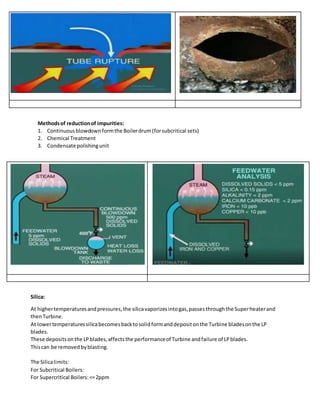
Boiler water chemistry is important to prevent problems like scale deposits, carryover of water with steam, and corrosion of boiler tubes. Impurities in feedwater like magnesium, calcium, silica, iron and copper can deposit as hard scales on boiler tubes as their concentration increases during evaporation. This impairs heat transfer and can cause tube failure. Proper treatment of feedwater and continuous blowdown are needed to control impurity levels. Silica vaporizes but condenses as deposits on low-pressure turbine blades, hurting performance. Carryover of water occurs with high solids concentrations and causes deposition in superheaters and damage to turbine blades. Internal corrosion from acid, caustic or dissolved gases reduces tube thickness and can cause