Bones and joints of the thorax
- 1. Thoracic wall Dr.Mohamed Mahmoud Mosaed
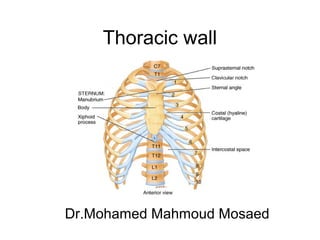
- 2. Thoracic wall The thoracic cage is the framework of the walls of the thorax and is formed by; • the vertebral column behind, • the ribs and intercostal spaces on either side, • the sternum and costal cartilages in front. Functions of the thoracic cage • It protects the lungs and heart. • It affords attachment for the muscles of the thorax, upper extremity, abdomen, and back
- 5. Structure of the Thoracic Wall • The thoracic skeleton includes; • The sternum • 12 pairs of ribs and costal cartilages, The ribs and their cartilages are separated by intercostal spaces • 12 thoracic vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
- 6. Sternum • Site: The sternum is a flat bone lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall. • Parts Three parts: manubrium sterni, body of the sternum, and xiphoid process. • The manubrium sterni is the upper part of the sternum. It articulates with the body of the sternum at the manubriosternal joint. • It also articulates with the clavicles and with the first costal cartilage and the upper part of the second costal cartilages on each side • It lies opposite the third and fourth thoracic vertebrae.
- 8. • The body of the sternum articulates; • Above with the manubrium at the manubriosternal joint and • Below with the xiphoid process at the xiphisternal joint. • On each side it articulates with the second to the seventh costal cartilages • The xiphoid process is a thin plate of cartilage that becomes ossified at its proximal end during adult life. No ribs or costal cartilages are attached to it.
- 9. The sternal angle) angle of Louis), formed by the articulation of the manubrium with the body of the sternum, can be recognized by the presence of a transverse ridge on the anterior aspect of the sternum. • The transverse ridge lies at the level of the second costal cartilage, the point from which all costal cartilages and ribs are counted. • The sternal angle lies opposite the intervertebral disc between the fourth and fifth thoracic vertebrae. The xiphisternal joint lies opposite the body of the ninth thoracic vertebra
- 10. Ribs • There are 12 pairs of ribs, all of which are attached posteriorly to the thoracic vertebrae . The ribs are divided into three categories: • True ribs: The upper seven pairs are attached anteriorly to the sternum by their costal cartilages. • False ribs: The 8th , 9th , and 10th pairs of ribs are attached anteriorly to each other and to the 7th rib by means of their costal cartilages and small synovial joints. • Floating ribs: The 11th and 12th pairs have no anterior attachment.
- 12. Typical Rib • The ribs from the 3rd to the 9th have the same general anatomical features so they are refereed to typical rib • A typical rib is a long, twisted, flat bone • It has a shaft, anterior and posterior ends. The anterior (costal) end • The anterior end of each rib is attached to the corresponding costal cartilage . The shaft • The shaft is thin and flattened and twisted on its long axis. It has superior and inferior borders. • The superior border is rounded and smooth • The inferior border is sharp and thin. It overhangs and forms the costal groove, which accommodates the intercostal vessels and nerve. The angle is where the shaft of the rib bends sharply forward
- 13. • The posterior (vertebral) end • It has a head, neck and tubercle: • The head • It has two facets. The lower and larger facet articulates with the body of the corresponding vertebra, the upper facet articulates with the vertebra above. • The neck • It is a constricted portion situated between the head and the tubercle • The tubercle • It is a prominence on the outer surface of the rib at the junction of the neck with the shaft • It has a facet for articulation with the transverse process of the numerically corresponding vertebra
- 16. Atypical Rib • First rib • This rib is small and flattened from above downward. • The head bears circular facet, to articulates with the body of the first thoracic vertebra. • The Shaft is flat and has superior and inferior surfaces, and inner and outer borders; • The first rib is important clinically because of its close relationship to the lower nerves of the brachial plexus and the subclavian artery and vein. • The scalenus anterior muscle is attached to its upper surface and inner border. • Anterior to the scalenus anterior, the subclavian vein crosses the rib; posterior to the muscle attachment, • the subclavian artery and the lower trunk of the brachial plexus cross the rib and lie in contact with the bone.
