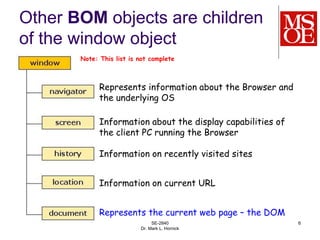
The Browser Object Model (BOM) provides JavaScript access to browser objects. The BOM includes objects like window, navigator, screen, history, and location. The window object is the global/top-level object that contains other BOM objects as its properties. It allows access to browser methods like alert() without needing to specify the window object. Key BOM objects provide information about the browser, screen, history, and current URL. In the past, BOM implementations differed between browsers but standards compliance has improved.