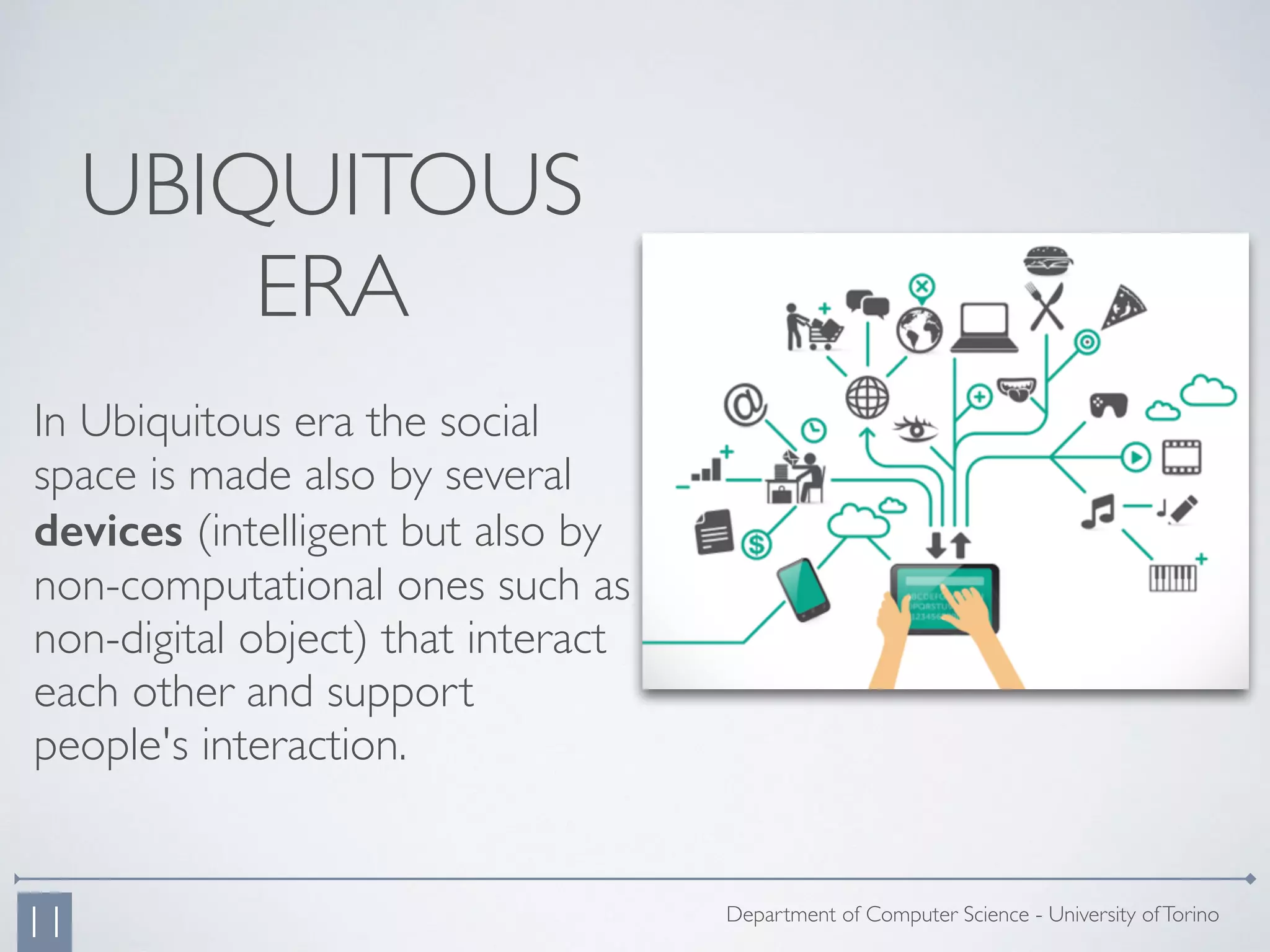
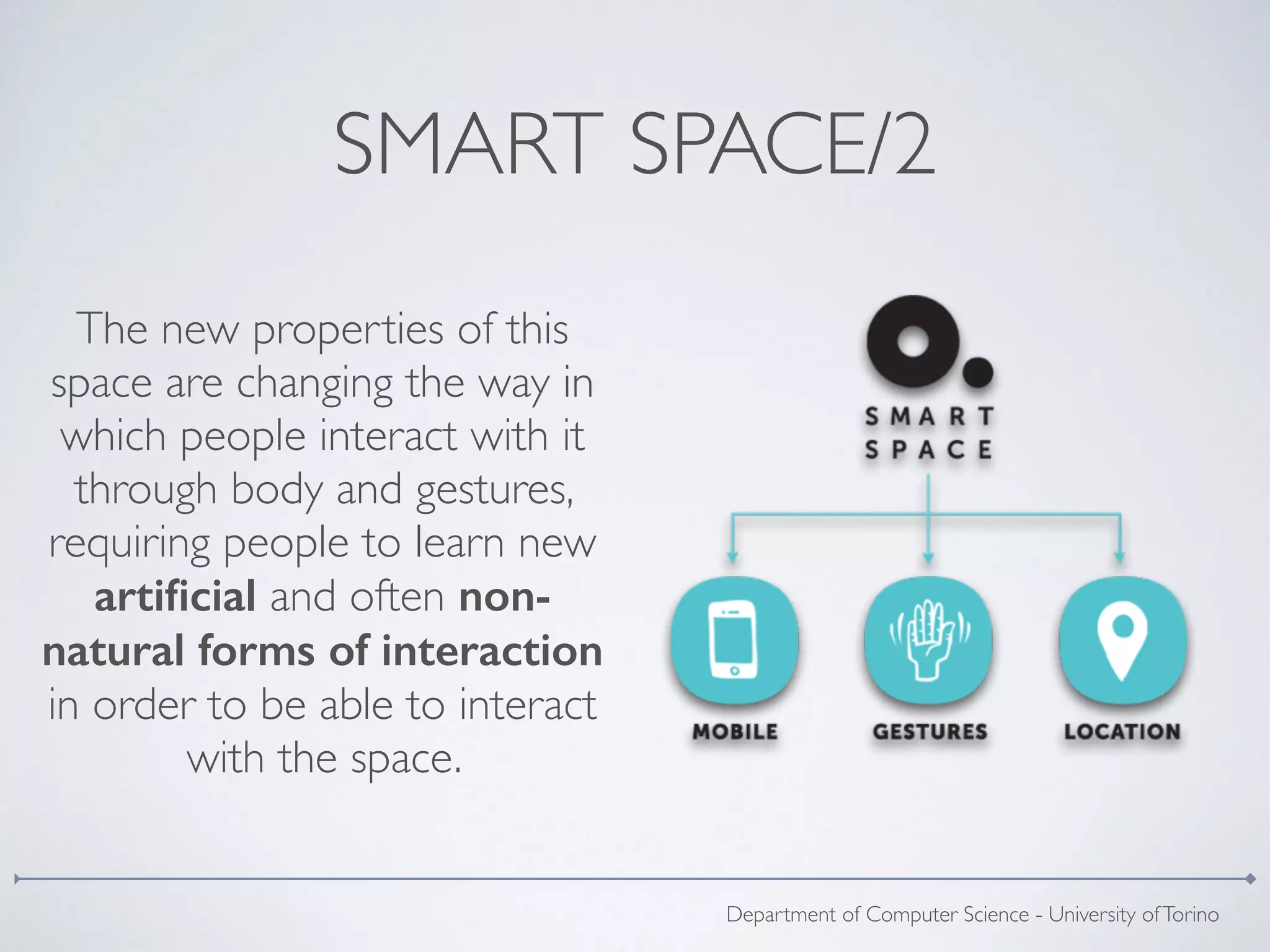
The document discusses the design of a new gestural corpus aimed at facilitating natural interactions in social smart spaces, emphasizing the relationship between the body and space in the ubiquitous era. It outlines a three-step research approach involving observation, bodystorming, and the creation of a gestural system to enhance communication and interaction through gestures in smart environments. The ultimate goal is to develop a meaningful set of gestures that leverage smart technologies to improve human interaction with their surroundings.