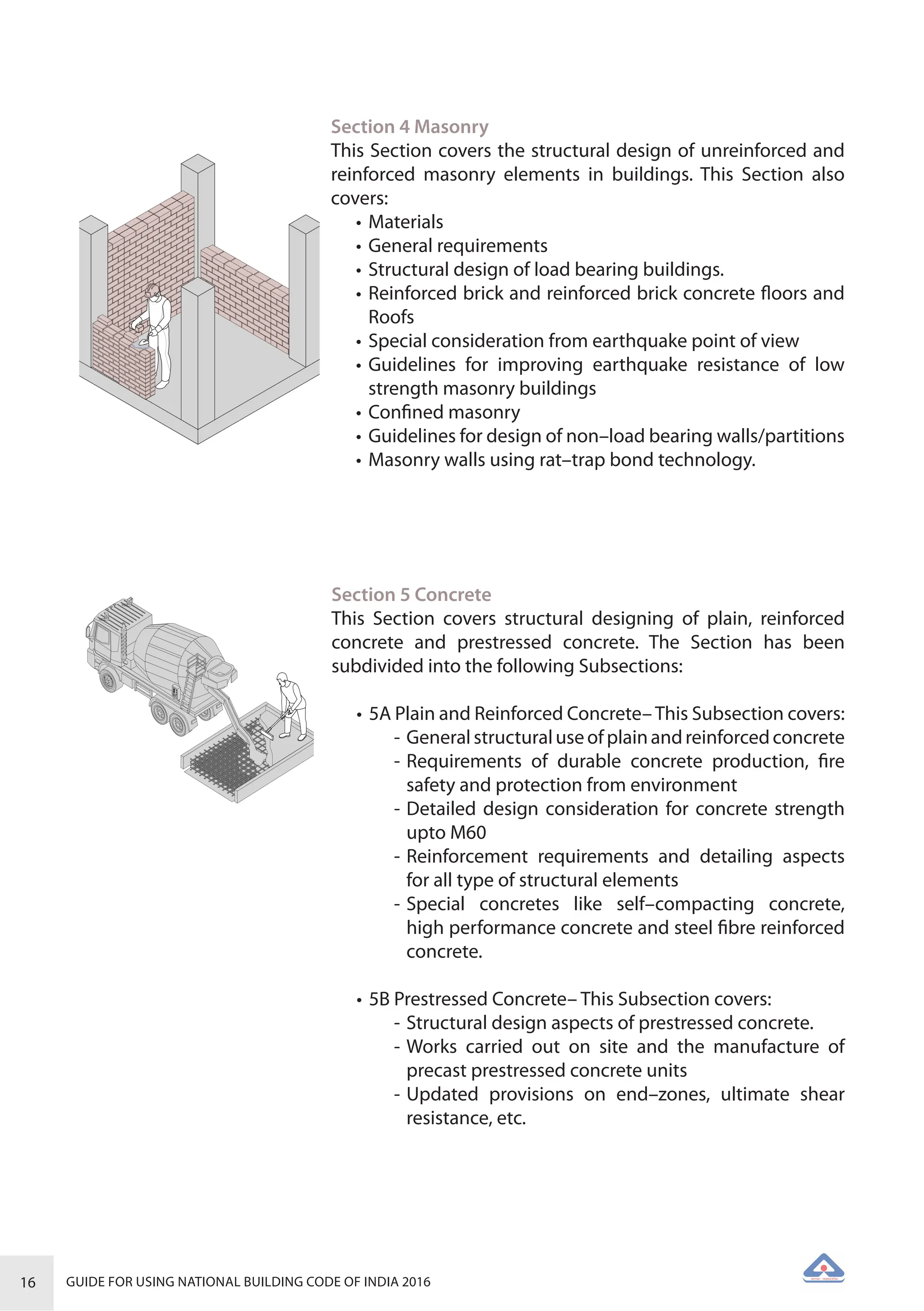
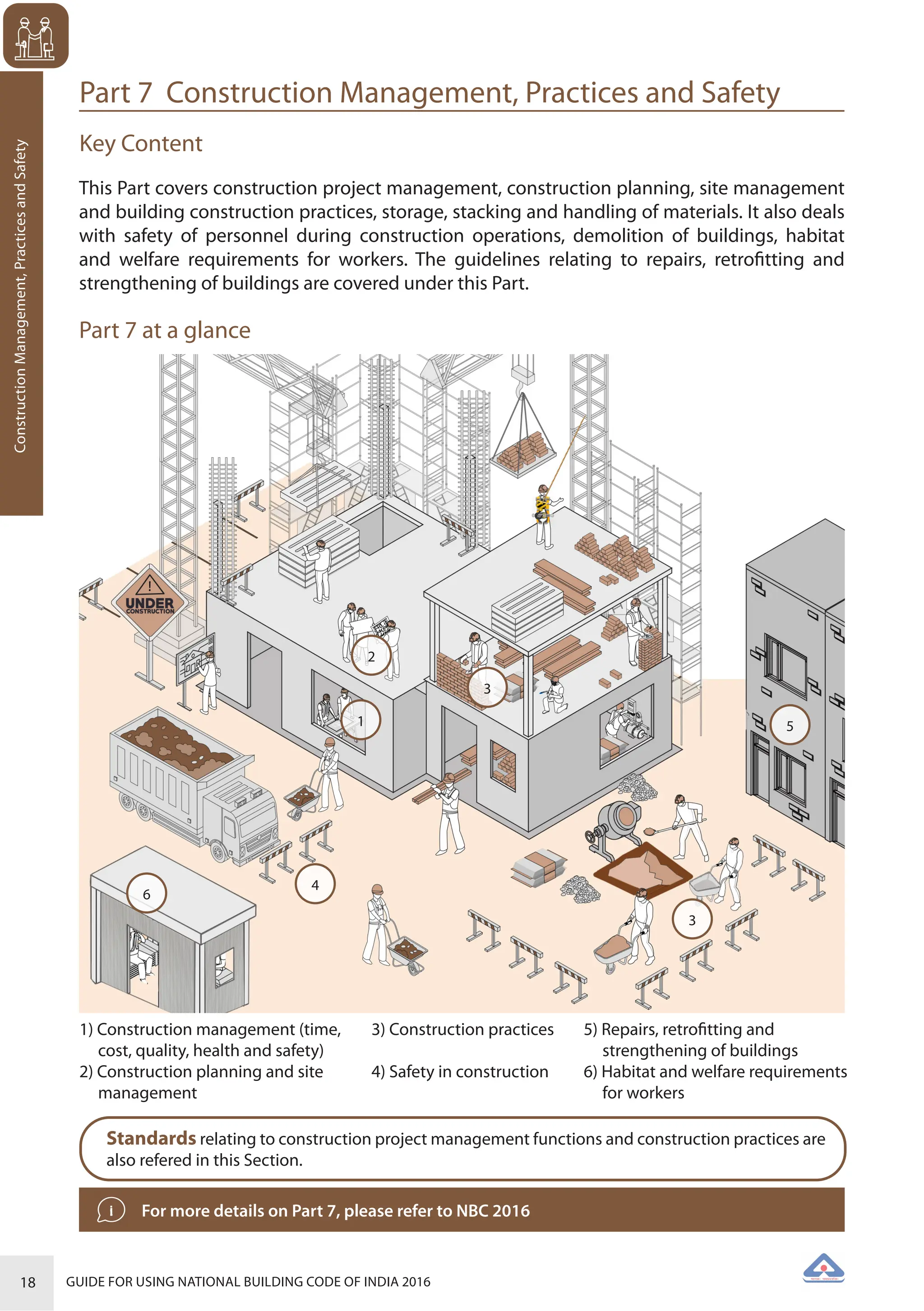
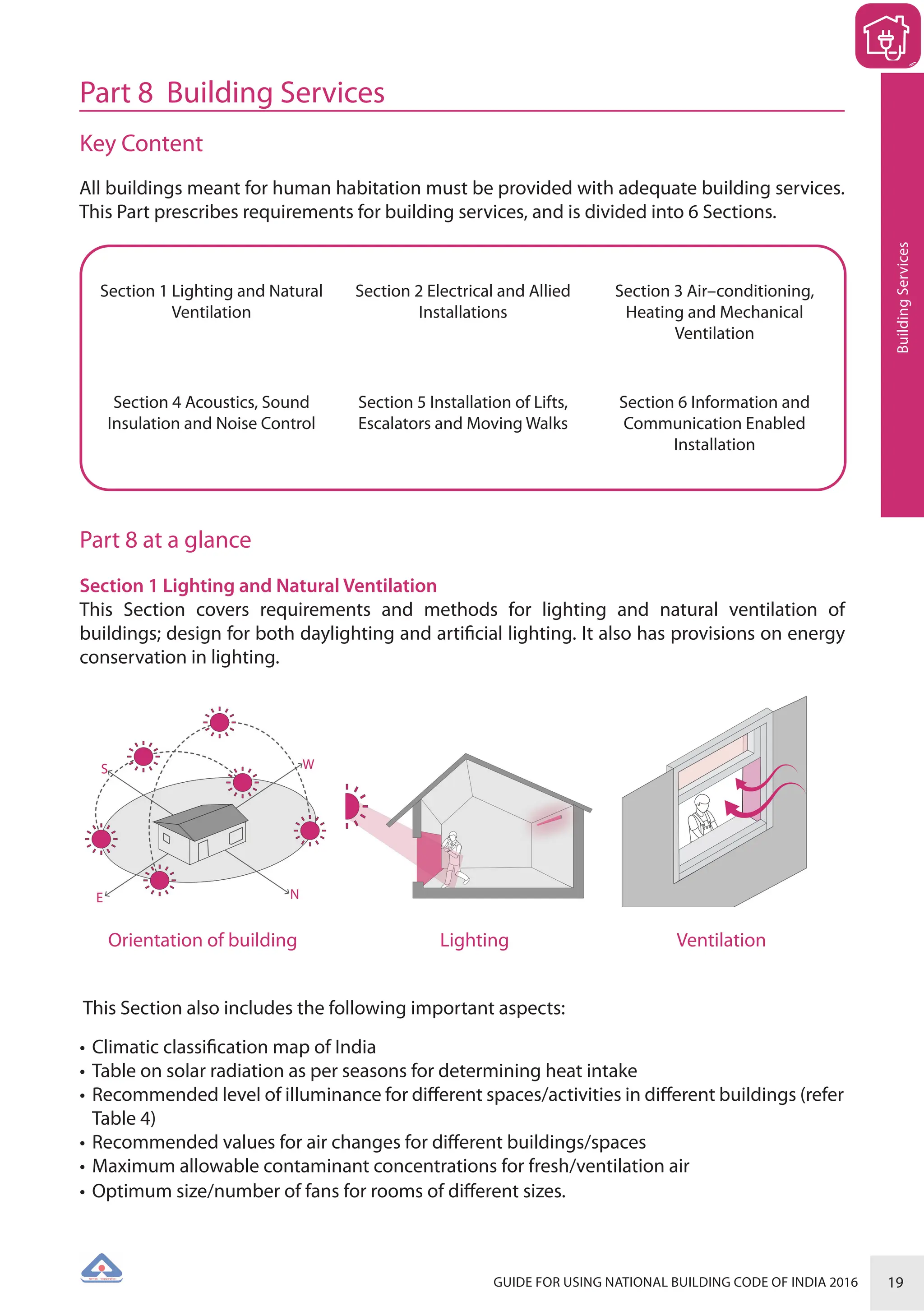