- 18. Costal Cartilages • Costal cartilages are bars of cartilage connecting the upper seven ribs to the lateral edge of the sternum and the 8th , 9th , and 10th ribs to the cartilage immediately above. The cartilages of the 11th and 12th ribs end in the abdominal musculature • The costal cartilages contribute significantly to the elasticity and mobility of the thoracic walls. In old age, the costal cartilages tend to lose some of their flexibility as the result of superficial calcification
- 19. Joints of the Chest Wall
- 20. Joints of the Sternum • The manubriosternal joint is a cartilaginous joint between the manubrium and the body of the sternum. A small amount of angular movement is possible during respiration. • The xiphisternal joint is a cartilaginous joint between the xiphoid process (cartilage) and the body of the sternum. The xiphoid process usually fuses with the body of the sternum during middle age.
- 21. Joints of the Ribs Joints of the Heads of the Ribs • The first rib and the three lowest ribs (10th ,11th ,12th) have a single synovial joint with their corresponding vertebral body. • For the second to the ninth ribs, the head articulates by 2 synovial joints with the corresponding vertebral body and that of the vertebra above it. There is a strong intraarticular ligament that connects the head to the intervertebral disc. Joints of the Tubercles of the Ribs • The tubercle of a rib articulates by a synovial joint with the transverse process of the corresponding vertebra (This joint is absent on the 11th and 12th ribs.) Joints of the Ribs and Costal Cartilages • These joints are cartilaginous joints. No movement is possible.
- 22. Joints of the Costal Cartilages with the Sternum • The first costal cartilages articulate with the manubrium, by cartilaginous joints that permit no movement. • The 2nd to the 7th costal cartilages articulate with the lateral border of the sternum by synovial joints. • In addition, the 6th , 7th , 8th , 9th , and 10th costal cartilages articulate with one another along their borders by small synovial joints. The cartilages of the 11th and 12th ribs are embedded in the abdominal musculature. Movements of the Ribs and Costal Cartilages • The 1st ribs and their costal cartilages are fixed to the manubrium and are immobile. • The raising and lowering of the ribs during respiration are accompanied by movements in both the joints of the head and the tubercle, permitting the neck of each rib to rotate around its own axis.
- 24. Openings of the Thorax 1. The superior thoracic aperture (the thoracic outlet) The thoracic cavity communicates with the neck through the superior thoracic aperture. • Structures entering and leaving the thoracic cavity through this aperture include the trachea, esophagus, vessels, and nerves. • The opening is obliquely placed facing upward and forward. Because of the obliquity of the opening, the apices of the lung and pleurae project upward into the neck. • The superior thoracic aperture is bounded: • Posteriorly: by the first thoracic (T1) vertebra. • Laterally: by medial border of the first ribs and their costal cartilages. • Anteriorly: by the superior border of the manubrium sterni.
- 25. 2. The inferior thoracic aperture The thoracic cavity communicates with the abdomen through the inferior thoracic aperture, • The diaphragm separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. • The inferior thoracic aperture is more large than the superior thoracic aperture. Structures passing to or from the thorax to the abdomen pass through openings in the diaphragm. • The opening is bounded posteriorly by the 12th thoracic vertebra, laterally by the curving costal margin, and anteriorly by the xiphisternal joint.
- 26. The structure of the Vertebra • The vertebra consists of: Body and vertebral arch with vertebral foramen in between • The vertebral arch carries seven processes • 2 transverse • 1 spinous • 4 articular (2 superior and 2 inferior articular processes) • The pedicles lies between the body and the transverse process • The lamina lies between the transverse process and the spine
- 28. Thoracic vertebrae There are twelve thoracic vertebrae, each of which is characterized by articulations with ribs. A typical thoracic vertebra • typical thoracic vertebra has: • A heart-shaped vertebral body, with roughly equal dimensions in the transverse and anteroposterior directions. • The vertebral foramen is generally circular and the laminae are broad. • The superior articular processes are flat, with their articular surfaces facing almost directly posteriorly. • The inferior articular processes project from the laminae and their articular facets face anteriorly. • The spine is long and points sharply downward
