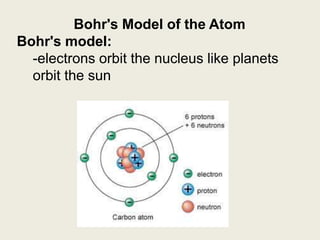
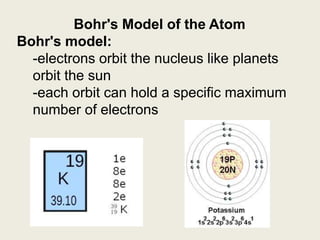
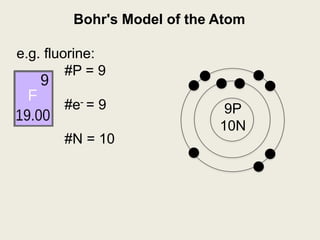
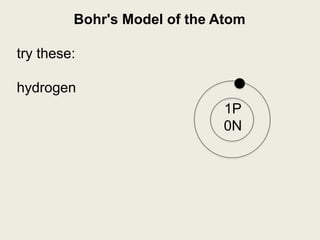
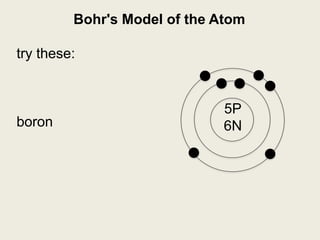
Niels Bohr proposed the Bohr model of the atom in 1913 to explain the unique colors of light emitted by different elements. The model had electrons orbiting the nucleus in fixed shells, with each shell holding a specific maximum number of electrons. Electrons fill the inner shells first, and jump between shells to emit or absorb light. Bohr used this model to successfully depict atoms like fluorine, hydrogen, boron, and magnesium.