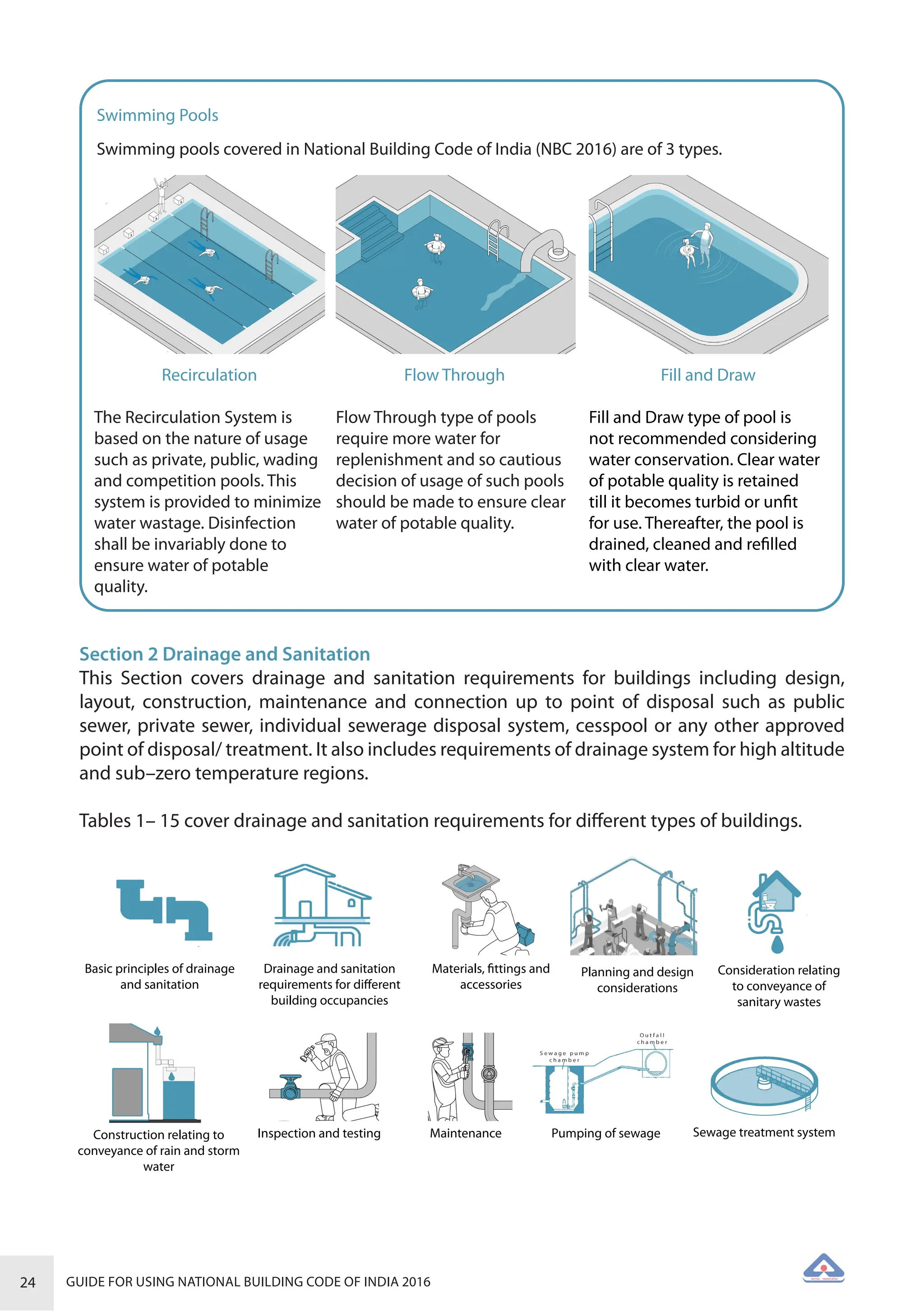
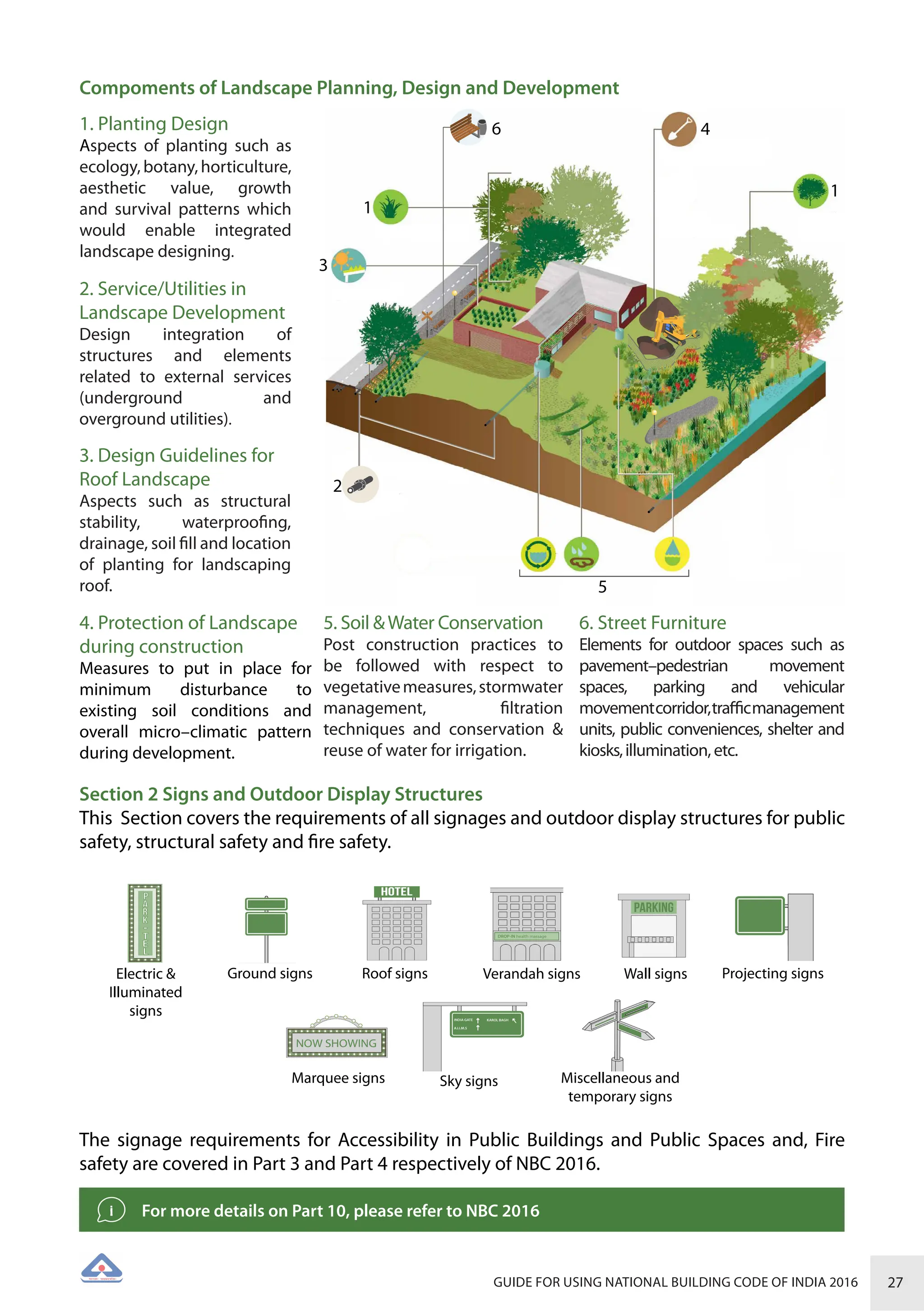
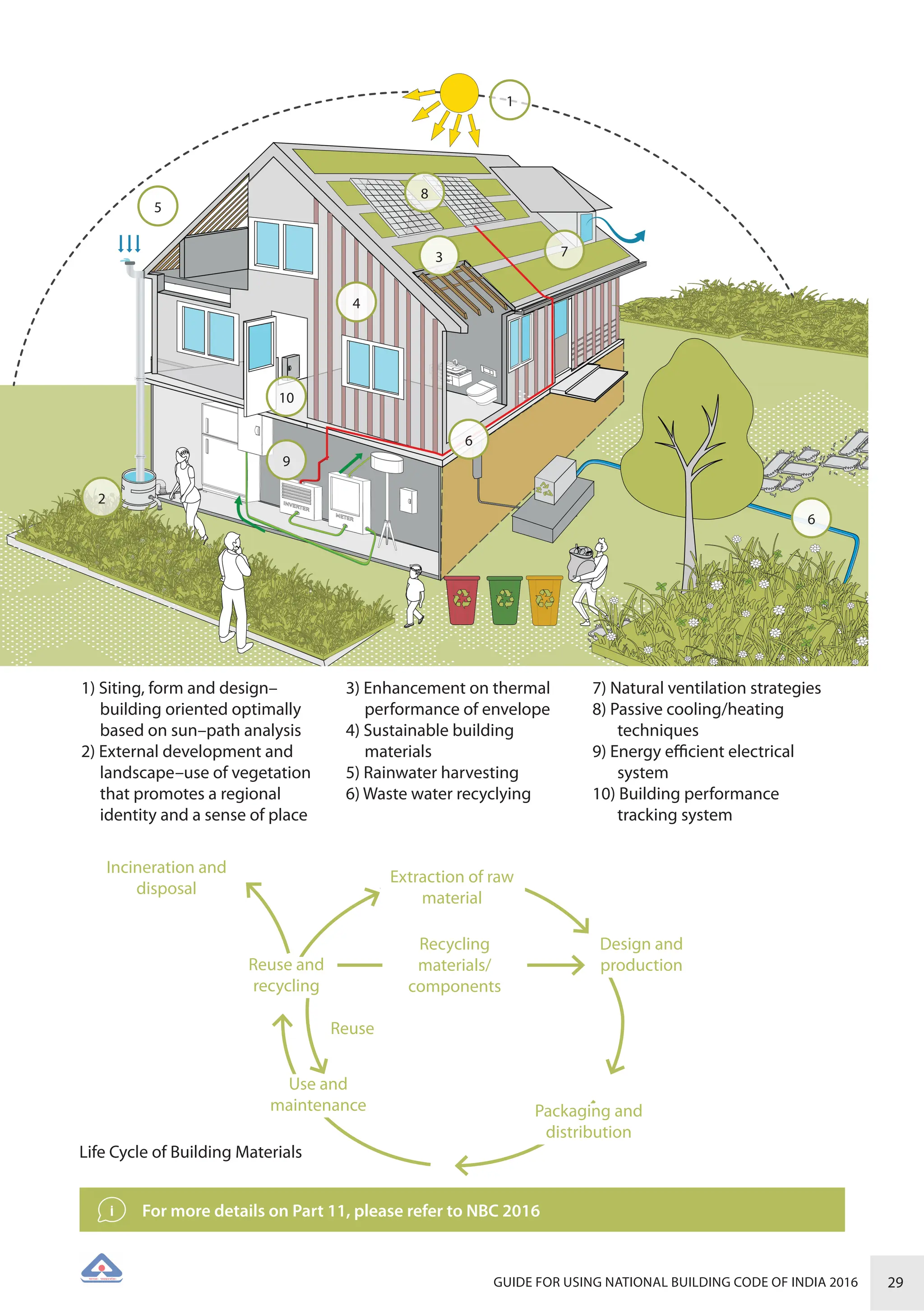
The document is a guide for using the National Building Code of India 2016, which provides comprehensive regulations for building construction across the country, including safety, materials, and administrative processes. It details the organization of building departments, rules for various construction disciplines, and requirements for accessibility and sustainability. The guide serves to assist various stakeholders in understanding and applying the provisions of the NBC 2016 effectively.